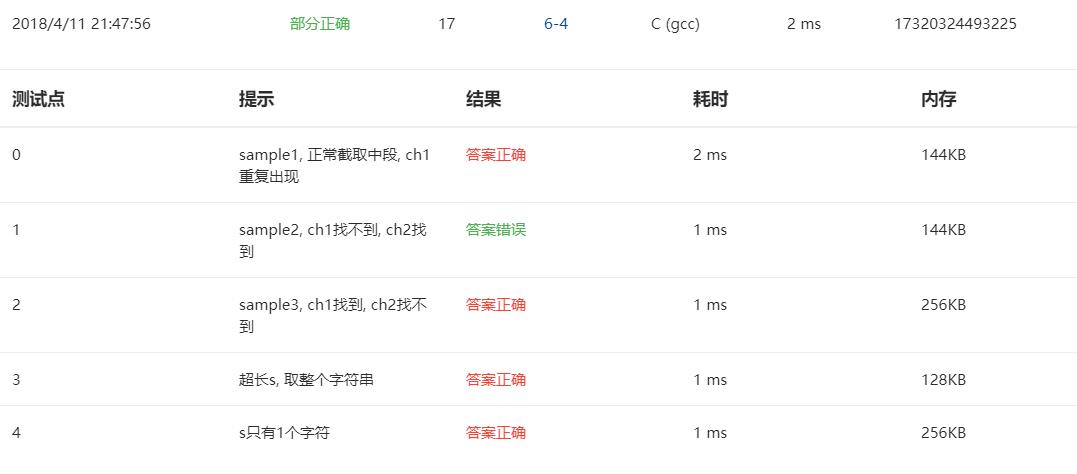
C高级第三次作业(1)
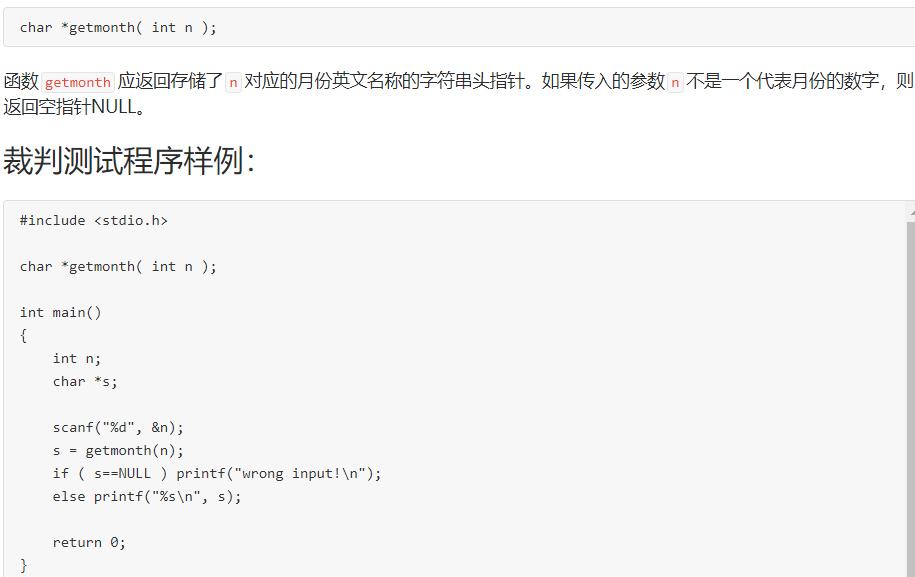
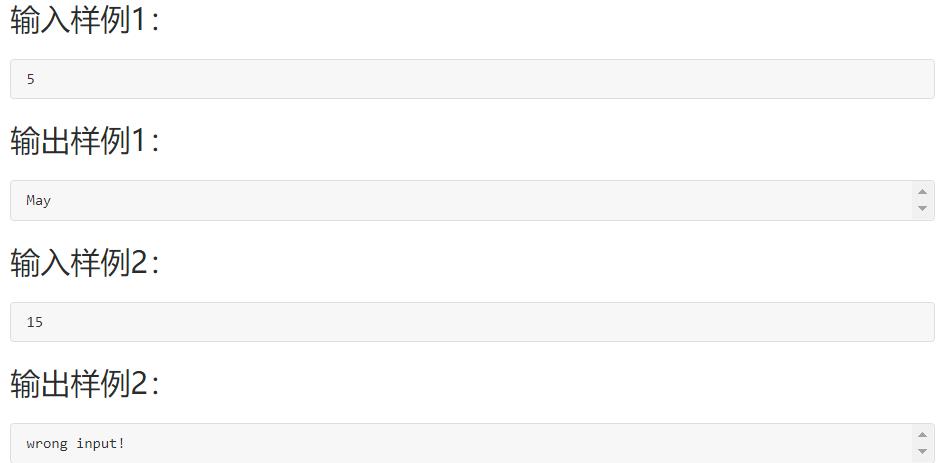
6-1 输出月份英文名

1.设计思路
(1)算法:
第一步:定义整型变量n,字符指针s,输入一个数赋给n。
第二步:调用函数getmonth将值赋给s。
第三步:在函数getmonth中使用switch—case语句来实现,返回月份的英文名。
第四步:在主函数中如果s==NULL就输出wrong input,否则输出s。
(2)流程图:
2.实验代码:
char *getmonth( int n ){
char *a;
switch(n){
case 1:strcpy(a,"January");break;
case 2:strcpy(a,"February");break;
case 3:strcpy(a,"March");break;
case 4:strcpy(a,"April");break;
case 5:strcpy(a,"May");break;
case 6:strcpy(a,"June");break;
case 7:strcpy(a,"July");break;
case 8:strcpy(a,"August");break;
case 9:strcpy(a,"September");break;
case 10:strcpy(a,"October");break;
case 11:strcpy(a,"November");break;
case 12:strcpy(a,"December");break;
default:strcpy(a,"NULL");
}
return(a);
}
修改后的代码
char *getmonth( int n ){
switch(n){
case 1:return "January";
case 2:return "February";
case 3:return "March";
case 4:return "April";
case 5:return "May";
case 6:return "June";
case 7:return "July";
case 8:return "August";
case 9:return "Septemer";
case 10:return "October";
case 11:return "November";
case 12:return "December";
default:return NULL;
}
}
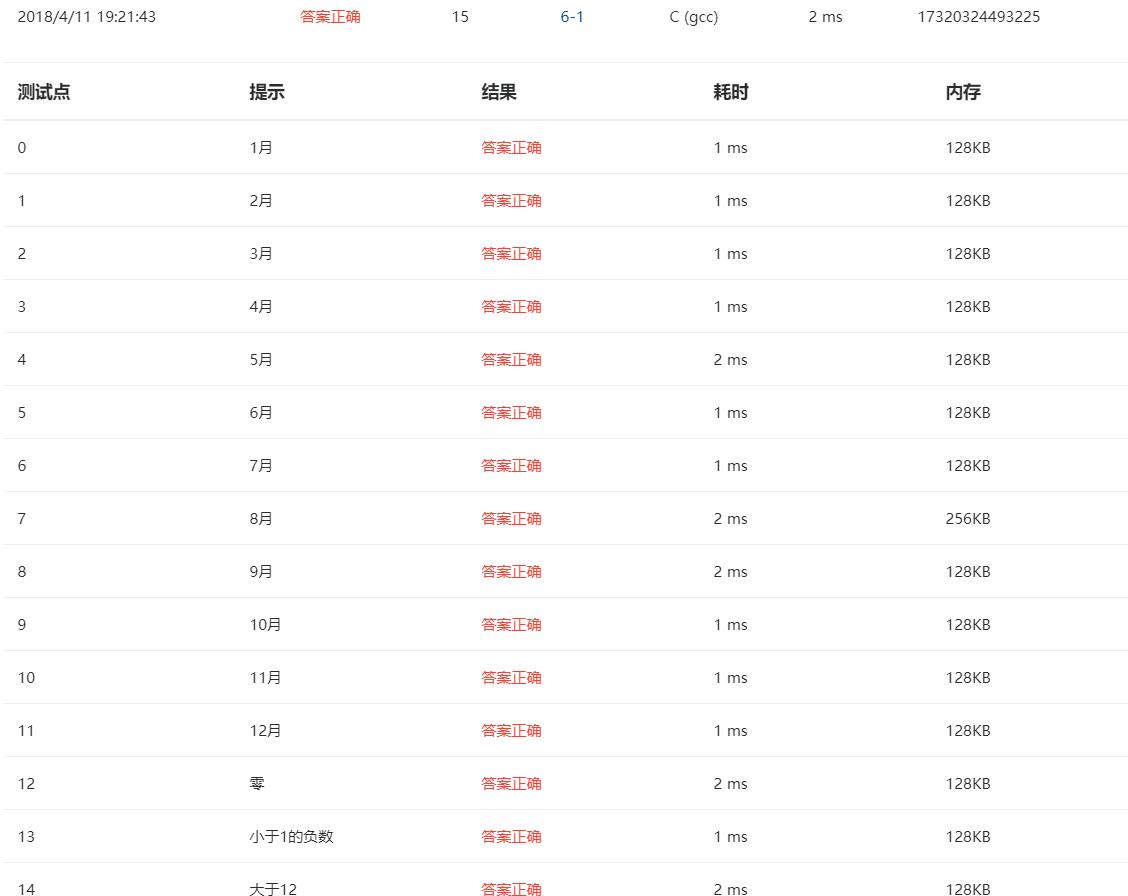
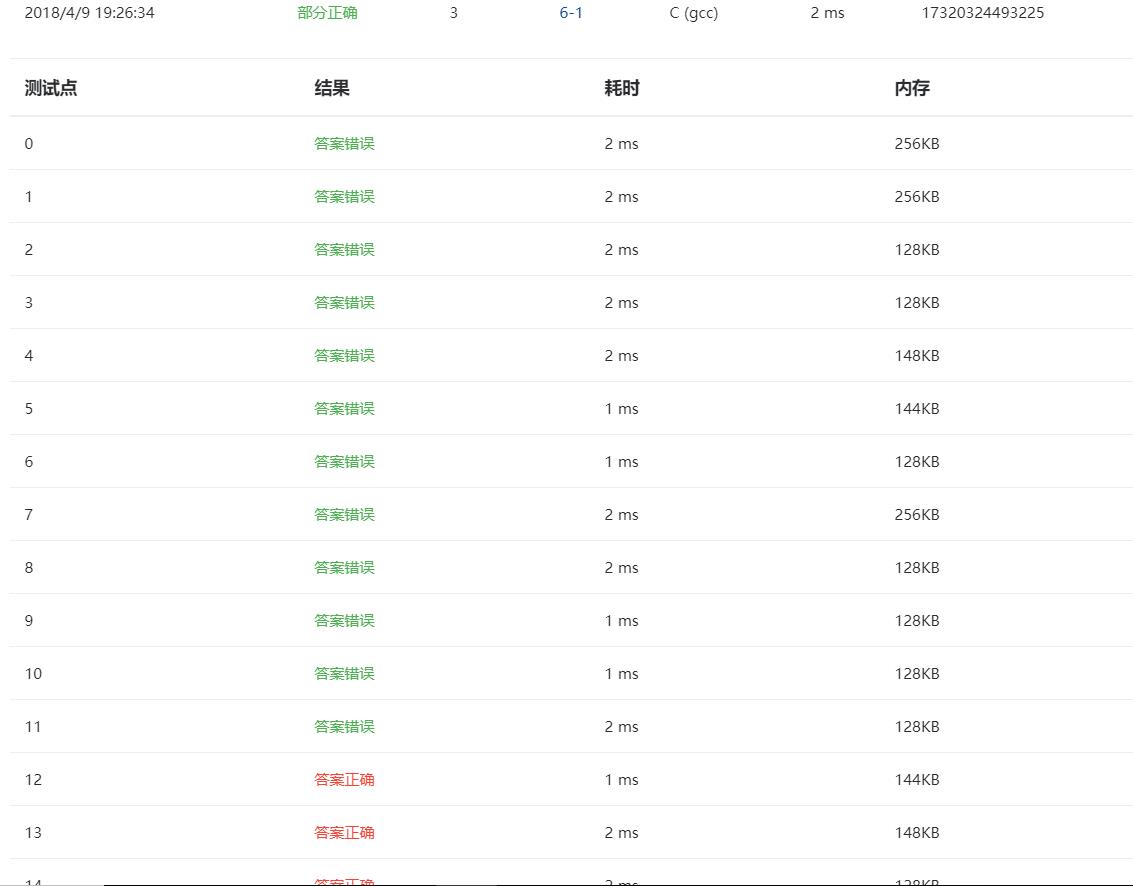
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
