equals
Posted 尘埃未定
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了equals相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
equals方法:
先来看下equals方法的定义:
由上边我们可以看出,String类中的equals方法是对父类Object类中的equals方法的覆盖,先来看下Object类的equals方法怎么写的:
- * @param obj the reference object with which to compare.
- * @return {@code true} if this object is the same as the obj
- * argument; {@code false} otherwise.
- * @see #hashCode()
- * @see java.util.HashMap
- */
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- return (this == obj);
- }
即直接return (this==obj)此处 某个对象调用该方法,this 就指代那个对象。
再来看看String类中的equals方法是如何覆盖以上方法的:
- /**
- * Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code
- * true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code
- * String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this
- * object.
- *
- * @param anObject
- * The object to compare this {@code String} against
- *
- * @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String}
- * equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise
- *
- * @see #compareTo(String)
- * @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String)
- */
- public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
- if (this == anObject) {
- return true;
- }
- if (anObject instanceof String) {
- String anotherString = (String) anObject;
- int n = value.length;
- if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = anotherString.value;
- int i = 0;
- while (n-- != 0) {
- if (v1[i] != v2[i])
- return false;
- i++;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
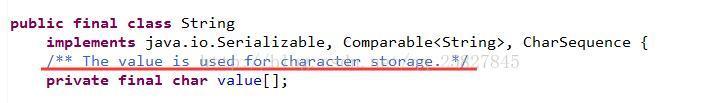
可以看到,在此equals方法中有一个value的数组。找到其定义:
可以看出,value是一个char类型的数组,用于存放字符串中的每个字符。和上边String类的定义相吻合(废话么这不是)。
判断条件:
若当前对象和比较的对象是同一个对象,即return true。也就是Object中的equals方法。
若当前传入的对象是String类型,则比较两个字符串的长度,即value.length的长度。
若长度不相同,则return false
若长度相同,则按照数组value中的每一位进行比较,不同,则返回false。若每一位都相同,则返回true。
若当前传入的对象不是String类型,则直接返回false
*******************************************String类的equals方法的变体形式******************************************
要求:
自己写一个类MyString,里边有一个char[ ] value,实现里边的equalsString方法,要求可以比较两个MyString类的对象。相等返回0,大于返回1,小于返回-1,若比较的不是MyString类型的对象,则返回-100。
代码如下:
- package cn.ywq.test;
- class MyString {
- char[] value;
- public MyString(char[] value) {
- this.value=value; //通过构造方法将字符传入
- }
- public int equalsString(Object obj) {
- if(this==obj){
- return 0;
- }
- //若该对象是MyString类型的
- if(obj instanceof MyString){
- MyString string =(MyString) obj;
- int n=this.value.length;
- if (n>string.value.length) { //先判断长度的关系
- return 1;
- }else if(n<string.value.length){
- return -1;
- }else{ //若长度相等
- char v1[] = this.value;
- char v2[] = string.value;
- int i = 0;
- while (n-- != 0) { //按照数组的每一位进行比较
- if (v1[i] > v2[i]){
- return 1;
- }else if(v1[i] < v2[i]){
- return -1;
- }
- i++;
- }
- return 0; //若while循环正常结束,则说明相等,返回0
- }
- }
- return -100; //若传入的不是MyString类型的对象
- }
- }
测试代码:
- package cn.ywq.test;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- char[] value={‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘};
- // char[] value2={‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘};
- // char[] value3={‘c‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘};
- char[] value4={‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,};
- MyString myString = new MyString(value);
- MyString s=new MyString(value4);
- int i = myString.equalsString(s);
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
以上是关于equals的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章