3611: [Heoi2014]大工程
Time Limit: 60 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MB
Submit: 2000 Solved: 837
[Submit][Status][Discuss]
Description
国家有一个大工程,要给一个非常大的交通网络里建一些新的通道。
我们这个国家位置非常特殊,可以看成是一个单位边权的树,城市位于顶点上。
在 2 个国家 a,b 之间建一条新通道需要的代价为树上 a,b 的最短路径。
现在国家有很多个计划,每个计划都是这样,我们选中了 k 个点,然后在它们两两之间 新建 C(k,2)条 新通道。
现在对于每个计划,我们想知道:
1.这些新通道的代价和
2.这些新通道中代价最小的是多少
3.这些新通道中代价最大的是多少
Input
第一行 n 表示点数。
接下来 n-1 行,每行两个数 a,b 表示 a 和 b 之间有一条边。
点从 1 开始标号。 接下来一行 q 表示计划数。
对每个计划有 2 行,第一行 k 表示这个计划选中了几个点。
第二行用空格隔开的 k 个互不相同的数表示选了哪 k 个点。
Output
输出 q 行,每行三个数分别表示代价和,最小代价,最大代价。
Sample Input
10 2 1 3 2 4 1 5 2 6 4 7 5 8 6 9 7 10 9 5 2 5 4 2 10 4 2 5 2 2 6 1 2 6 1
Sample Output
3 3 3 6 6 6 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2
HINT
n<=1000000
q<=50000并且保证所有k之和<=2*n
Source
题解:
其实数据范围第二句话就摆明是虚树了。。
然后看看这道题要我们做啥,求虚树关键点间最长链,最短链,两两距离和。。
关于距离和,我们只用在dfs时考虑一下当前点,和它儿子结点的边会有多少点经过就行。
设总关键点为k,一个点x子树所包含关键点数量为sz[x]
当然就是(k - sz[son]) * sz[son]次啦。设每个点到它父亲边经过次数为cnti
距离就是 dep[son] - dep[now]就行。设为这个距离为wi
答案就是
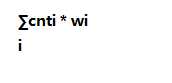
就这样我们把第一个询问做出来了。
第二第三询问树上最长最短链,noip--难度。但是有树上有关键点之间的lca啊,当它为链的起点或终点时答案会增大。
然后仔细一想我们只有在当前点为关键点时才会计算单条链贡献。
因为虚点都是关键点间lca所以不会出现虚点为叶子结点,这样就保证起点和终点不会是虚点了。
然后就简单虚树上dp了。
AC代码:
# include <iostream> # include <cstdio> # include <cstring> # include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int N = 1e6 + 12; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int sz[N],hson[N],top[N],dep[N],que[N],k,a[N],g[N];LL f[N]; int head[N],dt,tot,fa[N],id[N],n,m,mx[N],mi[N],ans1,ans2; struct Edge{ int to,nex; }edge[N << 1]; void AddEdge(int u,int v) { if(u == v)return; edge[++dt] = (Edge){v,head[u]}; head[u] = dt; } void dfs(int u) { sz[u] = 1; for(int i = head[u];i;i = edge[i].nex) { if(sz[edge[i].to])continue; dep[edge[i].to] = dep[u] + 1; fa[edge[i].to] = u; dfs(edge[i].to); sz[u] += sz[edge[i].to]; if(sz[hson[u]] < sz[edge[i].to])hson[u] = edge[i].to; } } void dfs(int u,int tp) { top[u] = tp;id[u] = ++tot; if(hson[u])dfs(hson[u],tp); for(int i = head[u];i;i = edge[i].nex) if(!id[edge[i].to])dfs(edge[i].to,edge[i].to); head[u] = 0; } int lca(int u,int v) { while(top[u] != top[v]) { if(dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]])swap(u,v); u = fa[top[u]]; } return dep[u] < dep[v] ? u : v; } bool cmp(int x,int y){return id[x] < id[y];} void dp(int u) { sz[u] = g[u];mx[u] = 0;mi[u] = inf;f[u] = 0; for(int i = head[u];i;i = edge[i].nex) { int w = dep[edge[i].to] - dep[u]; dp(edge[i].to);sz[u] += sz[edge[i].to]; ans1 = min(ans1,mi[u] + mi[edge[i].to] + w);mi[u] = min(mi[u],mi[edge[i].to] + w); ans2 = max(ans2,mx[u] + mx[edge[i].to] + w);mx[u] = max(mx[u],mx[edge[i].to] + w); f[u] += f[edge[i].to] + 1LL * sz[edge[i].to] * (k - sz[edge[i].to]) * w; } if(g[u])ans1 = min(ans1,mi[u]),ans2 = max(ans2,mx[u]),mi[u] = 0; head[u] = g[u] = 0; } void solve() { scanf("%d",&k);int top,gr;ans1 = inf;top = dt = ans2 = 0;ans1 = inf; for(int i = 1;i <= k;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]),g[a[i]] = 1; sort(a + 1,a + k + 1,cmp); for(int i = 1;i <= k;i++) { if(!top){que[++top] = a[i];continue;} gr = lca(que[top],a[i]); while(id[gr] < id[que[top]]) { if(id[gr] >= id[que[top - 1]]) { AddEdge(gr,que[top]); if(que[--top] != gr)que[++top] = gr; break; } AddEdge(que[top - 1],que[top]);top--; } if(que[top] != a[i])que[++top] = a[i]; } top--; while(top)AddEdge(que[top],que[top + 1]),top--; dp(que[1]); printf("%lld %d %d\\n",f[que[1]],ans1,ans2); } int main() { scanf("%d",&n);int x,y; for(int i = 1;i < n;i++) { scanf("%d %d",&x,&y); AddEdge(x,y);AddEdge(y,x); } dfs(1);dfs(1,1); scanf("%d",&m); while(m--)solve(); }