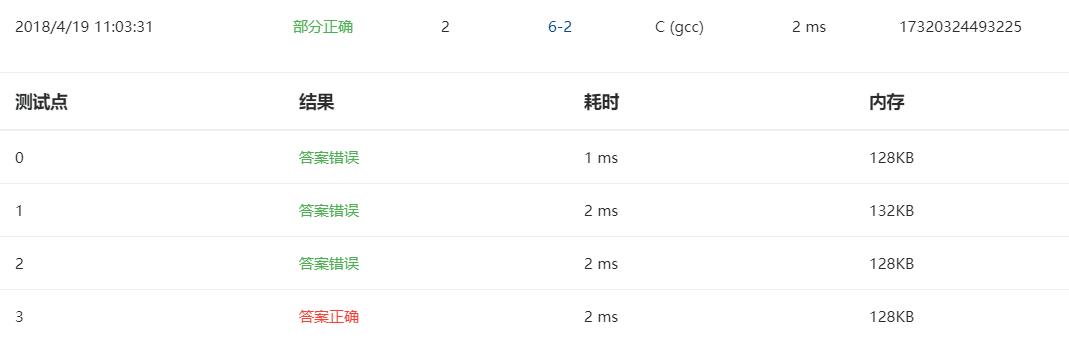
问题1:部分正确
错误的原因:没有声明string函数库,无法调用strcpy函数。
修正方法:自己想不出来在网上搜解题思路,自己重新写。
6-2 查找星期


1.设计思路:
(1)算法:
第一步:定义整型变量i,字符数组s[MAXS],输入一个字符串赋给s。
第二步:调用函数getindex,n=getindex的返回值。
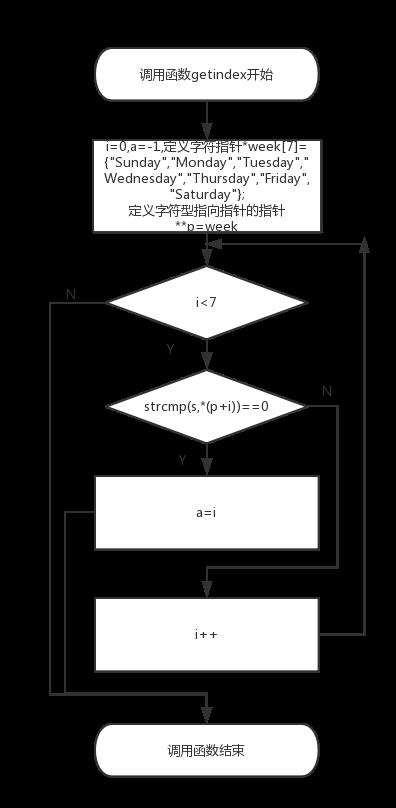
第三步:在getindex函数中,定义整型变量a=-1,i=0,字符指针数组*week[7]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"},定义字符型指向指针的指针**p=week在for循环中i为循环变量,条件为i<7,如果strcmp(s,week[i])0,就执行a=i,然后跳出这个循环,执行完for循环最后返回a。
第四步:在主函数中如果n-1,就执行wrong input!,否则就输出n的值
(2)流程图:
2.实验代码
int getindex( char *s ){
int a=-1,i;
char *week[7]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
char **p=week;
for(i=0;i<7;i++){
if(strcmp(s,*(p+i))==0){
a=i;
break;
}
}
return a;
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
6-3 计算最长的字符串长度

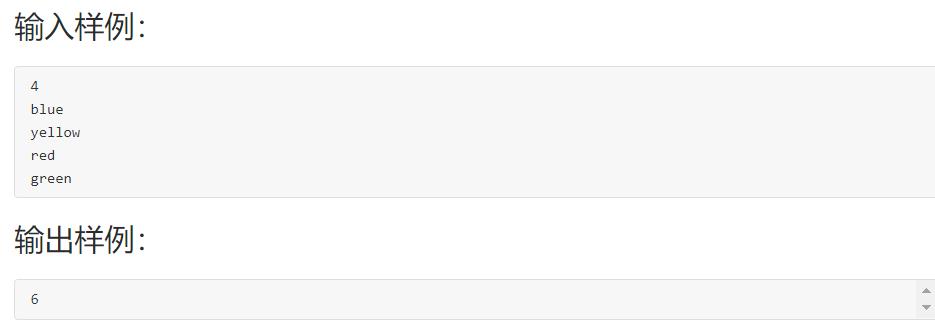
1.设计思路:
(1)算法:
第一步:常量MAXN 10,MAXS 20,定义整型变量i,n,字符指针数组string[MAXN] = {NULL},输入一个数赋给n。
第二步:借助for循环i=0;条件为i<n;在for循环中动态分配内存大小为20字节,输入一个字符串赋给string[i]。
第三步:调用max_len函数,将函数max_len的返回值输出。
第四步:在函数max_len中,定义整型变量i,count=0,j,整型数组q[20]={0};借助for循环求出(*(s+i))中的字符串的长度,将值赋给q[i];
第五步:count=q[0],借助for循环找到q[i]的最大值赋给count,最后返回count的值。
(2)流程图
2.实验代码:
int max_len( char *s[], int n ){
int i,count=0,j,q[20]={0};
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;*(*(s+i)+j)!=\'\\0\';j++){
}
q[i]=j;
}
count=q[0];
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
