3506: [Cqoi2014]排序机械臂
题目描述
为了把工厂中高低不等的物品按从低到高排好序,工程师发明了一种排序机械臂。它遵循一个简单的排序规则,第一次操作找到高度最低的物品的位置 P_1P1? ,并把左起第一个物品至 P_1P1? 间的物品 (即区间 [1,P_1][1,P1?] 间的物品) 反序;第二次找到第二低的物品的位置 P_2P2? ,并把左起第二个至 P_2P2? 间的物品 (即区间 [2,P_2][2,P2?] 间的物品) 反序……最终所有的物品都会被排好序。
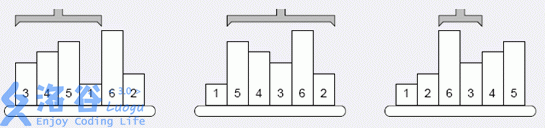
上图给出有六个物品的示例,第一次操作前,高度最低的物品在位置 44 ,于是把第一至第四的物品反序;第二次操作前,第二低的物品在位罝六,于是把第二至六的物品反序……
你的任务便是编写一个程序,确定一个操作序列,即每次操作前第 ii 低的物品所在位置 P_iPi? ,以便机械臂工作。需要注意的是,如果有高度相同的物品,必须保证排序后它们的相对位置关系与初始时相同。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行包含正整数n,表示需要排序的物品数星。
第二行包含n个空格分隔的整数ai,表示每个物品的高度。
输出格式:
输出一行包含n个空格分隔的整数Pi。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
6
3 4 5 1 6 2
输出样例#1:
4 6 4 5 6 6
HINT
N<=100000
Pi<=10^7
维护一个数列,支持区间翻转,所以可以用SPLAY来维护
我们可以先将数排序,这样他们节点数组的下标对应的就是排名
然后就是区间翻转的操作
注意SPLAY的时候要先pushdown

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #define LL long long 6 #define lc t[x].ch[0] 7 #define rc t[x].ch[1] 8 using namespace std; 9 10 const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10; 11 12 LL ans = 0; 13 int sum = 0; 14 int n; 15 int root; 16 int loc[MAXN]; 17 struct node { 18 int size; 19 int val; 20 int id; 21 int fa; 22 int ch[2]; 23 int lazy; 24 } t[MAXN]; 25 26 void pushdown(int x) 27 { 28 if(t[x].lazy) { 29 swap(lc, rc); 30 t[lc].lazy ^= 1; 31 t[rc].lazy ^= 1; 32 t[x].lazy ^= 1; 33 } 34 } 35 36 void pushup(int x) 37 { 38 t[x].size = t[lc].size + t[rc].size + 1; 39 } 40 inline LL read() 41 { 42 LL x = 0, w = 1; char ch = 0; 43 while(ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) { 44 if(ch == ‘-‘) { 45 w = -1; 46 } 47 ch = getchar(); 48 } 49 while(ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) { 50 x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘; 51 ch = getchar(); 52 } 53 return x * w; 54 } 55 56 void rotate(int x, int &k) 57 { 58 int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa; 59 int l, r; 60 if(y == k) { 61 k = x; 62 } else { 63 if(t[z].ch[0] == y) { 64 t[z].ch[0] = x; 65 } else { 66 t[z].ch[1] = x; 67 } 68 } 69 if(t[y].ch[0] == x) { 70 l = 0; 71 } else { 72 l = 1; 73 } 74 r = l ^ 1; 75 t[y].ch[l] = t[x].ch[r], t[t[x].ch[r]].fa = y; 76 t[x].fa = z, t[y].fa = x, t[x].ch[r] = y; 77 pushup(y); 78 pushup(x); 79 } 80 81 void splay(int x, int &k) 82 { 83 while(x != k) { 84 int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa; 85 if(y != k) { 86 if((t[z].ch[0] == y) ^ (t[y].ch[0] == x)) { 87 rotate(x, k); 88 } else { 89 rotate(y, k); 90 } 91 } 92 rotate(x, k); 93 } 94 } 95 96 int query(int k, int x) 97 { 98 pushdown(x); 99 while(t[lc].size + 1 != k) { 100 if(t[lc].size >= k) { 101 x = lc; 102 } else { 103 k = k - t[lc].size - 1; 104 x = rc; 105 } 106 pushdown(x); 107 } 108 return x; 109 } 110 111 bool cmp(node a, node b) 112 { 113 if(a.val == b.val) { 114 return a.id < b.id; 115 } 116 return a.val < b.val; 117 } 118 119 void build(int l, int r, int &x, int last) 120 { 121 if(l > r) { 122 x = 0; 123 return; 124 } 125 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 126 x = loc[mid]; 127 t[x].fa = last; 128 build(l, mid - 1, lc, x); 129 build(mid + 1, r, rc, x); 130 pushup(x); 131 } 132 133 void push(int x) 134 { 135 int sum = 0; 136 if(t[x].fa) { 137 push(t[x].fa); 138 pushdown(x); 139 } 140 } 141 142 void print(int x) 143 { 144 cout<<x<<" "<<t[x].size<<" "<<lc<<" "<<rc<<endl; 145 if(lc) { 146 print(lc); 147 } 148 if(rc) { 149 print(rc); 150 } 151 } 152 153 int main() 154 { 155 n = read(); 156 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 157 t[i].id = i; 158 t[i].val = read(); 159 } 160 sort(t + 1, t + n + 1, cmp); 161 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 162 loc[t[i].id] = i; 163 } 164 loc[0] = n + 2, loc[n + 1] = n + 1; 165 build(0, n + 1, root, 0); 166 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 167 push(i); 168 splay(i, root); 169 ans = t[t[root].ch[0]].size; 170 printf("%lld ", ans); 171 int loc = query(i, root); 172 splay(loc, root); 173 loc = query(ans + 2, root); 174 splay(loc, t[root].ch[1]); 175 t[t[loc].ch[0]].lazy ^= 1; 176 } 177 return 0; 178 } 179 180 181 /* 182 6 183 3 4 5 1 6 2 184 185 */
