前言
上一篇给大家简单介绍了一下轮询算法,这一篇就来介绍一下加权轮询算法。
既然有了轮询算法的基础,那么对于加权轮询的理解就简单多了。
同先举个例子看看加权轮询算法是如何运作的。
假设我们的API站点有2台负载(10.0.10.1,10.0.10.2),但是.2这台机器的配置要比较高,所以会把它的权重设置的高一点。
换句话就是说,我们是希望将比较多的请求可以落实到.2这台机器上。
假设给.2这台机器设置的权重是2,.1的权重是1。那么我们希望的结果就是,在3次请求中,2次落到.2上,1次落到.1上。
下面来简单看看如何实现
简单实现
其实最简单的做法就是在轮询算法那里传入多个一样的值就是代表它的权重。
var lbUrls = new List<string>
{
"http://10.0.10.1/api/values",
"http://10.0.10.2/api/values",
"http://10.0.10.2/api/values",
};
像这样传入,就代表在3次请求中会有2次落到.2。
其实这样做也不是不可以,负载的机器的数量少可以这样玩,当数量一多,不得眼花瞭乱啊!而且这样做,加权轮询就没有什么存在的意义了。
它更大的意义其实是在于均匀的分配。
举个简单的例子说明一下。
.1 权重 5
.2 权重 1
.3 权重 1
请问,下面的请求序列,那个更合适?
A. .1->.1->.1->.1->.1->.2->.3
B. .1->.1->.2->.1->.3->.1->.1
像A这样的请求序列,一次性来5个到.1,这样就失去了负载的意义了。
像B这样的请求序列均匀的分布,是比较合适的。
我们围绕的重点如下:
- 服务器列表和权重
- 下一次要访问的是那台机器
目前来说,貌似有两种算法来实现这个加权轮询,一种是最大公约数的,一种是nginx的加权轮询算法。
但是,最大公约数生成的请求序列并不是十分的均匀,所以这里就没有采用,用的是Nginx的这种处理方法。
下面是实现
public class WeightedRoundRobin<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// The server dict.
/// </summary>
private readonly IDictionary<T, int> _serverDict;
/// <summary>
/// The server list.
/// </summary>
private readonly IList<ServerConfig> _serverList = new List<ServerConfig>();
/// <summary>
/// The sync lock.
/// </summary>
private readonly object _syncLock = new object();
public WeightedRoundRobin(IDictionary<T, int> serverDict)
{
this._serverDict = serverDict;
foreach (var item in _serverDict)
{
_serverList.Add(new ServerConfig
{
Current_Weight = 0,
Weight = item.Value,
Server = item.Key
});
}
}
public T GetNextItem()
{
int index = -1;
int total = 0;
int size = _serverList.Count;
lock(_syncLock)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