if(q[i]>count){
count=q[i];
}
}
return count;
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
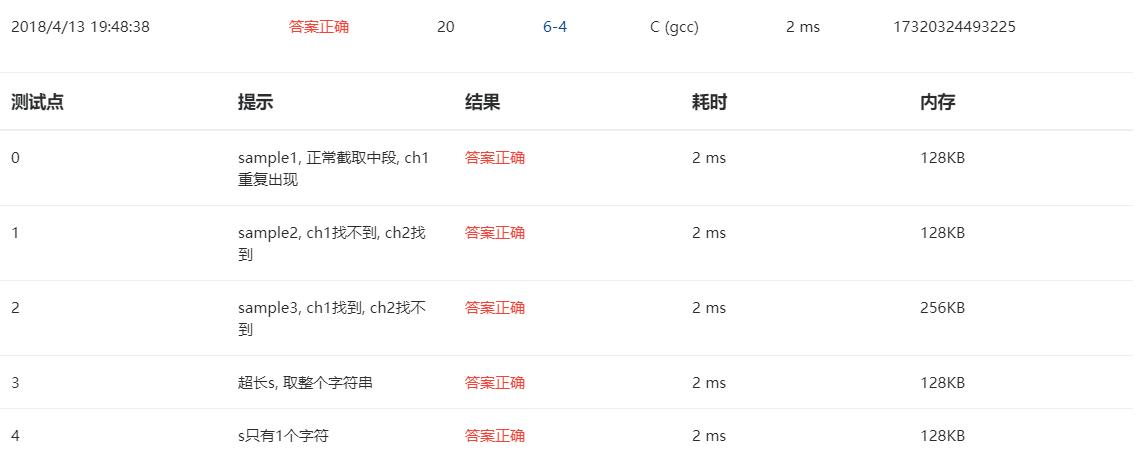
6-4 指定位置输出字符串
1.设计思路
(1)算法:
第一步:定义字符数组str[10],字符变量ch_start, ch_end,字符型指针变量p,
第二步:独树一格字符串给str,读入两个字符分别赋给ch_start, ch_end,
第三步:调用函数match,将函数的返回值赋给p。
第四步:在函数match中定义整型变量i,j,字符型指针q=NULL,i=0,借助for循环条件为(s+i)!=\'\\0\',在for循环中如果(s+i)==ch1,定义字符型指针a=&s[i],j=i,借助for循环条件为((s+j)!=ch2)&&((s+j)!=\'\\0\'),输出字符(s+j),执行完第二个for循环判断如果(s+j)!=\'\\0\',就输出字符(s+j),并且换行,返回a的地址,执行完第一个for循环直到条件不满足,就换行并且返回q的地址。
第五步:输出字符串p。
(2)流程图:
2.实验代码:
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 ){
int i,j;
char *q=s;
for(i=0;*(s+i)!=\'\\0\';i++){
if(*(s+i)==ch1){
for(j=i;*(s+j)!=ch2;j++){
*(q)=*(s+j);
q++;
}
*q=ch2;
}
}
*q=\'\\0\';
printf("%s\\n",q);
}
修改后的代码:
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 ){
int i,j;
char *q=NULL;
for(i=0;*(s+i)!=\'\\0\';i++){
if(*(s+i)==ch1){
char *a= &s[i];
for(j=i;(*(s+j)!=ch2)&&(*(s+j)!=\'\\0\');j++){
printf("%c",*(s+j));
}
if(*(s+j)!=\'\\0\')
printf("%c",*(s+j));
printf("\\n");
return a;
}
}
printf("\\n");
return q;
}
在修改后的代码:
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 ){
int i,j;
char *q=NULL;
for(i=0;*(s+i)!=\'\\0\';i++){
if(*(s+i)==ch1){
char *a= &s[i];
for(j=i;(*(s+j)!=ch2)&&(*(s+j)!=\'\\0\');j++){
printf("%c",*(s+j));
