第一部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/8478993.html
第二部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/8481825.html
第三部分: https://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/8525541.html
第四部分: https://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/8536350.html
这部分就讲从angular5的客户端上传图片到asp.net core 2.0的 web api.
这是需要的源码: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Eqc4MRiQDwOHmu0OHyttqA
当前的效果如下:
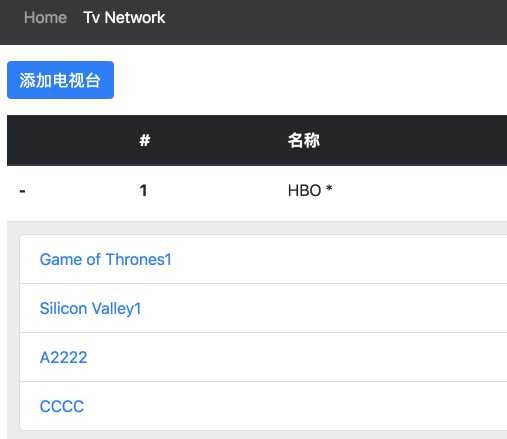
点击这个超链接后:

好的, 下面开始编写上传相关的代码.
Asp.net core 2.0 文件上传
按照顺序, 先建立Photo的domain model:
建立Models/Photo.cs:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace Tv.Models { public class Photo { public int Id { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(255)] public string FileName { get; set; } } }
然后编辑TvShow.cs:
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace Tv.Models { public class TvShow { public TvShow() { Photoes = new List<Photo>(); } public int Id { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(50)] public string Name { get; set; } public int TvNetworkId { get; set; } public TvNetwork TvNetwork { get; set; } public ICollection<Photo> Photoes { get; set; } } }
TvContext.cs:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Tv.Models; namespace Tv.Database { public class TvContext : DbContext { public TvContext(DbContextOptions<TvContext> options) : base(options) { } public DbSet<TvNetwork> TvNetworks { get; set; } public DbSet<TvShow> TvShows { get; set; } public DbSet<Photo> Photoes { get; set; } } }
然后添加迁移和更新数据库, 您应该知道怎么做了, 这部分就略了.
添加PhotoViewModel.cs:
namespace Tv.ViewModels { public class PhotoViewModel { public int Id { get; set; } public string FileName { get; set; } } }
不要忘了做一下Mapping映射, 这里我就不写了.
然后建立PhotoesController.cs:
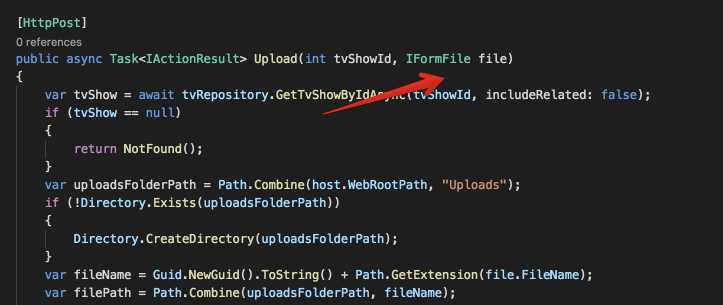
using System; using System.IO; using System.Threading.Tasks; using AutoMapper; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Tv.Database; using Tv.Models; using Tv.ViewModels; namespace Tv.Controllers { [Route("api/tvshows/{tvShowId}/photoes")] public class PhotoesController : Controller { private readonly IHostingEnvironment host; private readonly ITvRepository tvRepository; private readonly IUnitOfWork unitOfWork; private readonly IMapper mapper; public PhotoesController(IHostingEnvironment host, ITvRepository tvRepository, IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, IMapper mapper) { this.host = host; this.tvRepository = tvRepository; this.unitOfWork = unitOfWork; this.mapper = mapper; } [HttpPost] public async Task<IActionResult> Upload(int tvShowId, IFormFile file) { var tvShow = await tvRepository.GetTvShowByIdAsync(tvShowId, includeRelated: false); if (tvShow == null) { return NotFound(); } var uploadsFolderPath = Path.Combine(host.WebRootPath, "Uploads"); if (!Directory.Exists(uploadsFolderPath)) { Directory.CreateDirectory(uploadsFolderPath); } var fileName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString() + Path.GetExtension(file.FileName); var filePath = Path.Combine(uploadsFolderPath, fileName); using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create)) { await file.CopyToAsync(stream); } var photo = new Photo { FileName = fileName }; tvShow.Photoes.Add(photo); await unitOfWork.SaveAsync(); var result = mapper.Map<Photo, PhotoViewModel>(photo); return Ok(result); } } }
这里要简单讲一下. asp.net core 上传文件的文档在这: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/models/file-uploads
首先该controller的路由应该遵循web api的规范, 注意controller 的路由地址.
