一、题目6-1 输出月份英文名##
1.实验代码###
`#include <stdio.h>
char *getmonth( int n );
int main()
{
int n;
char *s;
scanf("%d", &n);
s = getmonth(n);
if ( s==NULL ) printf("wrong input!\\n");
else printf("%s\\n", s);
return 0;
}
char *getmonth( int n )
{
switch(n){
case 1:return "January";
case 2:return "February";
case 3:return "March";
case 4:return "April";
case 5:return "May";
case 6:return "June";
case 7:return "July";
case 8:return "August";
case 9:return "September";
case 10:return "October";
case 11:return "November";
case 12:return "December";
default:return NULL;
}
} `
2.设计思路###
第一步:主函数:先输入了月份的数字n,调用函数求出所对应的月份并赋给s,判断s是否为null,如果是输出wrong input,如果不是输出月份。
第二步:在函数中,运用一个switch语句在每个语句后面返回相应的月份。
3.问题###
无
二、题目6-2.查找星期##
1.实验代码###
`#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXS 80
int getindex( char *s );
int main()
{
int n;
char s[MAXS];
scanf("%s", s);
n = getindex(s);
if ( n==-1 ) printf("wrong input!\\n");
else printf("%d\\n", n);
return 0;
}
int getindex( char *s )
{
int i;
char day[7][10] = { "Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday" };
for (i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
{
if (strcmp(s, day[i]) == 0) break;
}
if (i == 7)
{
i = -1;}
return i;
} `
2.设计思路###
第一步:主函数:首先输入一个星期的字符s,调用函数求出相应数组并赋值给n,判断s是否为-1,如果是输出wrong input,如果不是输出星期所对应的数字。
第二步:将各个星期存入day数组中,用一个for循环遍历day数组,用一个if语句判断所需查找的是不是所需字符,如果是跳出循环。在for循环后用if语句判断i是否等于7,如果是令i等于-1.最后返回i的值。
3.问题###
无
三、题目6-3 计算最长的字符串长度##
1.实验代码###
`#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXN 10
#define MAXS 20
int max_len( char *s[], int n );
int main()
{
int i, n;
char *string[MAXN] = {NULL};
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*MAXS);
scanf("%s", string[i]);
}
printf("%d\\n", max_len(string, n));
return 0;
}
int max_len( char *s[], int n )
{
int i,num = 0;
for(i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(num < strlen(*(s + i))){
num = strlen(*(s + i));
}
}
return num;
} `
2.设计思路###
第一步:主函数:输入字符串个数,用for循环进行输入,最后调用函数求出最长字符串的长度并输出。
第二步:用一个for语句对字符串进行循环,用if语句判断最长长度是否小于当前所遍历字符串长度如果小于将当前长度赋值给最长长度。for语句结束后返回最长长度的值。
3.问题###
无
四、题目6-4 指定位置输出字符串##
1.实验代码###
`char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 ) {
int i,j,start=-1,end;
char *p=NULL;
int len = strlen(s);
for(i = 0;i < len;i ++){
if(s[i] == ch1){
start = i;
p=&s[i];
break;
}
}
if(start == -1){
p=&s[i];
printf("\\n");
return p;
}
for(j = start;j < len;j ++){
if(s[j]!=ch2){
printf("%c", s[j]);
}
if(s[j]==ch2){
printf("%c\\n", s[j]);
return p;
}
if(j == len -1){
printf("\\n");
return p;
}
}
}`
2.设计思路###
第一步:先用一个for语句遍历字符串,并用if语句判断当前字符与所需截取的字符是否相等,如果相等记录下当前位置的下标并跳出循环。
第二步:判断当前是不是存在第一个字符并进行输出,用for语句进行遍历其中用if语句判断当前所遍历字符是否和最后一个字符相等如果相等输出当前字符,如果相等则输出当前字符并返回主函数,再用一个if语句判断是否为最后一项如果是返回主函数。
3.流程图###
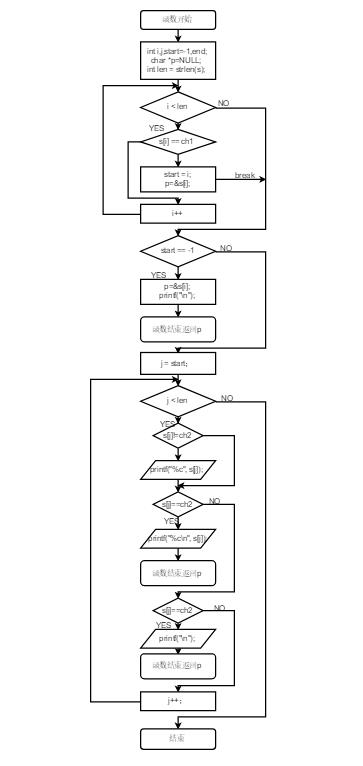
4.问题###
在第二点测试(有第二个没有第一个)一直在错。
是因为在判断有没有第一个数的时候,在没有第一个数的前提下没有加上“p=&s[i];”这句。
五、题目6-5 奇数值结点链表##
1.实验代码###
`struct ListNode *readlist()
{
struct ListNode *p=NULL,*tail=NULL,*head=NULL;
int data=0,count=0;
