决策树算法简单应用
Posted xuyiqing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了决策树算法简单应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
采用ID3算法
(信息熵:H(X)=?∑i=0np(xi)log2p(xi))
下载一个决策树可视化软件:Graphviz
(注意环境变量Path加:C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Graphviz2.38\\bin)
代码:
导入需要用到的库:
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer import csv from sklearn import tree from sklearn import preprocessing
读取表格:
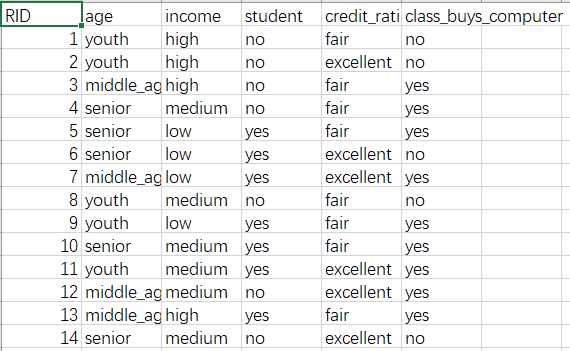
这里一些数据(属性),决定一位客户是否要买这台电脑
读取表格并做一些简单的数据处理:
allElectronicsData = open(r‘D:\\demo.csv‘, ‘rt‘) reader = csv.reader(allElectronicsData) headers = next(reader) featureList = [] labelList = [] for row in reader: labelList.append(row[len(row)-1]) rowDict = {} for i in range(1, len(row)-1): rowDict[headers[i]] = row[i] featureList.append(rowDict) print(featureList)
看一下结果:
[
{‘age‘: ‘youth‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘high‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘youth‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘high‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘},
{‘age‘: ‘middle_aged‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘high‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘senior‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘senior‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘low‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘senior‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘low‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘},
{‘age‘: ‘middle_aged‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘low‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘},
{‘age‘: ‘youth‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘youth‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘low‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘senior‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘youth‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘},
{‘age‘: ‘middle_aged‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘},
{‘age‘: ‘middle_aged‘, ‘student‘: ‘yes‘, ‘income‘: ‘high‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘fair‘},
{‘age‘: ‘senior‘, ‘student‘: ‘no‘, ‘income‘: ‘medium‘, ‘credit_rating‘: ‘excellent‘}
]
处理的不错:
调用sklearn的函数进一步处理数据:
vec = DictVectorizer()
dummyX = vec.fit_transform(featureList) .toarray()
lb = preprocessing.LabelBinarizer()
dummyY = lb.fit_transform(labelList)
查看下处理的结果:
print("dummyX: \\n" + str(dummyX)) print(vec.get_feature_names()) print("labelList: " + str(labelList)) print("dummyY: \\n" + str(dummyY))
结果:
注意要把数据转换成数字矩阵,便于学习
dummyX: [[0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.] [1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.] [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0.] [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.] [0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.] [1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.] [0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.] [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1.] [0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1.] [1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0.] [1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1.] [0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0.]] [‘age=middle_aged‘, ‘age=senior‘, ‘age=youth‘, ‘credit_rating=excellent‘, ‘credit_rating=fair‘, ‘income=high‘, ‘income=low‘, ‘income=medium‘, ‘student=no‘, ‘student=yes‘] labelList: [‘no‘, ‘no‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘no‘, ‘yes‘, ‘no‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘yes‘, ‘no‘] dummyY: [[0] [0] [1] [1] [1] [0] [1] [0] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [0]]
用决策树ID3算法和训练数据拟合分类器模型:
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion=‘entropy‘) clf = clf.fit(dummyX, dummyY)
可以利用下载的可视化软件画图观察下:
with open(r"D:\\demo.dot", ‘w‘) as f: f = tree.export_graphviz(clf, feature_names=vec.get_feature_names(), out_file=f)
然后调出cmd:
画好后是pdf形式的,看一下:
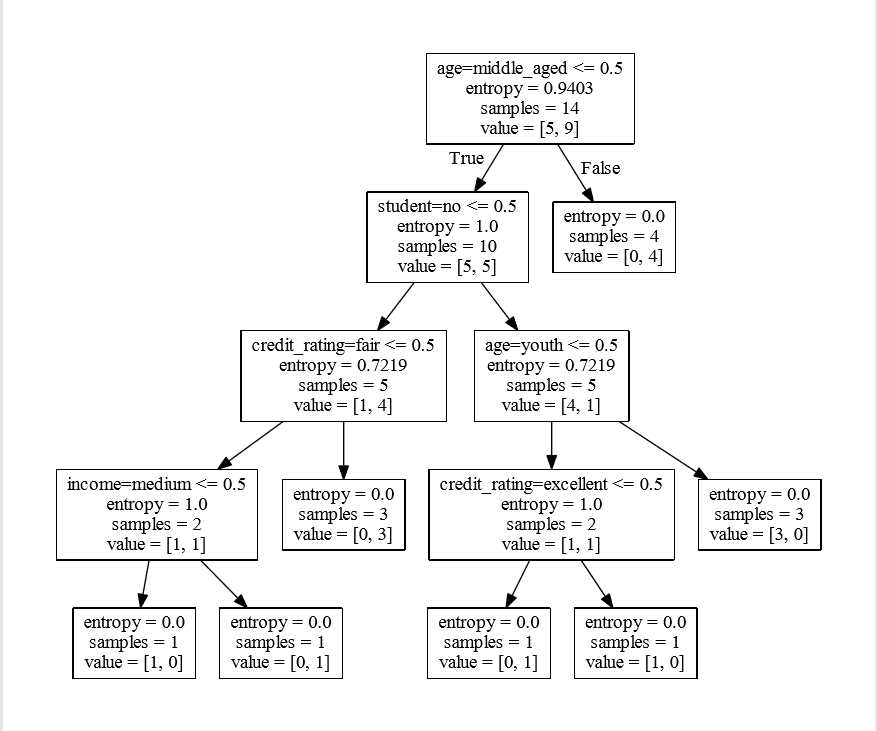
模型建好了,我们可以做一个预测:
在第一个数据的基础上修改下,然后预测是否买电脑:
oneRowX = dummyX[0, :] print("oneRowX: " + str(oneRowX)) newRowX = oneRowX newRowX[0] = 1 newRowX[2] = 0 print("newRowX: " + str(newRowX)) predictedY = clf.predict(newRowX.reshape(1, -1)) print("predictedY: " + str(predictedY))
结果:
oneRowX: [0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.] newRowX: [1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.] predictedY: [1]
结论:这个人要买这台电脑
以上是关于决策树算法简单应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章