}
if(*(s+j)!=\'\\0\')
printf("%c",*(s+j));
printf("\\n");
return a;
}
}
printf("\\n");
return s+i;
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
错误信息1:段错误
错误原因:自己没有读懂题意就写代码,一方面自己最后只是输出两个字符之间的所有字符,另一方面当函数找不到时返回得值不值空指针,代码不能满足所有的测试点。
改正方法:在一开始就定义指针为空指针,当找到的的话就重新定义一个指针,他的值为ch1的地址,输出在两个字符之间的所有字符,输出完换行并且返回指针变量,没有找到,就换行并且返回空指针。
错误信息2:部分正确有一个测试点错误
错误原因:在最后的返回值返回的是空指针原来返回的是q空指针
改正方法:将返回值改成s+i
码云代码存放:
C高级第三次作业(2)
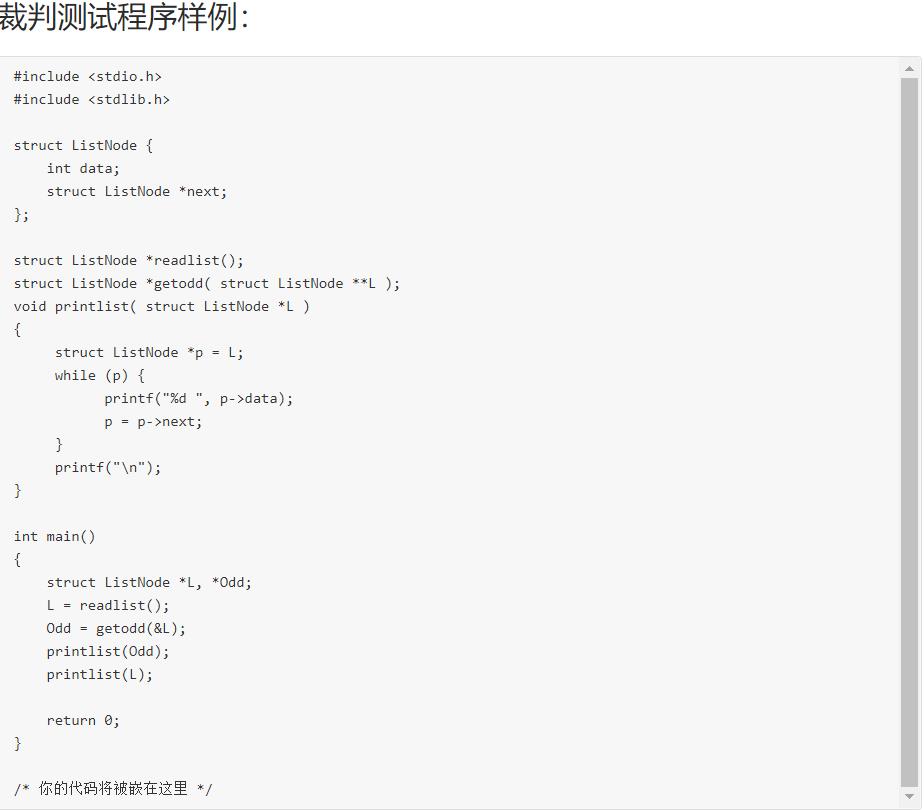
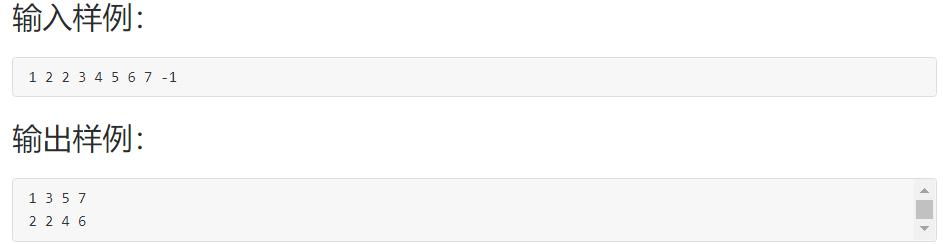
6-1 奇数值结点链表
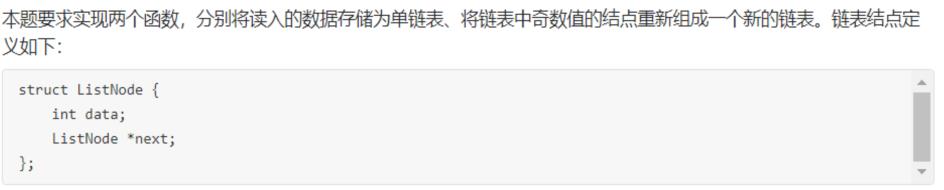

1.设计思路
(1)算法:
第一步:声明结构体类型,整型变量data,结构体指针变量next
第二步:在主函数中,定义结构体指针变量L,Odd,调用函数readlist将函数的返回值给L,调用函数getodd,将函数的返回值给Odd,
第三步:在readlist函数中,定义结构体指针变量head=NULL,p=NULL,q=NULL,整型数data,对p,q动态分配内存类型强制转化为结构体指针,大小为sizeof(struct ListNode),读入一个书给p->data,使用while语句条件为p->data!=-1,在循环语句中如果headNULL,head=p,否则q->next=p,在if语句结束之后q=p,在对p动态分配内存类型强制转化为结构体指针,大小为sizeof(struct ListNode),读入一个数给p->data,在执行完while语句后q->next=NULL,返回head。
第四步:在getodd函数中,定义结构体指针变量head=NULL,q=NULL,p,w=NULL,head1=NULL,如果L!=NULL就执行for循环,for循环条件1为head=*L,条件2为head!=NULL,条件3为head=head->next,在for循环中如果head->data%2!=0执行head1=head,否则执行p->next=head,在if语句之后p=head,如果head->data%2!=0不满足,就执行如果qNULL,q=head,否则w->next=head,在if语句之后执行w=head,执行完for循环后p->next=NULL,如果w!=NULL执行w->next=NULL。最后*L=q。在第一个if不满足时返回NULL,在最后返回head1.
