pythoning—— 5:实战篇(购物车)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pythoning—— 5:实战篇(购物车)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
要求
1、实现多用户登录,注册功能。
2、实现商场购物,查询历史购物详单。
3、实现商品分类。
4、商品可一次购买多个,可重复购买,购买后查看已购买商品时,只显示一条
5、实现充值、更改密码功能
分析
从题目要求和当前所掌握的知识来看,要实现该功能会用到文本操作,用来存储用户信息,多用户登录使用字典的key值作为用户名,其他如密码、历史购买信息、余额等统一作为values较为合理。注册功能便是在用户登录时做判断,如果没有该用户,则会提示注册,注册时只需添加一个以用户名为key,密码、历史购物、余额为子字典的values的键值对即可。历史购物则使用列表较为妥当,其实使用元组比列表要合理一些,但无奈json中元组是会报错的。剩下的就是对字典、列表的操作,so,come on。
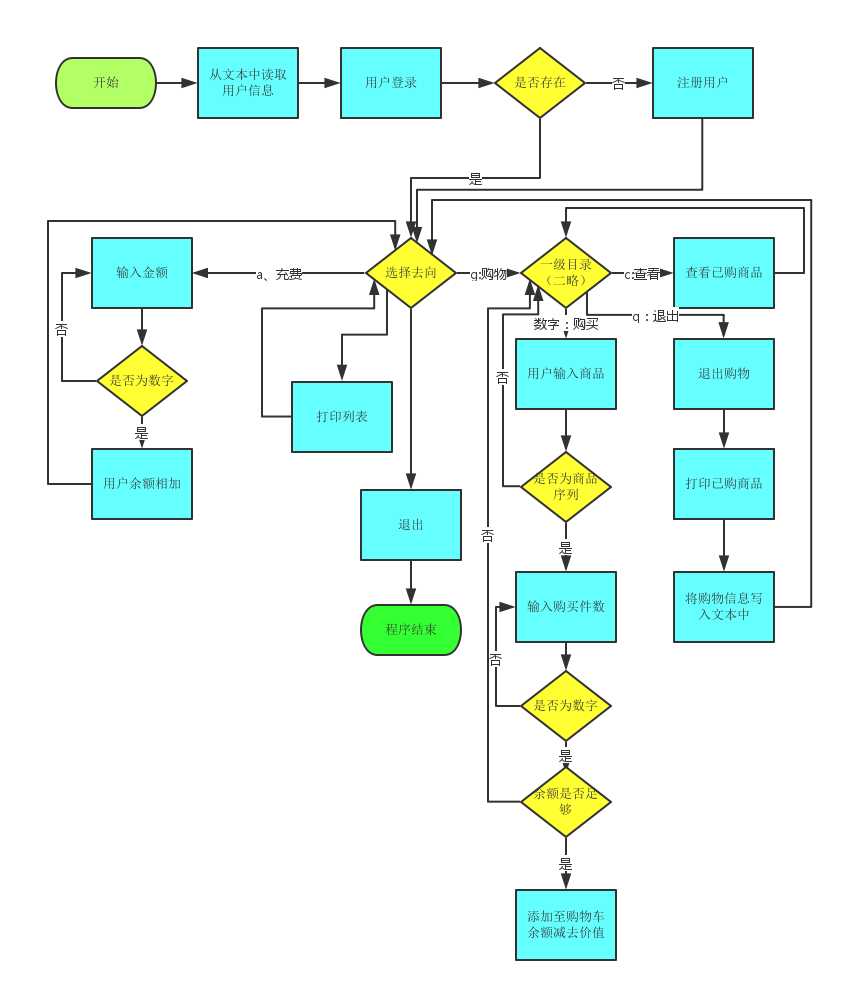
流程图
数据存储格式
数据存储格式以下例为准。
{ "fukuda":{ "money": 184280, "passwd": "king123", "oldshoping": [ ["冰箱", 3, 15000, "2016-05-20 21:59:28"], ["休闲裤", 4, 720, "2016-05-20 21:59:38"] ] } }
用到的知识
会用到json、datetime、文本操作等新知识。
json主要用到其两个函数dumps和loads,dumps主要是将其他数据类型(元组、列表、字典等的结合体)转换为字符串,而loads则是反着来。这对本题的文本操作有很大的作用。
datetime主要会用到datetime.now,来获取当前时间,并截取字段,将值转换为YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss的格式,以完善丰富用户购买信息。
文本的话会用到open,open的用法是f = open(‘textname‘,‘[r|a|w]‘),r代表只读,w代表写入,且如果没有该文本,则会创建,a则是二者结合。
模块编写
额。本来是应该有这块的吧,可惜代码实现的略糙,没法拿出来现了,直接全贴到下面拉倒。
实现
#!/user/bin/evn python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # Author : hft import json import datetime def get_time():#获取当前时间 time_now = datetime.datetime.now() time_now = str(time_now) time_now = time_now[:time_now.index(".")] return time_now def recode_shop(user_msg):#记录购买日志 f = open("test.txt","w") user_msg = json.dumps(user_msg) f.write(user_msg) f.close() def shopcar_to_old(shop_car,oldshopping):#将购物车添加至历史购物信息中 if len(shop_car) == 0: return oldshopping else: oldshopping.extend(shop_car) return oldshopping def show_shopping(shopping):#显示购买信息 print("商品\\t\\t数目\\t\\t金额\\t\\t时间") for item in shopping: print(item[0],"\\t\\t",item[1],"\\t\\t\\t",item[2],"\\t\\t",item[3]) pro_list = [["家电类",["电视机",1500],["冰箱",5000],["空调",3000]], ["衣服类",["衬衫",100],["卫衣",150],["休闲裤",180]], ["手机类",["小米",1120],["苹果",5888],["魅族",2000]]] format = ‘%s%-*s%*s%s‘#定义格式化输出,如“+商品名: 电视机+”为format%("+",20,"商品名:",20,"电视机","+") if __name__ == "__main__":#主函数 f = open("test.txt","r")#读入文本 user_msg = f.read() f.close() user_msg = json.loads(user_msg) print("登录".center(20,"*")) while True: input_name = input("username:") if input_name in user_msg: input_pass = input("password:") if input_pass == user_msg[input_name]["passwd"]: print("登录成功!".center(20,"*")) break else: print("密码错误!") else: user_new = input("该用户不存在,是否需要注册该用户(Y/N):") if user_new == ‘Y‘ or user_new == ‘y‘: print("注册-[%s]-".center(20,"#")%input_name) input_pass = input("请输入密码:") user_msg[input_name] = {"passwd":input_pass,"money":0,"oldshoping":[]} break else: login_con = input("继续登录(Y/N):") if login_con == ‘N‘ or login_con == ‘n‘: exit("欢迎下次光临") elif login_con == ‘Y‘ or login_con == ‘y‘: continue else: print("输入有误") while True: print("欢迎光临".center(50,"*")) user_cho = input("A:充值、C:更改密码、O:查看历史购物、S:购物、Q:结束\\n%s请选择:"%("*"*20))#用户输入去向 shop_car = []#定义购物车 if user_cho == ‘A‘ or user_cho == ‘a‘:#充费 while True: input_add = input("请输入充值金额:") if input_add.isdigit(): user_msg[input_name]["money"] = user_msg[input_name]["money"] + int(input_add) print("充值成功,充值金额为:[%s],余额为:[%s]"%(input_add,user_msg[input_name]["money"])) break else: print("输入有误,请重新输入(输入必须为数字):") elif user_cho == ‘C‘ or user_cho == ‘c‘:#变更密码 change_pass = input("请输入变更后的密码:") change_pass_sure = input("请确认密码:") if change_pass == change_pass_sure: user_msg[input_name]["passwd"] = change_pass else: print("两次输入不一致!") elif user_cho == ‘S‘ or user_cho == ‘s‘:#购物,你妹夫的,终于写到这了。 break_flat = False#定义跳出购物参数 while break_flat == False:#购物开始,这次真的开始 print ("购物".center(40,"=")) for item in pro_list: print(pro_list.index(item)+1,".\\t",item[0]) cho_menu = input("请输入您要购买的商品类型(按Q退出,按C查看已购商品,按E退出程序):") if cho_menu.isdigit() and int(cho_menu) in range(1,len(pro_list)+1): while True:#分类购物 cho_menu = int(cho_menu) print(str(pro_list[cho_menu-1][0]).center(30,"=")) for items in pro_list[cho_menu-1][1:]: a = 15-len(items[0]) print(("=%-2s.%-*s%10s¥ =")%(pro_list[cho_menu-1].index(items),a,items[0],items[1])) print("="*33) cho_shop = input("请输入您要购买的商品(按Q退出,按C查看已购商品,按B返回上级目录,按E退出程序):") if cho_shop.isdigit(): cho_shop = int(cho_shop) if cho_shop <= len(pro_list) and cho_shop > 0: items = pro_list[cho_menu-1][cho_shop] while True: cho_count = input("请输入要购买的件数:") if cho_count.isdigit() and int(cho_count) > 0: cho_count = int(cho_count) if cho_count*items[1] <= user_msg[input_name]["money"]: user_msg[input_name]["money"] = user_msg[input_name]["money"] - cho_count*items[1]#求余额 