基本信息
2017 IGARSS (顶会)
Can Semantic Labeling Methods Generalize to Any City? The Inria Aerial Image Labeling Benchmark
笔记
作者的认为现在遥感领域的算法受限于数据集。
-
数据集所涵盖的面积比较小,遥感数据和地点关系比较大,所以算法的泛化能力也受到了数据集的限制。
those images cover limited geographic areas and the evaluation procedure does not assess how the methods generalize to different contexts or more abstract semantic classes.
> the image tiles tend to be self-similar and with uniform color histograms
所以,提出一个开放的数据集合:
Dataset features:
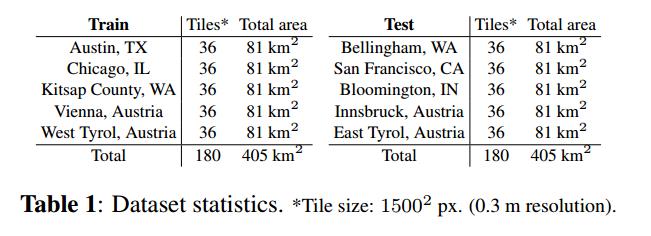
- Coverage of 810 km² (405 km² for training and 405 km² for testing)
- Aerial orthorectified color imagery with a spatial resolution of 0.3 m
- Ground truth data for two semantic classes: building and not building (publicly disclosed only for the training subset)
具体如下:
同时开放一个检测平台contest,提供测试集的测试服务,也是一个比赛。
作者的另一个贡献是,自己做了实验,定了一个baseline,
实验
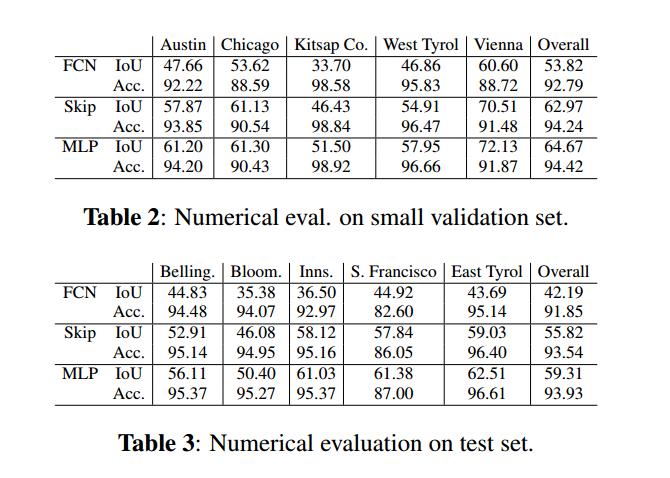
第一步,将训练集合分成训练集合和验证集合,也就是small vallidation set。
先是做了base-FCN的实验,然后参考论文(Emmanuel Maggiori, Yuliya Tarabalka, Guillaume Charpiat, and Pierre Alliez, “High-resolution semantic labeling with convolutional neural networks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.01962, 2016. )结合各层特征,做了Skip 的实验。自己再修正,重点介绍了关于MLP的实验。
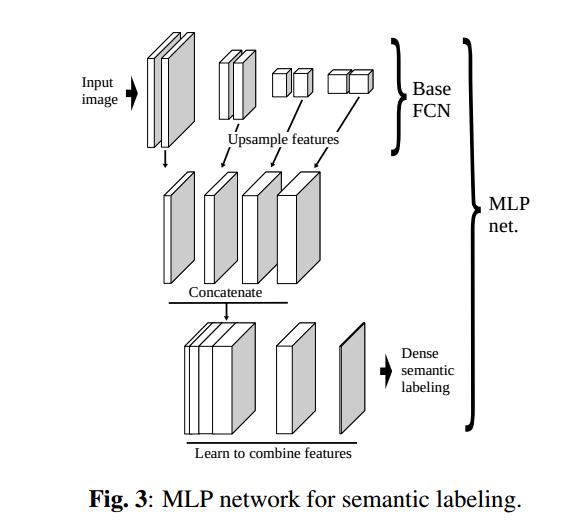
主要的改进是Concatenate各个特征层,然后,利用一个只有一个hidden层MLP来,实现分类。
总结
整个测试,注重两个指标:
- First, the accuracy,defined as the percentage of correctly classified pixels.
- Secondly, the intersection over union (IoU) of the positive (building) class.
关于IOU的提升空间还很大~
The MLP network reaches about 60% IoU on the entire test set. This means that the output objects overlap the real ones by 60%, as assessed over a significant amount of test data. While there is certainly room for improvement·····