1、项目代码:
| Contributor | Commits |
|---|---|
| 李露阳 | 14 ( 249++ 265--) |
| 鲁平 | 21 (339++ 92--) |
| 蒋志远 | 18 (1035++ 339--) |
贡献情况
| 项目阶段 | 姓名 | 贡献率 |
|---|---|---|
| 基本作业 | 蒋志远 | 0.36 |
| 李露阳 | 0.33 | |
| 鲁平 | 0.31 | |
| 扩展作业 | 鲁平 | 0.36 |
| 蒋志远 | 0.33 | |
| 李露阳 | 0.31 | |
| 高级作业 | 李露阳 | 0.34 |
| 鲁平 | 0.33 | |
| 蒋志远 | 0.33 |
2、PSP
| PSP2.1 | PSP阶段 | 预估耗时实际耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 15 | 23 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 530 | 892 |
| - Analysis | - 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 100 | 339 |
| - Design Spec | - 生成设计文档 | 100 | 150 |
| - Coding Standard | - 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 8 |
| - Design | - 具体设计 | 30 | 23 |
| - Coding | - 具体编码 | 200 | 220 |
| - Code Review | - 代码复审 | 30 | 34 |
| - Test | - 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 190 | 309 |
| - Test Report | - 测试报告 | 60 | 65 |
| - Size Measurement | - 计算工作量 | 10 | 12 |
| - Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | - 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 120 | 232 |
| 合计 | 780 | 1272 |
3、模块划分
我们将程序划分成两个大模块,分别管控 IO 、核心功能的实现。
各模块设计如下:
1. Main
/**
* com.hust.wcPro
* Created by Blues on 2018/3/27.
*/
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
static public void main(String[] args) {
IOController io_control = new IOController();
String valid_file = io_control.get(args);
if (valid_file.equals("")) {
return ;
}
WordCounter wordcounter = new WordCounter();
HashMap<String, Integer> result = wordcounter.count(valid_file);
io_control.save(result);
}
}
Main函数负责所有接口的调用,逻辑很简单,即IO获取有效的文件参数,调用 WordCounter 类的核心函数,IO 将结果排序后存入 result.txt 中。
2. IOController
IOController 类负责管控 io,具体设计如下:
class IOController {
IOController() {}
/**
* Parses the main function arguments
*
* @param args the main function arguments
* @return a valid file name
*/
public String get(String[] args);
/**
* Saves the result sorted
*
* @param result the result contain word as key as count as value
* @return the state code of operation
*/
public int save(HashMap<String, Integer> result);
}
get()负责解析主函数的参数,返回一个合法的,存在的文件名。save()负责将输出传入的结果排序后输出到 result.txt 文件中。
3. WordCounter
public class WordCounter {
WordCounter() {
}
/**
* Counts the words in the specific file
*
* @param filename the file to be counted
* @return the result saves the word(lowercased) as key and count as value
*/
public HashMap<String, Integer> count(String filename);
}
WordCounter 类负责实现核心功能 count() 函数,负责统计传入的文件中的各字符的数量,结果以 Map 的形式返回。
4、项目管理
为了能高效的合作以及更好的项目管理,我们选择使用 Gradle 进行项目的管理以及依赖管理,使用也可以更好的使用 Junit5 进行单元测试。因为多成员合作,我们使用 Git 进行源代码管理。
其中,Gradle 的配置文件 build.gradle 内容如下,可供参考:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath \'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-gradle-plugin:1.1.0\'
}
}
plugins {
id \'com.gradle.build-scan\' version \'1.12.1\'
id \'java\'
id \'eclipse\'
id \'idea\'
id \'maven\'
}
buildScan {
licenseAgreementUrl = "https://gradle.com/terms-of-service"
licenseAgree = "yes"
}
apply plugin: \'org.junit.platform.gradle.plugin\'
int javaVersion = Integer.valueOf((String) JavaVersion.current().getMajorVersion())
if (javaVersion < 10) apply plugin: \'jacoco\'
jar {
baseName = \'wcPro\'
version = \'0.0.1\'
manifest {
attributes \'Main-Class\': \'Main\'
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testCompile (
\'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.0.3\',
\'org.json:json:20090211\'
)
testRuntime(
\'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.0.3\',
\'org.junit.vintage:junit-vintage-engine:4.12.1\',
\'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher:1.0.1\',
\'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-runner:1.0.1\'
)
}
task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
description = \'Generates gradlew[.bat] scripts\'
gradleVersion = \'4.6\'
}
5、测试
1、单元测试
单元测试我们测试的粒度是到接口,因为项目主要包含 3 个大的接口,所以我们要对其分别进行测试。主要接口:
- IOController.get()
- IOController.save()
- WordCounter.count()
我们设计了 UnitTest 类来进行接口测试,测试内容如下:
class UnitTest {
UnitTest() {}
private String getTestResourcePath() {
String path = "build/resources/test/";
String osName = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
if (osName.startsWith("win")) {
path.replace(\'/\', \'\\\\\');
}
return path;
}
@Test
void testSortMap() {
//...
