Tree Restoring
Posted oc_co
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tree Restoring相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目描述
Aoki loves numerical sequences and trees.
One day, Takahashi gave him an integer sequence of length N, a1,a2,…,aN, which made him want to construct a tree.
Aoki wants to construct a tree with N vertices numbered 1 through N, such that for each i=1,2,…,N, the distance between vertex i and the farthest vertex from it is ai, assuming that the length of each edge is 1.
Determine whether such a tree exists.
Constraints
2≤N≤100
1≤ai≤N−1
One day, Takahashi gave him an integer sequence of length N, a1,a2,…,aN, which made him want to construct a tree.
Aoki wants to construct a tree with N vertices numbered 1 through N, such that for each i=1,2,…,N, the distance between vertex i and the farthest vertex from it is ai, assuming that the length of each edge is 1.
Determine whether such a tree exists.
Constraints
2≤N≤100
1≤ai≤N−1
输入
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
a1 a2 … aN
N
a1 a2 … aN
输出
If there exists a tree that satisfies the condition, print \'Possible\'. Otherwise, print \'Impossible\'.
样例输入
5
3 2 2 3 3
样例输出
Possible
提示
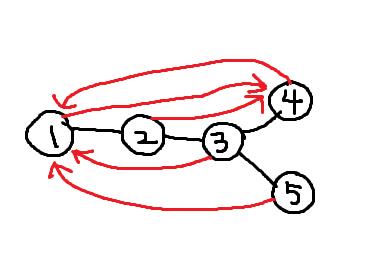
The diagram above shows an example of a tree that satisfies the conditions. The red arrows show paths from each vertex to the farthest vertex from it.
解析
代码比较长,整体思路就是先排序,找到最长的那一路,然后确定这个长度为主干(比如说最长的是n,那主干长度是n+1),然后把其他的分支都可以插在中间,但是这些分路构成的长度不能长于主干长度,因此这些分支的距离就是主干中间的最长距离加一,就比如说样例,主干长度是3,因此有4个数为主干,因此这四个数的最长距离为3、2、2、3,剩下的一个可以在中间的两个二中任选一个加一,就是3、2、2、3、3。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; int s[200]; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int i,j,k,m,n; int ans=0,cnt=0; int flag=0; int flag1=0; cin>>n; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>s[i]; sort(s+1,s+n+1); int gen=s[n],num=0; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) if(s[i]==gen) num++; if(num==1) cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; else { if(gen%2!=0) { k=(gen+1)/2; m=k; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(s[i]==k) { cnt++; } if(cnt>2) { cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; return 0; } } for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { if(s[i]<k) { cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; return 0; } if(m==s[i]) { ans++; } if(ans==2) { ans=0; m++; } if(m==(gen+1)) { cout<<"Possible"<<endl; return 0; } } cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; } else { k=gen/2; m=k; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(s[i]==k) { cnt++; } if(cnt>1) { cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; return 0; } } for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { if(s[i]<k) { cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; return 0; } if(m==s[i]) { ans++; } if(ans==2&&flag) { ans=0; m++; } else if(ans==1&&!flag) { ans=0; m++; flag=1; } if(m==gen+1) { cout<<"Possible"<<endl; return 0; } } cout<<"Impossible"<<endl; } } return 0; }
以上是关于Tree Restoring的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