print("购买成功".center(30,"+")) print(format % ("+", 20, "商品名",10-int(len(items[0]))-1,items[0], "+")) print(format % ("+", 20, "数量", 10,cho_count, "+")) print(format % ("+", 20, "花费", 10,items[1]*cho_count, "+")) print(format % ("+", 20, "余额", 10,user_msg[input_name]["money"], "+")) print("end".center(34,"+")) shop_car_pro = [] for i in shop_car: shop_car_pro.append(i[0]) if items[0] in shop_car_pro: shop_car[shop_car_pro.index(items[0])][1] = shop_car[shop_car_pro.index(items[0])][1] + cho_count shop_car[shop_car_pro.index(items[0])][2] = shop_car[shop_car_pro.index(items[0])][1]*items[1] shop_car[shop_car_pro.index(items[0])][3] = get_time() else: a = [items[0],cho_count,items[1]*cho_count,get_time()] shop_car.append(a) else: print("余额不足,余额为[%s]"%(user_msg[input_name]["money"])) break else: print("输入需为大于0数字!") else: print("请输入正确的数字") elif cho_shop == ‘Q‘ or cho_shop == ‘q‘: user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"] = shopcar_to_old(shop_car,user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"]) print ("退出购物") break_flat = True recode_shop(user_msg) break elif cho_shop == ‘C‘ or cho_shop == ‘c‘: show_shopping(shop_car) elif cho_shop == ‘E‘ or cho_shop == ‘e‘: user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"] = shopcar_to_old(shop_car,user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"]) recode_shop(user_msg) exit ("欢迎下次光临!") elif cho_shop == ‘B‘ or cho_shop == ‘b‘: break else: print("输入有误") elif cho_menu == ‘Q‘ or cho_menu == ‘q‘: user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"] = shopcar_to_old(shop_car,user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"]) print("退出购物") break_flat = True elif cho_menu == ‘E‘ or cho_menu == ‘e‘: user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"] = shopcar_to_old(shop_car,user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"]) recode_shop(user_msg) exit("欢迎下次光临!") elif cho_menu == ‘C‘ or cho_menu == ‘c‘: show_shopping(shop_car) else: print("输入有误,重新输入!") elif user_cho == ‘O‘ or user_cho == ‘o‘: show_shopping(user_msg[input_name]["oldshoping"]) elif user_cho == ‘Q‘ or user_cho == ‘q‘: print("欢迎下次光临!") recode_shop(user_msg) break
以上是关于pythoning—— 5:实战篇(购物车)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章