第五步:两次调用函数printlist,将奇数和偶数的链表分别打印出来。
(2)流程图:
2.实验代码:
struct ListNode *readlist(){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
int data;
p=q=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
while(p->data!=-1){
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L ){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*q=NULL,*p,*w=NULL,*head1=NULL;
if(*L!=NULL){
for(head=*L;head!=NULL;head=head->next){
if(head->data%2!=0){
if(head1==NULL){
head1=head;p=head1;
}else{
e->next=p;
}
for(q=*L;q->data%2==0&&q->next!=NULL;q=q->next){
w=q;
}
if(q->data%2!=0){
if(q=*L){
*L=q->next;
}else{
w->next=q->next;
}
}//
}
}
w->next=NULL;
}else{
return NULL;
}
e->next=NULL;
return head1;
}
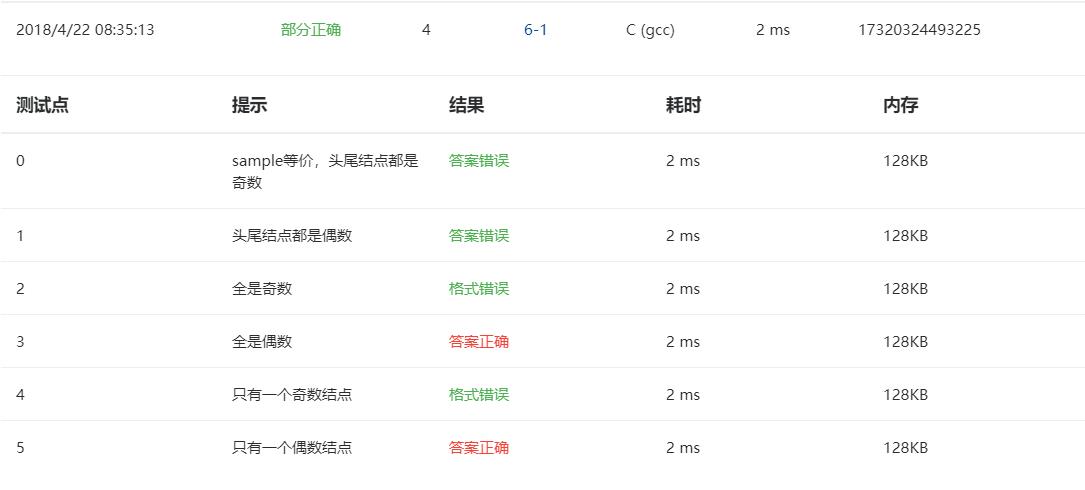
修改后的代码:
struct ListNode *readlist(){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
int data;
p=q=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
while(p->data!=-1){
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
}
q->next=NULL;
return(head);
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L ){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*q=NULL,*p,*w=NULL,*head1=NULL;
if(*L!=NULL){
for(head=*L;head!=NULL;head=head->next){
if(head->data%2!=0){
if(head1==NULL){
head1=head;
}else{
p->next=head;
}
p=head;
}else{
if(q==NULL){
q=head;w=q;
}else{
w->next=head;
}
}
}
p->next=NULL;
if(w!=NULL)
w->next=NULL;
*L=q;
}else{
return NULL;
}
return(head1);
}
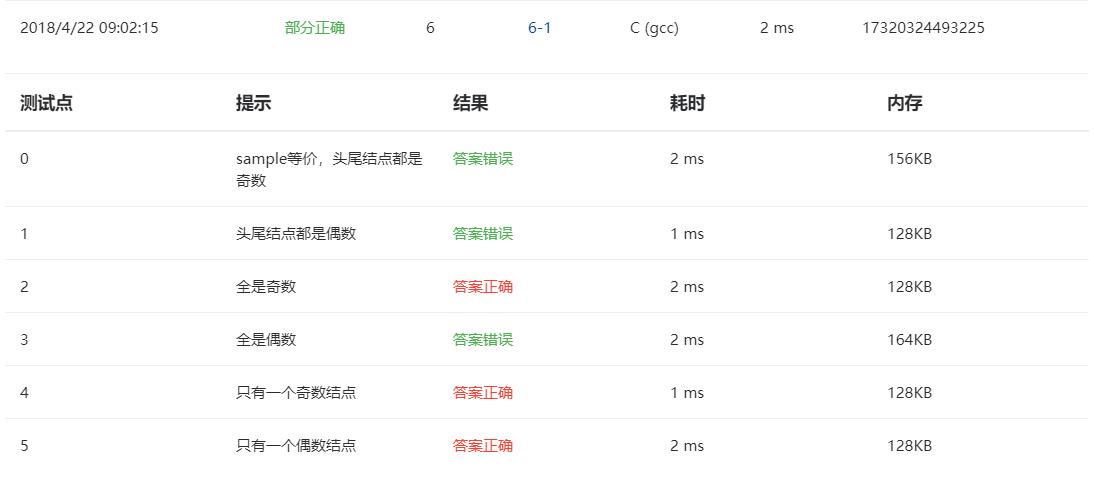
再次修改
struct ListNode *readlist(){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
int data;
p=q=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
while(p->data!=-1){
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
}
q->next=NULL;
return(head);
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L ){
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*q=NULL,*p,*w=NULL,*head1=NULL;
if(*L!=NULL){
for(head=*L;head!=NULL;head=head->next){
if(head->data%2!=0){
if(head1==NULL){
head1=head;
}else{
p->next=head;
}
p=head;
}else{
if(q==NULL){
q=head;
}else{
w->next=head;
}
w=head;
}
}
p->next=NULL;
if(w!=NULL)
w->next=NULL;
*L=q;
}else{
return NULL;
}
return(head1);
}
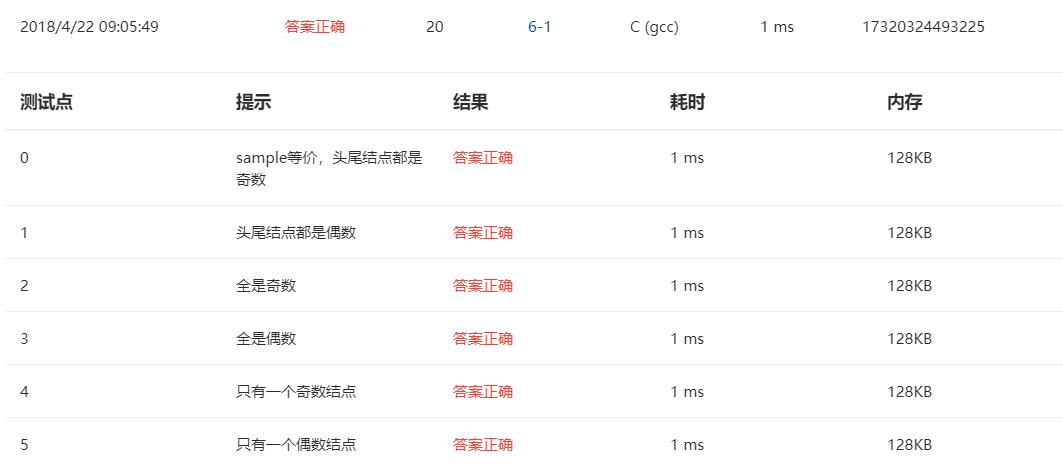
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
错误信息1:
错误的原因:调试的过程中知道1在建立链表时没将最后一个节点的值赋值为NULL。2.p的地址一直都是head1的起始地址,没有将p的地址变化
修改方法在建立链表的函数中最后加上p->next=NULL,在getodd函数中p=head。
错误信息2.