}
@Test
// @DisplayName("Custom test name containing spaces")
@DisplayName("Custom test file that doesn\'t exist")
void testIOHandling() {
//...
}
/**
* Use reflection to test {@code private} method {@isEngChar()}
*/
@Test
void testIsEngChar() {
//...
}
/**
* Use reflection to test {@code private} method {@isHyphen()}
*/
@Test
void testIsHyphen() {
//...
}
String fileParentPath = "src/test/resources/";
@Test
void testCountEmptyFile() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: wc.count(endWithHyphen.txt)")
void testCountFileEndWithHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Bord test: wc.count(startWithHyphen.txt)")
void testCountFileStartWithHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Bord test: wc.count(startWithHyphen.txt)")
void testNumberStartWithHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Bord test: wc.count(startWithHyphen.txt)")
void testCountFileWithQuatation() {
//...
}
@Test
void testCountHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: single quotation mark")
void testCountSingleQuotationMark() {
String fileName = "singleQuotationMark.txt";
String relativePath = fileParentPath + fileName;
WordCounter wc = new WordCounter();
HashMap result = wc.count(relativePath);
assertEquals(2, result.size());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: single quotation mark")
void testCountFileWithContinuedHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: single quotation mark")
void testFileWithContinuedHyphen() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: double quotation mark")
void testCountDoubleQuotationMark() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: word with number")
void testCountWordWithNumber() {
//...
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Border test: word with multiple kinds of char")
void testCountMultiple() {
//...
}
}
上诉测试主要利用了 Junit5 测试引擎,在配置方面踩了不少的坑,从项目管理工具的选用到配置文件的编写。最后到测试用例的设计。设计测试时我们使用了白盒测试的方法,针对程序的各个分支以及状态设计了上述测试用例。