_serverList[i].Current_Weight += _serverList[i].Weight;
total += _serverList[i].Weight;
if (index == -1 || _serverList[index].Current_Weight < _serverList[i].Current_Weight)
{
index = i;
}
}
_serverList[index].Current_Weight -= total;
}
return _serverList[index].Server;
}
/// <summary>
/// Server config.
/// </summary>
public class ServerConfig
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the weight.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The weight.</value>
public int Weight { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the current weight.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The current weight.</value>
public int Current_Weight { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the server.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The server.</value>
public T Server { get; set; }
}
}
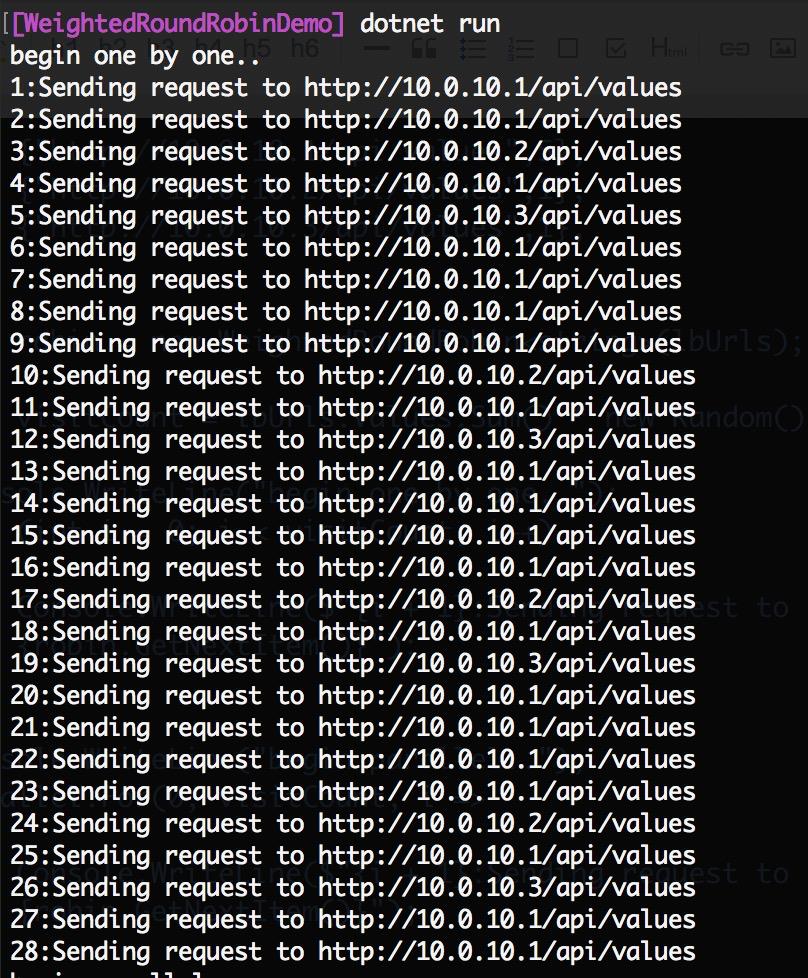
下面测试一下
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var lbUrls = new Dictionary<string,int>
{
{"http://10.0.10.1/api/values",5},
{"http://10.0.10.2/api/values",1},
{"http://10.0.10.3/api/values",1},
};
var robin = new WeightedRoundRobin<string>(lbUrls);
var visitCount = lbUrls.Values.Sum() * new Random().Next(3, 5);
Console.WriteLine("begin one by one..");
for (int i = 0; i < visitCount; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i + 1}:Sending request to {robin.GetNextItem()}");
}
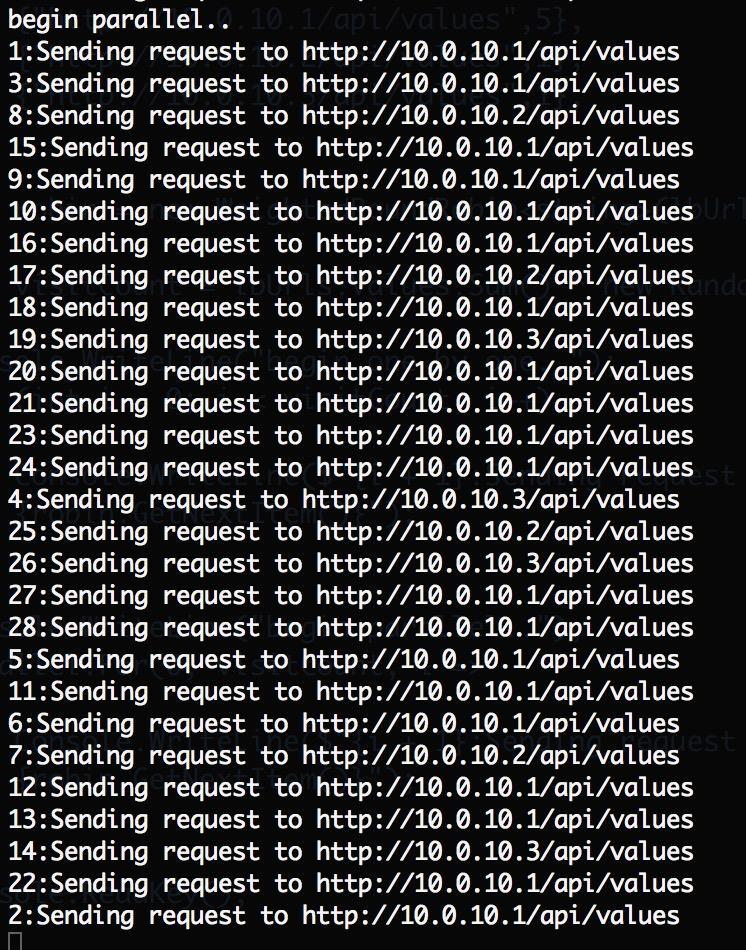
Console.WriteLine("begin parallel..");
Parallel.For(0, visitCount, i =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i + 1}:Sending request to {robin.GetNextItem()}");
});
Console.ReadKey();
}
结果:
示例代码: