异常概念和处理机制
什么是异常?
所谓异常就是指在程序运行的过程中发生的一些不正常事件。(如除0溢出,数组下标越界,所要读取的文件不存在);
异常导致的后果?
Java程序的执行过程中如出现异常事件,可以生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象封装了异常事件的信息,其将被提交给Java运行时系统,这个过程称为抛出异常,不处理的话会导致程序直接中断;
如何防止程序中断?
设计良好的程序应该在程序异常发生时提供处理这些异常的方法,使得程序不会因为异常的发生而阻断或产生不可预见的结果;
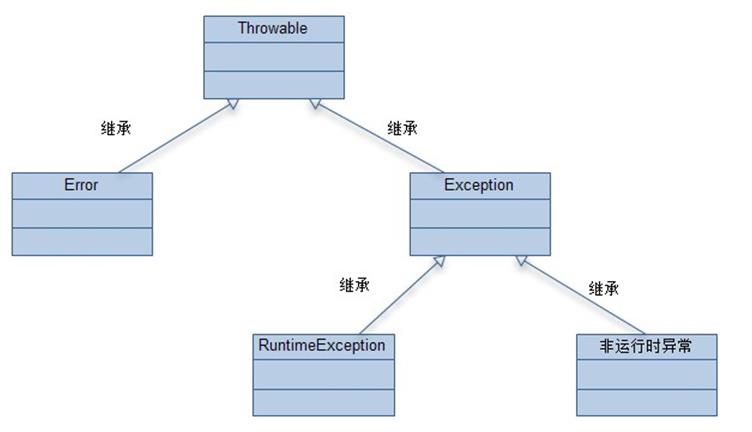
异常分类
|
异常类型 |
包括 |
来源 |
处理 |
|
受查异常 checkedException |
Exception及其子类(不包括 RuntimeException 及其子类) |
由代码控制能力之外的因素导致额运行时错误 |
必须要处理,否则通不过编译 |
|
非受查异常 uncheckedException |
Error和 RuntimeException 及其子类 |
RuntimeException 一般代表编译错误 |
可以不用处理 |
Java的异常通过两种机制来处理
捕获:try-catch-finally
抛出:throw,throws
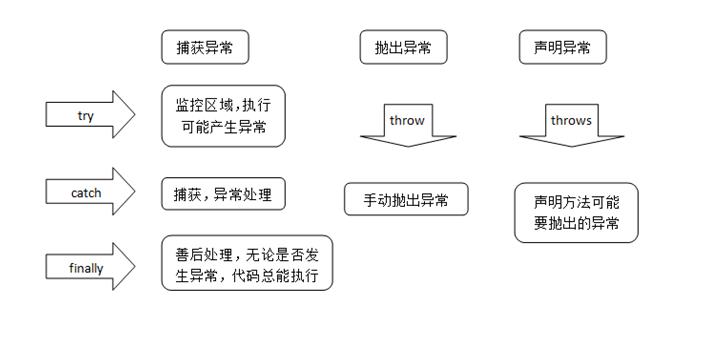
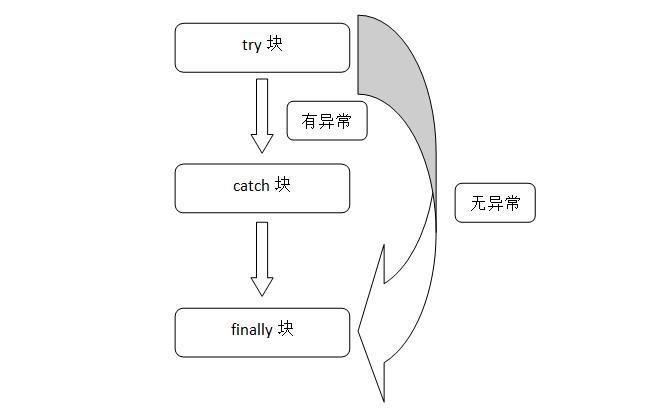
try-catch-finally
try{}语句块中放的是要检测的java代码,可能有会抛出异常,也可能会正常执行;
catch(异常类型){}块是当Java运行时系统接收到try块中所抛出的异常对象时,会寻找能处理这一异常的catch块来进行处理(可以有多个catch块);
finally{}块不管系统有没有抛出异常都会去执行,一般用来释放资源。除了在之前执行了System.exit(0);
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 import java.util.InputMismatchException;
3 public class ExceptionDemo1{
4 public static void main(String []args){
5 System.out.println("请输入一个数字");
6 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
7 int res=0;
8 try{
9 //return;//添加return之后,还是会执行finally语句块
10 //System.exit(0);//添加之后不会执行finally语句块
11 int number=input.nextInt();
12 res=10/number;
13 }catch(InputMismatchException e){
14 //输入字母时错误
15 //错误信息
16 System.out.println(e.getMessage());
17 //堆栈信息
18 e.printStackTrace();
19 }catch(ArithmeticException e){
20 //输入0时错误
21 //错误信息
22 System.out.println(e.getMessage());
23 //堆栈信息
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }catch(Exception e){
26 //该异常为父类,若不清楚是何异常,可以使用该类
27 //若都使用时,应该先使用子类再用该类
28 System.out.println(e.getMessage());
29 e.printStackTrace();
30 }
31 finally{
32 //释放资源,比如关闭打开的文件,删除一些临时文件等
33 System.out.println("结果为:"+res);
34 }
35 }
36 }
空指针异常
1 public class ExceptionDemo1{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 //testTryFinally("张三");//输出2 end
4 testTryFinally(null);//空指针异常
5 }
6
7 public static void testTryFinally(String name){
8 try{
9 System.out.println(name.length());
10 }finally{
11 System.out.println("end");
12 }
13 }
14 }
throw和throws
throw用于手动抛出异常。作为程序员可以再任意位置手动抛出异常;
throws用于在方法上标识要暴露的异常。抛出的异常交由调用者处理;
两者区别:
① throw用在方法内,后面跟上要抛出的异常类对象;
② throws修饰在方法上,告诉调用者此方法可能会抛出异常,后面跟上要抛出的异常类名;
未处理异常
1 public class ExceptionDemo2{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 bar.enter(15);
5 //未打印end
6 System.out.println("end");
7 }
8 }
9
10 class Bar{
11 public void enter(int age){
12 if(age<18){
13 //受查异常(必须捕获,否则编译不通过)和非受查异常
14 throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不合格");
15 }else{
16 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
17 }
18 }
19 }
在调用方法时处理异常
1 public class ExceptionDemo2{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 try{
5 bar.enter(15);
6 }catch(IllegalArgumentException e){
7 System.out.println("错误信息:"+e.getMessage());
8 }
9 System.out.println("end");