对于私有方法的测试,我们使用了反射的方式来进行访问测试,完整代码参考 这里 。
2、静态测试
静态测试我们借助了 intelliJ 的 Alibaba P3C 的 idea 插件来完成。
在检查过程中发现以下错误:
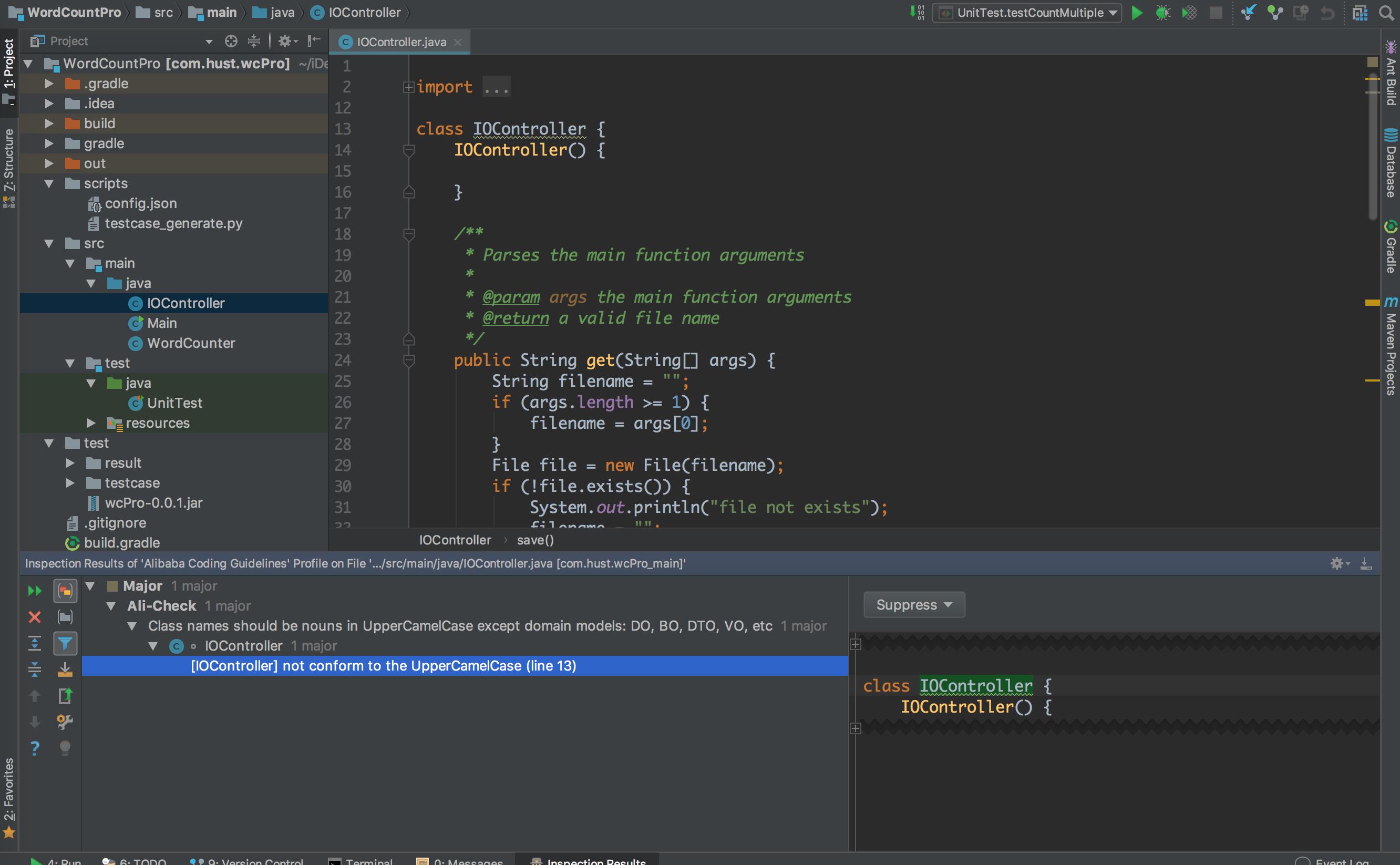
这个错误提示的是命名规范错误,但是针对 IO 一词我局的并不需要进行驼峰写法,这里我们选择以误报处理。
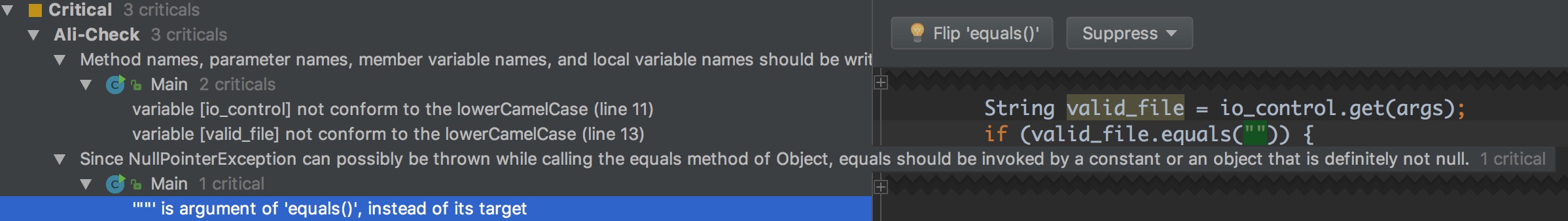
这个错误提示的很好,因为在 nowWord.equals("") 的写法中,如果当 nowWord 变量是空指针是,会崩溃,而换一种写法 "".equals(nowWord) 则更加安全。
3、黑盒测试
为了能高效进行测试,我们采用了自动化脚本的方式进行测试能更好的进行压力测试。
首先我们需要大量的、正确的测试用例,每个测试用例的大小必须要足够大、内容也要保证正确。为此,手写测试用例是绝对不实际的,所以我们需要自动生成正确的测试用例。为了达到这个目的,我们用 Python 写了一个简单的脚本,用来自动生成测试用例,内容随机但是大小可控:
from functools import reduce
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import randint
import json
import sys, os, re
elements = {
"words": "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz-",
"symbol": "!@#$%^&*()~`_+=|\\\\:;\\"\'<>?/ \\t\\r\\n1234567890-"
}
def generate_usecase(configs):
global elements
path = os.path.join(\'test\', \'testcase\')
result_path = os.path.join(\'test\', \'result\')
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
if not os.path.exists(result_path):
os.makedirs(result_path)
for config_idx, config in enumerate(configs):
word_dict = {}
i = 0
# 这里用于生成一个合法的单词
while i < config[\'num_of_type\']:
word_len = randint(*config[\'word_size\'])
word_elements = randint(0, len(elements[\'words\']), word_len)
word = np.array(list(elements[\'words\']))[word_elements]
word = \'\'.join(word)
# 这里将单词中不合法的 ‘-’ 转化删除掉
word = re.sub(r\'-{2,}\',\'-\', word)
word = re.sub(r\'^-*\', \'\', word)
word = re.sub(r\'-*$\', \'\', word)
if len(word) == 0: # 运气不好全是 ‘-’ 那么单词生成失败,从新生成单词
continue
word_dict[word] = 0
i += 1
total_count = 0
# 设置单词重复出现的次数
for key in word_dict.keys():
word_dict[key] = randint(*config[\'word_repeat\'])
total_count += word_dict[key]
word_dict_tmp = word_dict.copy()
final_string = \'\'
# 构造最终的用例文本
for i in range(total_count):
key, val = None, 0
while (val == 0):
