[算法]循环打印矩阵,蛇形矩阵专题
Posted 陈驰字新宇
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[算法]循环打印矩阵,蛇形矩阵专题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 循环打印矩阵
比方提供以下矩阵:
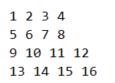
按照如下顺序打印出来:
1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
这道题直接写也没问题,就是特别容易出错,稍不留意就写错,而且这类题型我想要一种普适性的解法。
我想到的一种方法就是一圈一圈打印,从外到内,我们确定一个矩形,通常通过左上角的坐标和右下角的坐标即可,即(tR,tC)和(dR,dC),我们先写出打印一圈的方法,然后循环调用,如果我们发现左上角的坐标跑到了右下角坐标的右边或者下边,整个过程就停止,这样额外的空间复杂度是O(1)。No bibi,show me the code.
package com.darrenchan; /** * 转圈打印矩阵 * @author Think * */ public class SheXingPrint2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] m = new int[][]{{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8},{9,10,11,12},{13,14,15,16}}; int tR = 0, tC = 0, dR = 0, dC = 3; while(tR <= dR && tC <= dC){ printEdge(m, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--); } } public static void printEdge(int[][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC){ if(tR == dR){ for (int i = tC; i <= dC; i++) { System.out.print(m[tR][i] + " "); } }else if(tC == dC){ for (int i = tR; i <= dR; i++) { System.out.print(m[i][tC] + " "); } }else{ int curRow = tR; int curCol = tC; while(curCol != dC){ System.out.print(m[tR][curCol] + " "); curCol++; } while(curRow != dR){ System.out.print(m[curRow][dC] + " "); curRow++; } while(curCol != tC){ System.out.print(m[dR][curCol] + " "); curCol--; } while(curRow != tR){ System.out.print(m[curRow][tC] + " "); curRow--; } } } }
2. 蛇形矩阵
给出一个数字,比方是4,直接生成如下矩阵:

思路和上一个类似,只是稍微改一下即可:
package com.darrenchan; /** * 打印蛇形矩阵 * @author Think * */ public class SheXingPrint3 { public static int num = 1; public static void main(String[] args) { //给出多大的数字,就构造多大的矩阵 int length = 4; int[][] m = new int[length][length]; int tR = 0, tC = 0, dR = m.length - 1, dC = m[0].length - 1; while (tR <= dR && tC <= dC) { generateEdge(m, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--); } for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(m[i][j] + "\\t"); } System.out.println(); } } public static void generateEdge(int[][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) { if(tR == dR){//处理length为奇数,最中间一个元素 m[tR][tC] = num; }else{ int curRow = tR; int curCol = tC; while(curCol != dC){ m[tR][curCol] = num; num++; curCol++; } while(curRow != dR){ m[curRow][dC] = num; num++; curRow++; } while(curCol != tC){ m[dR][curCol] = num; num++; curCol--; } while(curRow != tR){ m[curRow][tC] = num; num++; curRow--; } } } }
3. 双循环打印矩阵
一个起始点在左上角,和以前一样,顺时针走,另一个起始点在右下角,也是顺时针走,别人走过的,就不能重复走了。
比方