上传单个文件需要使用IFormFile作为Action的参数. 如果上传的是多个文件, 那么应该使用IFormCollection.
这里我做的是单文件上传, 所以使用IFormFile.
随后使用注入的IHostingEnvironment获得wwwroot目录, 我想要把文件上传到wwwroot/uploads下, 判断该目录是否存在, 如果不存在则创建该目录.
为了防黑, 把文件名改成Guid, 后缀名不变.
然后使用FileStream创建该文件.
后边的内容就是把文件名保存到数据库了.
接下来, 使用Postman来测试这个api.
打开postman, 按照图示输入:
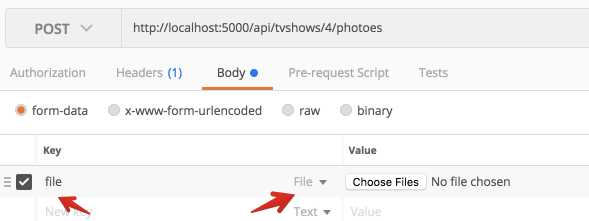
注意这里的参数的key为file, 这个名字要与action的参数名一致:
send:
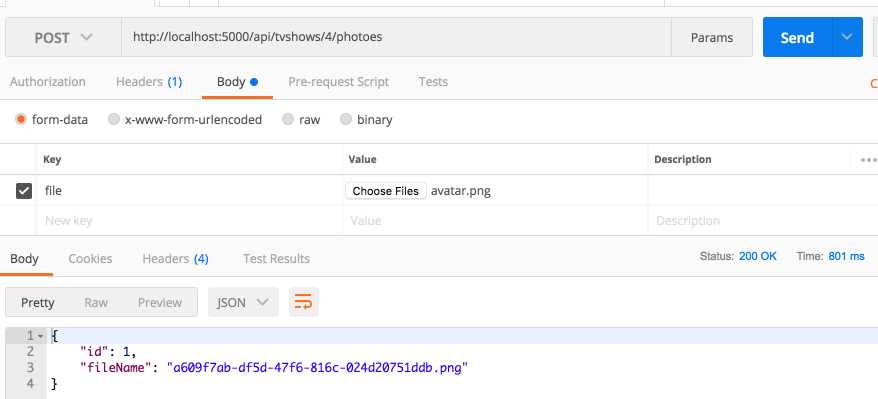
很好, 测试通过.
下面为Action添加一些验证:
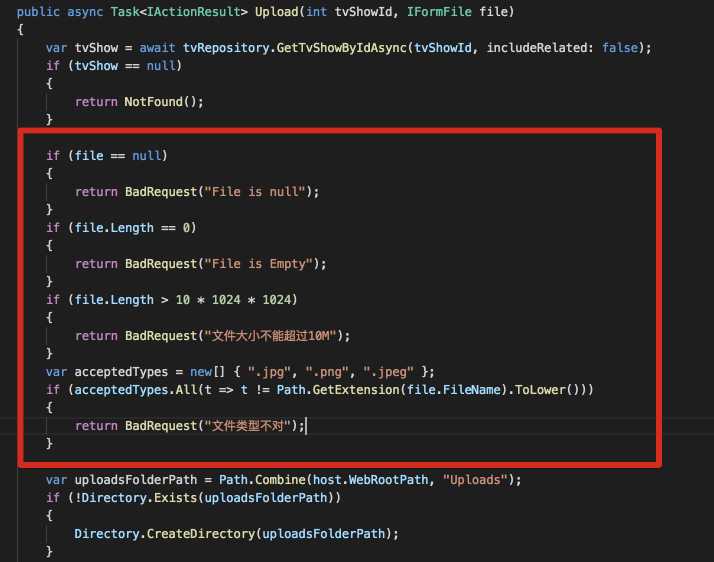
这就是一些常规的验证, 没有什么特别的, 就不累述了.
针对这些东西, 您可以使用配置类, 并把相关的值放在appSettings.json里面. 这部分您自己学一下吧 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/configuration/?tabs=basicconfiguration.
下面是客户端
Angular 5 文件上传
先做ui, tv-show-detail.component.html:
<form> <h2>基本信息</h2> <div class="form-group row"> <label for="name" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">名称</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" readonly class="form-control-plaintext" id="name" value="{{model.name}}"> </div> </div> <h2>电视剧照片</h2> <div class="form-group row"> <label for="file" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">照片</label> <input type="file" name="file" id="file" class="form-control" #fileInput (change)="upload()"> </div> </form>
注意这里使用了template reference.
然后创建一个photo.service:
import { Injectable } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { HttpHeaders, HttpClient } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
@Injectable()
export class PhotoService {
constructor(
private http: HttpClient
) { }
upload(tvShowId: number, photo) {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append(‘file‘, photo);
return this.http.post(`/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`, formData);
}
}
其中post的参数类型是FormData, 它是js原生对象. formData里面文件的key要和后台Action方法的参数名一样.
最后改一下tv-show-detail.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit, ElementRef, ViewChild } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { TvShowService } from ‘../../services/tv-show.service‘;
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { TvShow } from ‘../../models/tv-show‘;
import { Subscription } from ‘rxjs/Subscription‘;
import { ToastrService } from ‘ngx-toastr‘;
import { PhotoService } from ‘../../services/photo.service‘;
@Component({
selector: ‘app-tv-show-detail‘,
templateUrl: ‘./tv-show-detail.component.html‘,
styleUrls: [‘./tv-show-detail.component.css‘]
})
export class TvShowDetailComponent implements OnInit {
tvShowId: number;
@ViewChild(‘fileInput‘) fileInput: ElementRef;
model: TvShow = new TvShow();
busy: Subscription;
constructor(
private tvShowService: TvShowService,
private router: Router,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private toastr: ToastrService,
private photoService: PhotoService
) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.route.paramMap.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => {
this.tvShowId = +params.get(‘id‘);
return this.tvShowService.getById(this.tvShowId);
}).subscribe(item => {
this.model = item;
});
}
upload() {
const ele = this.fileInput.nativeElement;
this.photoService.upload(this.tvShowId, ele.files[0]).subscribe(x => {
console.log(x);
});
}
}
如果上传成功, 那么回来先只做打印到log. 试一下:
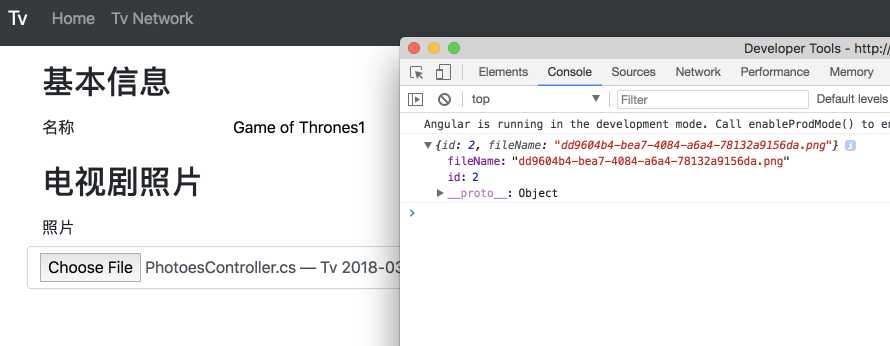
上传成功. 文件即出现在wwwroot下, 文件名也保存到了数据库.
回显照片:
首先修改Photo.cs:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace Tv.Models { public class Photo { public int Id { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(255)] public string FileName { get; set; } public int TvShowId { get; set; } public TvShow TvShow { get; set; } } }
不要忘记迁移数据库.