错误原因:同样的问题w的地址一直都是q的起始地址没有叫它改变,
改正方法:使w=head。
6-2 学生成绩链表处理

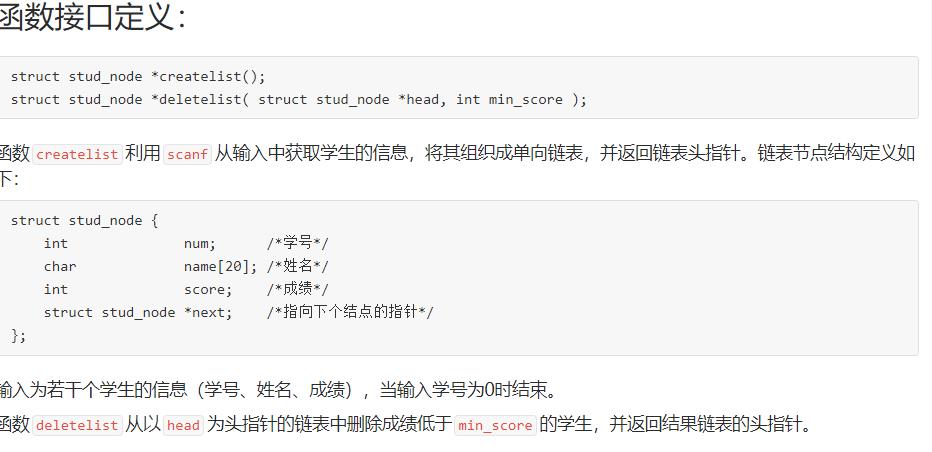

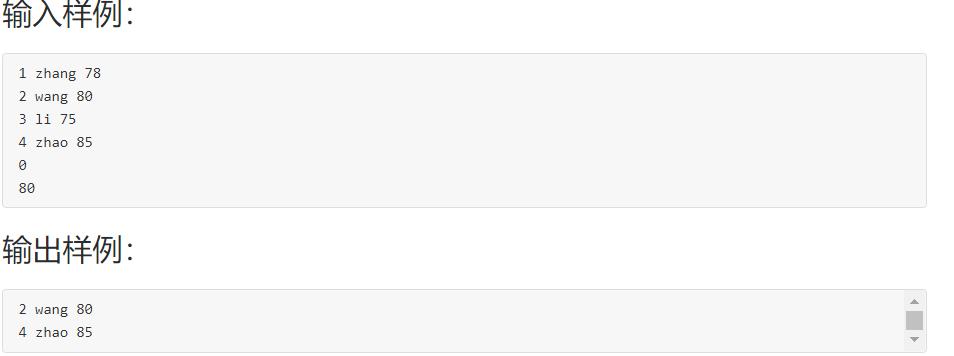
1.设计思路
(1)算法
第一步:声明结构体类型,整型数num,字符数组name[20],整型数score结构体指针变量next,
第二步:主函数中,定义整型min_score,结构体指针变量p,head=NULL,调用函数creatlist,将creatlist的返回值赋给head,
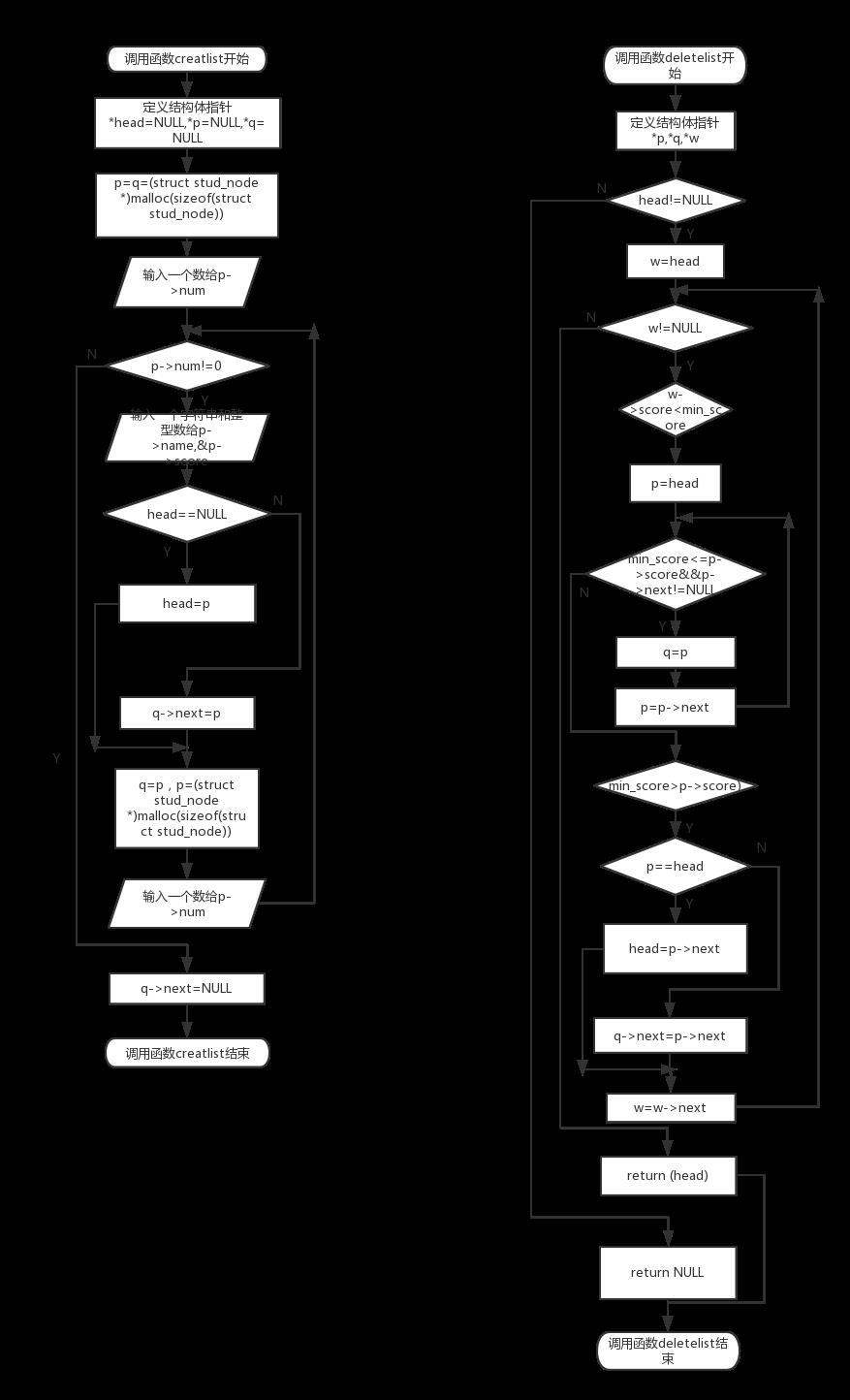
第三步在creatlist函数中,定义结构体指针变量head,p=NULL,q=NULL,对p和q动态分配内存类型强制转化为结构体指针,大小为sizeof(struct stud_node),读入一个数赋给p->num,使用while循环条件为p->num!=0,在循环体中,读入一个字符串和整型数字给p->name和p->score,如果headNULL,head=p,否则q->next=p。if语句结束执行q=p 在对p动态分配内存类型强制转化为结构体指针,大小为sizeof(struct stud_node),,读入一个数赋给p->num,当while天剑不满足时执行q->next=NULL,返回head给主函数
第四步:在主函数中输入一个数给min_score,调用函数deletelist,将函数的返回值给head,
第五步:定义结构体指针变量p,q,*w,使用if语句,条件为head!=NULL,借助for循环条件1为w=head,条件2为w!=NULL条件3为w=w->next,在循环体中借助if语句条件为w->score<min_score,借助for循环条件1为p=head条件2为min_score<=p->score&&p->next!=NULL条件3为p=p->next,在循环体中执行q=p。直到结束使用if语句条件min_score>p->score,在判断语句中使用if语句条件为phead执行head=p->next否则执行q->next=p->next,在第一个if语句不满足时返回NULL,最后返回head
第六步:打印链表head,
(2).流程图:
2.实验代码
struct stud_node *createlist(){
struct stud_node *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
p=q=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
scanf("%d",&p->num);
while(p->num!=0){
scanf("%s %d",p->name,&p->score);
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
q->next=NULL;
return (head);
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score ){
struct stud_node *p,*q,*w;
int i;
if(p!=NULL){
for(w=head;w!=NULL;w=w->next){
p=head;
while(min_score<=p->score&&p->next!=NULL){
q=p;p=p->next;
}
if(min_score>p->score){
if(p==head){
head=p->next;
}else{
q->next=p->next;
}
}
}
}
return (head);
}
修改后的代码
struct stud_node *createlist(){
struct stud_node *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
p=q=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
while(p->num!=0){
scanf("%s %d",p->name,&p->score);
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
q->next=NULL;
return (head);
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score ){
struct stud_node *p,*q,*w;
if(head!=NULL){
for(w=head;w!=NULL;w=w->next){
if(w->score<min_score){
for(p=head;min_score<=p->score&&p->next!=NULL;p=p->next){
q=p;
}
if(min_score>p->score){
if(p==head){
head=p->next;
}else{
q->next=p->next;
}
}
}
}
return (head);
}
else{
return NULL;
}
}
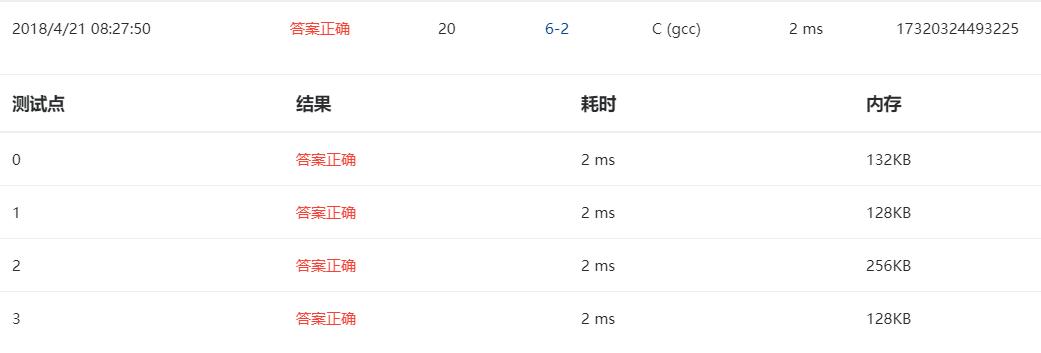