key_tmp = list(word_dict_tmp.keys())[randint(len(word_dict))]
val = word_dict_tmp[key_tmp]
if val != 0:
key = key_tmp
word_dict_tmp[key_tmp] = val-1
# 这里将单词的内容随机大小写
word_upper_case = randint(0, 2, len(key))
key = \'\'.join([s.upper() if word_upper_case[i] > 0 else s for i, s in enumerate(list(key))])
final_string += key
sep = \'\'
# 构造合法的分隔符
for _ in range(randint(*config[\'sep_size\'])):
sep += elements[\'symbol\'][randint(0, len(elements[\'symbol\']))]
if sep == \'-\':
while sep == \'-\':
sep = elements[\'symbol\'][randint(0, len(elements[\'symbol\']))]
final_string += sep
with open(os.path.join(path, \'{}_usecase.txt\').format(config_idx), \'w\') as f:
f.write(final_string)
sorted_key = sorted(word_dict.items(), key=lambda kv:(-kv[1], kv[0]))
result = \'\'
for key, val in sorted_key:
result += key + \': \' + str(val) + \'\\n\'
with open(os.path.join(path, \'{}_result_true.txt\'.format(config_idx)), \'w\') as f:
f.write(result)
print(\'test case {} generated\'.format(config_idx))
def main():
config = sys.argv[-1]
with open(config) as f:
config = json.load(f)
generate_usecase(config)
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
main()
其中的配置文件如下:
[
{
"num_of_type": 10,
"word_size": [1, 10],
"sep_size": [1,3],
"word_repeat": [1, 300]
},
{
"num_of_type": 20,
"word_size": [1, 20],
"sep_size": [1,3],
"word_repeat": [20, 300]
}
]
内容很简单,只需要配置有多少个单词,每个单词长度范围,分隔符的长度范围,每个单词重复出现的大小范围,即可生成相应的测试用例和正确的排序后的结果。
..........
YMtyibqY
zxz*^QtRWv*O=3KDvJKmpQb86MThOdnP
ZXZ>#aAys>&mthodnP>`qtRWv(QTRWV*YmTYiBqY^\\O9Zxz_?MthOdNP$ zxZ="MtHODnP#!yMTYibqY:o%2AaYS<#QTRwV8MTHOdnp!o#+MTHodNP)*QTRWV;YmtyiBQY ZXz$hesS`aayS_#FKcU=)AAys;fKcu-$Z$MthoDnp
YMTYIBqy/3aAyS!Zxz\'yMtyiBQY~1KdvjKMpQB\'@aAYs\'Z\'zXZ3z2hESs5aAys@yMtyiBQy4qtRWV3kDvJKMpQB:9yMTyIbqy_YmtyIBqY
KdvJKmpqB>YMtYibQy
>z2O
z`^FKCu$<QTRwv#<mtHOdnP%z+z"*FKCu9hESs<fkcu!YMtYiBqY"HesS9MtHODNp
ZxZ
.........
以上是关于WordCountPro 小计的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章