10 }
11 }
12
13 class Bar{
14 public void enter(int age){
15 if(age<18){
16 //受查异常(必须捕获,否则编译不通过)和非受查异常
17 throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不合格");
18 }else{
19 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
20 }
21 }
22 }
方法中未处理异常,但调用者可能不知道抛出什么异常,所有在方法上加上throws,用于方法中未处理异常,交由调用者处理
1 public class ExceptionDemo2{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 try{
5 bar.enter(15);
6 }catch(IllegalArgumentException e){
7 System.out.println("错误信息:"+e.getMessage());
8 }
9 System.out.println("end");
10 }
11 }
12
13 class Bar{
14 public void enter(int age)throws IllegalArgumentException{
15 if(age<18){
16 //受查异常(必须捕获,否则编译不通过)和非受查异常
17 throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不合格");
18 }else{
19 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
20 }
21 }
22 }
受查异常必须要捕获,否则编译不通过
1 public class ExceptionDemo2{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 //try{
5 bar.enter(15);
6 /*}catch(IllegalArgumentException e){
7 System.out.println("错误信息:"+e.getMessage());
8 }*/
9 System.out.println("end");
10 }
11 }
12
13 class Bar{
14 public void enter(int age) {
15 if(age<18){
16 //受查异常(必须捕获,否则编译不通过)和非受查异常
17 //throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不合格");//非受查异常
18 throw new Exception("年龄不合格");//受查异常
19 }else{
20 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
21 }
22 }
23 }
当抛出的是受查异常时,且方法中不自己捕获异常,必须加上throws,否则编译不通过
1 public class ExceptionDemo2{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 try{
5 bar.enter(15);
6 }catch(Exception e){
7 System.out.println("错误信息:"+e.getMessage());
8 }
9 System.out.println("end");
10 }
11 }
12
13 class Bar{
14 public void enter(int age)throws Exception{
15 if(age<18){
16 //受查异常(必须捕获,否则编译不通过)和非受查异常
17 //throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不合格");//非受查异常
18 throw new Exception("年龄不合格");//受查异常
19 }else{
20 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
21 }
22 }
23 }
自定义异常
常见异常:
非受查异常RuntimeException
受查异常IOException,SQLException,ClassNotFoundException
自定义异常:Java提供的异常体系不可能预见所有希望加以报告的错误;
自定义异常类必须从已有的异常类继承:用的最多的是Exception;
建立新的异常类型最简单的方法就是让编译器产生默认构造方法;
对异常来说,最重要的部分就是它的类名;
可以为异常类定义一个接受字符串参数的构造方法,字符串参数描述异常信息;
1 public class ExceptionDemo3{
2 public static void main(String []args){
3 Bar bar=new Bar();
4 try{
5 bar.enter(15);
6 }catch(AgeLessThanEighteenException e){
7 System.out.println("错误信息:"+e.getMessage());
8 }
9 System.out.println("end");
10 }
11 }
12
13 //自定义异常
14 class AgeLessThanEighteenException extends Exception{
15 private String message;//描述异常信息
16 public AgeLessThanEighteenException(String message){
17 this.message=message;
18 }
19 //重写getMessage()方法
20 public String getMessage(){
21 return message;
22 }
23 }
24
25 class Bar{
26 public void enter(int age)throws
AgeLessThanEighteenException{
27 if(age<18){
28 throw new AgeLessThanEighteenException("年龄不合格");
29 }else{
30 System.out.println("欢迎光临");
31 }
32 }
33 }