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
错误信息1
错误原因:只删除一个不满足条件的节点。
改正方法,使用for循环每找到一个不满足条件的就执行一次删除操作。
6-3 链表拼接
1.设计思路:
(1)算法:自己的思路有问题;
(2)流程图
2.实验代码:
struct ListNode *mergelists(struct ListNode *list1, struct ListNode *list2){
struct ListNode *head,*p,*q;
int a[10],i=0;
for(p=list1;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
a[i++]=p->data;
}
for(p=list2;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
a[i++]=p->data;
}
int j,n,k,temp;
n=i;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){
k=i;
for(j=i;j<n;j++){
if(a[j]<a[k]){
j=k;
}
}
if(k!=i){
temp=a[i];a[i]=a[k];a[k]=temp;
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
p->data=a[i];
if(head==NULL){
head=p;
}else{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
}
q->next=NULL;
return head;
}
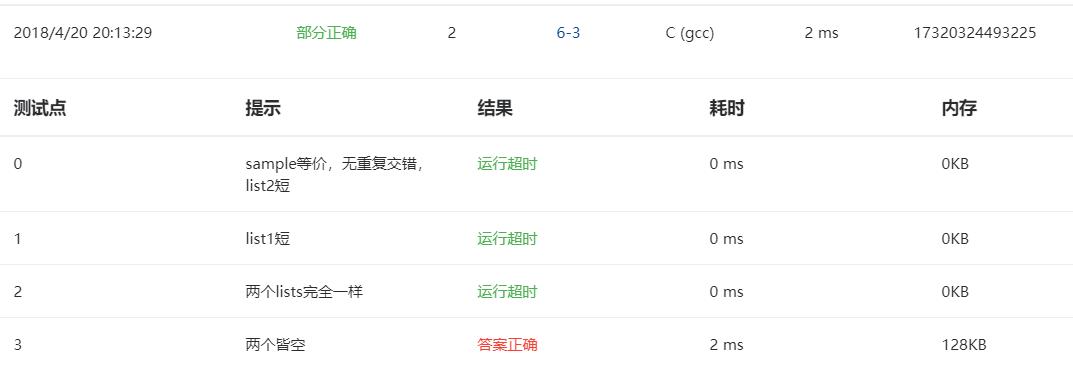
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法:
错误信息1: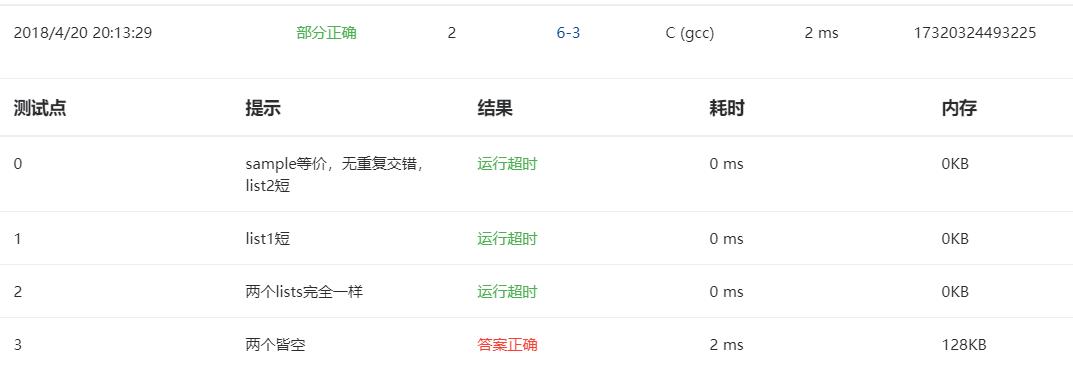
错误原因:考虑不全面
改正方法:不会。
博客上的题目

实验代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
long *zhishu(long *p,int a,int b);
void print(long *p,int a,int b);
int main()
{
int a=201,b=3936,i,j;
long n[a*b],*p;
for(i=0;i<a;i++){
for(j=0;j<b;j++){
n[(i+1)*(j+1)]=(i+1)*(j+1);
}
}
p=zhishu(n,a,b);
print(p,a,b);
return 0;
}
long *zhishu(long *p,int a,int b){
int i,j,c=2,d=0;
long *q=p;
j=a*b;
for(i=0;i<j&&c<=sqrt(a*b);i++){
d=0;
if(*(q+i)!=1){
if(*(q+i)%c!=0){
q[d++]=*(q+i);
}
}
j=d;
c=q[0];
}
return q;
}
void print(long *p,int a,int b){
int i;
for(i=0;*(p+i)<=a*b;i++){
if((i+1)%5!=0){
printf("%ld ",*(p+i));
}else{
printf("%ld\\n",*(p+i));
}
}
}
运行出错,不会写
修改后的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 20
#define M 39
void delete(int s[N][M],int x);
int main()
{
int i,j,a[N][M],num=1;
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
for(j=0;j<M;j++){
a[i][j]=num;
num++;
}
} //创建一个二维数组,元素从1 到N*M
a[0][0]=0; //a[0][0]=1不是质数,将它赋值为0
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
for(j=0;j<M;j++){
if(a[i][j]!=0){
delete(a,a[i][j]); //调用函数进行筛选法 ,每调用函数一次数组a,a的值都会发生变化,不是质数的元素赋值为0
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
for(j=0;j<M;j++){
if(a[i][j]!=0){
printf("%d\\t",a[i][j]);
}
}
} //将所有的指数(数组中不为0的数)输出
return 0;
}
void delete(int s[N][M],int x){
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
for(j=0;j<M;j++){
if(i!=0||j!=0){ //跳过a[0][0],