打印出:1 2 3 4
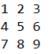
打印出:1 2 3 6 5 4 7 8 9

打印出:1 2 3 4 8 12 11 10 7 6 5 9 13 14 15 16
这道题的思路其实和上面第一个差不多,我还是采用的一圈一圈打印的思路,只不过原来一个指针打印一圈转4个方向,现在有两个指针,每个转2个方向,第一次转两个方向,第二次转另两个方向,依次类推。
其实这道题还可以进一步优化,因为两个指针完全关于矩阵中心点对称,所以确定一个,另一个就确定了。这里需要一个矩阵来记录该点是否已经走过。
代码如下:
package com.darrenchan; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * 双蛇形打印 * @author Think * */ public class SheXingPrint4 { public static int num = 1; public static void main(String[] args) { //给出多大的数字,就构造多大的矩阵 int length = 5; int[][] m = new int[length][length]; int temp = 1; for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++) { m[i][j] = temp++; } } int[][] visited = new int[m.length][m[0].length];//0是没有访问过,1是访问过 List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>(); List<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>(); int tr = 0; int tc = 0; int dr = m.length - 1; int dc = m[0].length - 1; int count = 1; while(tr <= dr && tc <= dc){ if(count % 2 == 1){ int curRow1 = tr; int curCol1 = tc; int curRow2 = dr; int curCol2 = dc; while(curCol1 != dc && curCol2 != tc){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0 && visited[curRow2][curCol2] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); curCol1++; visited[curRow2][curCol2] = 1; list2.add(0, m[curRow2][curCol2]); curCol2--; }else{ break; } } while(curRow1 != dr && curRow2 != tr){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0 && visited[curRow2][curCol2] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); curRow1++; visited[curRow2][curCol2] = 1; list2.add(0, m[curRow2][curCol2]); curRow2--; }else{ break; } } } if(count % 2 == 0){ int curRow1 = dr; int curCol1 = dc; int curRow2 = tr; int curCol2 = tc; while(curCol1 != tc && curCol2 != dc){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0 && visited[curRow2][curCol2] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); curCol1--; visited[curRow2][curCol2] = 1; list2.add(0, m[curRow2][curCol2]); curCol2++; }else{ break; } } while(curRow1 != tr && curRow2 != dr){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0 && visited[curRow2][curCol2] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); curRow1--; visited[curRow2][curCol2] = 1; list2.add(0, m[curRow2][curCol2]); curRow2++; }else{ break; } } } count++; tr++; tc++; dr--; dc--; } System.out.println(list1); System.out.println(list2); if(length % 2 == 0){ for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " "); } for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list2.get(i) + " "); } }else{ for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " "); } System.out.print(m[(length - 1) / 2][(length - 1) / 2] + " "); for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list2.get(i) + " "); } } } }
优化之后的代码如下:
package com.darrenchan; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * 双蛇形打印(优化版) * @author Think * */ public class SheXingPrint5 { public static int num = 1; public static void main(String[] args) { //给出多大的数字,就构造多大的矩阵 int length = 4; int[][] m = new int[length][length]; int temp = 1; for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++) { m[i][j] = temp++; } } int[][] visited = new int[m.length][m[0].length];//0是没有访问过,1是访问过 List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>(); List<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>(); int tr = 0; int tc = 0; int dr = m.length - 1; int dc = m[0].length - 1; int count = 1; while(tr <= dr && tc <= dc){ if(count % 2 == 1){ int curRow1 = tr; int curCol1 = tc; while(curCol1 != dc){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); visited[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1] = 1; list2.add(0, m[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1]); curCol1++; }else{ break; } } while(curRow1 != dr){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); visited[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1] = 1; list2.add(0, m[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1]); curRow1++; }else{ break; } } } if(count % 2 == 0){ int curRow1 = dr; int curCol1 = dc; while(curCol1 != tc){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); visited[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1] = 1; list2.add(0, m[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1]); curCol1--; }else{ break; } } while(curRow1 != tr){ if(visited[curRow1][curCol1] == 0){ visited[curRow1][curCol1] = 1; list1.add(m[curRow1][curCol1]); visited[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1] = 1; list2.add(0, m[length - 1 - curRow1][length - 1 - curCol1]); curRow1--; }else{ break; } } } count++; tr++; tc++; dr--; dc--; } /** * 打印 */ System.out.println(list1); System.out.println(list2); if(length % 2 == 0){ for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " "); } for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list2.get(i) + " "); } }else{ for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " "); } System.out.print(m[(length - 1) / 2][(length - 1) / 2] + " "); for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list2.get(i) + " "); } } } }
以上是关于[算法]循环打印矩阵,蛇形矩阵专题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章