p=tail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&data);
while(data!=-1)
{
p->data=data;
p->next=NULL;
count++;
if(count==1)
{
head=p;
}else
{
tail->next=p;
tail=p;
}
p=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&data);
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L )
{
struct ListNode *i=NULL,*head1=NULL,*head2=NULL,*m=NULL,*n=NULL;
i=*L;
head1=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head2=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head1->next=NULL;
head2->next=NULL;
m=head1;
n=head2;
while(i)
{
if(i->data%2!=0)
{
m->next=i;
m=i;
}else
{
n->next=i;
n=i;
}
i=i->next;
}
m->next=NULL;
n->next=NULL;
*L=head2->next;
return head1->next;
}`
2.设计思路###
第一步:本题需要两个函数,第一个函数是进行链表的输入,在输入时,首先需要进行定义所需的结构体变量,之后在定义结构体中所需要的各个变量;之后再进行输入操作,通过while判断,进行给链表的单向赋值,在赋值时,还需要进行动态分配内存的操作,最后返回头指针。
第二步:本题的第二个函数就是进行奇数与偶数的分离,大体上是通过两个链表进行分离。
第三步:通过while判断所传入的链表中的data是否能被2所整除,来进行奇偶的分离;最后返回头指针。
3.问题###
无
六、题目6-3 链表拼接##
1.实验代码###
`struct stud_node *createlist()
{
struct stud_node *tail=NULL,*head=NULL,*p=NULL;
int num=0,score=0;
char name[20];
scanf("%d",&num);
while(num!=0)
{
p=(struct stud_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
p->num=num;
scanf("%s %d",p->name,&p->score);
if(head==NULL)
{
head=p;
}else
{
tail->next=p;
}
tail=p;
scanf("%d",&num);
p->next=NULL;
}
return head;
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score )
{
struct stud_node *ptr1=NULL,*ptr2=NULL;
for(;head!=NULL;head=head->next)
{
if(head->score>=min_score)
{
if(ptr1==NULL)
{
ptr1=head;
}else
{
ptr2->next=head;
}
ptr2=head;
}
}
if(ptr1==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}else
{
ptr2->next=NULL;
}
return ptr1;
}`
2.设计思路###
第一步:
第二步:
3.
七、题目6-3 链表拼接##
1.实验代码###
`struct ListNode *mergelists(struct ListNode *list1, struct ListNode *list2) {
struct ListNode *p1=list1;
int length=0;
int array[100];
for(p1=list1;p1!=NULL;p1=p1->next) {
array[length] = p1->data;
length++;
}
p1=list2;
for(;p1!=NULL;p1=p1->next) {
array[length] = p1->data;
length++;
}
int i,j,t;
for(i=0;i<length-1;i++) {
for(j=i+1;j<length;j++) {
if(array[j]<array[i]) {
t =array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i] = t;
}
}
}
struct ListNode *q,*head1 = NULL,*tail1=NULL;
i=0;
while(i<length) {
q = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
q->data = array[i];
if(head1 == NULL) {
head1 = q;
} else {
tail1->next = q;
}
tail1 = q;
tail1->next = NULL;
i++;
}
return head1;
} `
2.设计思路###
第一步:根据题目要求,题目是进行链表排序,又因本题定义的结构体中只有一种整数类型,所以我们可以,先定义一个数组,先将链表里的数据储存在数组中,之后再通过数组进行排序操作。
第二步:数组排序完之后,再通过for语句遍历的进行把数组里的值重新赋给链表。
3.问题###
将函数最后的tail1->next=q与tail1=q位置放反,导致系统崩坏。
单步调试后发现顺序的问题,最后改正。
八、学习总结和进度##
1.近期所学知识点与问题###
(1)如何理解指针数组,它与指针、数组有何关系?为何可以用二级指针对指针数组进行操作?####
答:数组元素全为指针的数组称为指针数组。指针数组是一个数组,并且数组元素都为指针。二级指针是指一个指针指向的是另外一个指针,可以储存指针。
(2).用指针数组处理多个字符串有何优势?可以直接输入多个字符串给未初始化的指针数组吗?为什么?####
二维数组比较浪费内存空间,指针便可节省下这一空间(因为会根据字符大小而申请空间)
(3).近期所学知识点####
首先学了指向函数的指针(*函数指针名)(参数表)类型名指定函数返回值的类型,变量名是指向函数的指针变量的名称。之后,学到了链表,主要学了链表的建立,链表的遍历,插入结点,删除结点。
2.同学互评###
3.图表###