if(s[i][j]%x==0&&s[i][j]!=x){
s[i][j]=0;//将所有的能被想整除的数赋值为0
}
}
}
}
}
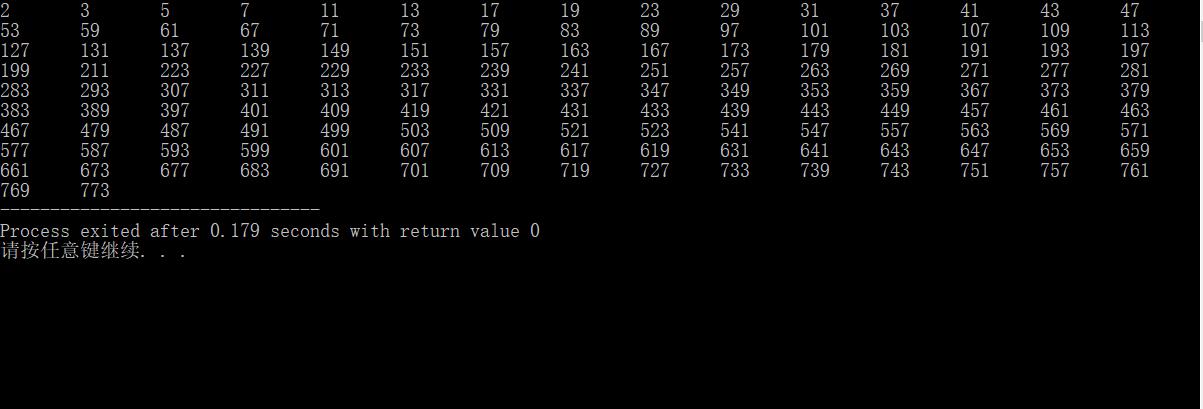
反思:
1.在做题之前好好读题,要读懂题的意思
2.不要固定自己的思维,一种方法不可以,可以换个方法。
3.当出现问题的时候,不要抱怨,自暴自弃,要多想一想
代码存放:
git
评论我的博客同学:
姜健https://i.cnblogs.com/EditPosts.aspx?postid=8778302
陆文奇:https://i.cnblogs.com/EditPosts.aspx?postid=8778302
党睿:https://i.cnblogs.com/EditPosts.aspx?postid=8778302
辛静瑶:https://i.cnblogs.com/EditPosts.aspx?postid=8778302
我所评论的同学:
姜健:http://www.cnblogs.com/jj990519/p/8763063.html
袁中:http://www.cnblogs.com/2719610441qqcom/p/8762037.html
王姝雯:http://www.cnblogs.com/phsudie/p/8759331.html
党睿:http://www.cnblogs.com/dangrui/p/8797836.html
辛静瑶:http://www.cnblogs.com/X-JY/p/8761685.html
知识点总结:
char *name[]={"Follow me","BASIC",......}
指针数组相当于二维数组;
name ——>二维数组的首元素的地址 =name[0]——>行指针——>第0行首元素的地址/第0个字符串的起始地址
name[1]——>行指针——>第一行首元素的地址 /第一个字符串的起始地址
*name——>列指针——>第0行第0列元素的地址/指向第0个字符串的第0个字符的地址
*(name+1)——>列指针——>第一行第0列元素的地址/指向第一个字符串的第0个字符的地址。
*(name+i)+n >第i行第n列元素的地址
((name+i)+n)>第i行第n列元素的值 例如 ((name+1)+1)=‘A’
链表其实就是结构递归定义,有一个头指针变量,还有表尾,表尾的地址部分放一个NULL表示链表结束。
形式
struct student{
int num;
float score;
......
struct student *next; //最主要的
};
在链表中要使用动态分配内存
malloc函数,malloc函数的返回值是一个分配域的起始地址
在链表中形式为:p=(struct student *)malloc(sizeof struct student );
对链表的操作:建立动态链表、输出、插入、删除;
建立链表的函数:
struct student *creat(void){
struct student *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
p=q=(struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
while(p->num!=0){
if(head==NULL)head=p;
else q->next=p;
q=p;
p=(struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
q->next=NULL;
return(head);
}
输出链表:
void print(struct student *head){
struct student *p;
for(p=head;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
printf("%d %f ...."p->num,p->score,.....);
}
}
删除节点:
struct student *deleatstruct student *head,int num){
struct student *p,*q;
if(head!=NULL){
for(p=head;p->next!=NULL&&p->num!=num;p=p->next){
q=p;
}
if(p->num==num){
if(p==head)head=p->next;
else q->next=p->next;
}
}else{
printf("没有找到");
}
return(head);
}
插入节点:
struct student *insert(struct student *head,struct student *stud){
struct student *p,*q;
if(head!=NULL){
for(p=head;p->num!=stud->num&&p->next!=NULL;p=p->head){
q=p;
}
if(p->num==stud->num){
if(p==head){head=stud;stud->next=p;}
else{q->next=stud;stud->next=p;}
}else{p->next=stud;stud->next=NULL}
}
return(head);
}