然后创建Repository, 并注册:
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Tv.Models; namespace Tv.Database { public interface IPhotoRepository { Task<List<Photo>> GetPhotoesByTvShowIdAsync(int tvShowId); } }
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Tv.Models; namespace Tv.Database { public class PhotoRepository : IPhotoRepository { private readonly TvContext context; public PhotoRepository(TvContext context) { this.context = context; } public async Task<List<Photo>> GetPhotoesByTvShowIdAsync(int tvShowId) { var photoes = await context.Photoes.Where(x => x.TvShowId == tvShowId).ToListAsync(); return photoes; } } }
最后修改PhotoesController:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using AutoMapper; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Tv.Database; using Tv.Models; using Tv.ViewModels; namespace Tv.Controllers { [Route("api/tvshows/{tvShowId}/photoes")] public class PhotoesController : Controller { private readonly IHostingEnvironment host; private readonly ITvRepository tvRepository; private readonly IUnitOfWork unitOfWork; private readonly IMapper mapper; private readonly IPhotoRepository photoRepository; public PhotoesController(IHostingEnvironment host, ITvRepository tvRepository, IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, IMapper mapper, IPhotoRepository photoRepository) { this.host = host; this.tvRepository = tvRepository; this.unitOfWork = unitOfWork; this.mapper = mapper; this.photoRepository = photoRepository; } [HttpPost] public async Task<IActionResult> Upload(int tvShowId, IFormFile file) { var tvShow = await tvRepository.GetTvShowByIdAsync(tvShowId, includeRelated: false); if (tvShow == null) { return NotFound(); } if (file == null) { return BadRequest("File is null"); } if (file.Length == 0) { return BadRequest("File is Empty"); } if (file.Length > 10 * 1024 * 1024) { return BadRequest("文件大小不能超过10M"); } var acceptedTypes = new[] { ".jpg", ".png", ".jpeg" }; if (acceptedTypes.All(t => t != Path.GetExtension(file.FileName).ToLower())) { return BadRequest("文件类型不对"); } var uploadsFolderPath = Path.Combine(host.WebRootPath, "Uploads"); if (!Directory.Exists(uploadsFolderPath)) { Directory.CreateDirectory(uploadsFolderPath); } var fileName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString() + Path.GetExtension(file.FileName); var filePath = Path.Combine(uploadsFolderPath, fileName); using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create)) { await file.CopyToAsync(stream); } var photo = new Photo { FileName = fileName }; tvShow.Photoes.Add(photo); await unitOfWork.SaveAsync(); var result = mapper.Map<Photo, PhotoViewModel>(photo); return Ok(result); } [HttpGet] public async Task<IActionResult> GetPhotoesByTvShowId(int tvShowId) { var photoes = await photoRepository.GetPhotoesByTvShowIdAsync(tvShowId); return Ok(photoes); } } }
然后修改angular部分:
添加Photo到model:
export class Photo {
id: number;
tvShowId: number;
fileName: string;
}
修改photo service:
import { Injectable } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { HttpHeaders, HttpClient } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import { Photo } from ‘../models/photo‘;
@Injectable()
export class PhotoService {
constructor(
private http: HttpClient
) { }
upload(tvShowId: number, photo): Observable<Photo> {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append(‘file‘, photo);
return this.http.post<Photo>(`/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`, formData);
}
getPhotoes(tvShowId: number): Observable<Photo[]> {
return this.http.get<Photo[]>(`/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`);
}
}
tv-show-detail.component.html:
<form>
<h2>基本信息</h2>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="name" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">名称</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" readonly class="form-control-plaintext" id="name" value="{{model.name}}">
</div>
</div>
<h2>电视剧照片</h2>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="file" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">照片</label>
<input type="file" name="file" id="file" class="form-control" #fileInput (change)="upload()">
</div>
<div>
<img [src]="‘http://localhost:5000/Uploads/‘ + p.fileName" [alt]="p.fileName" *ngFor="let p of photoes" class="m-1" width="200"
height="200" />
</div>
</form>
tv-show-detail.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit, ElementRef, ViewChild } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { TvShowService } from ‘../../services/tv-show.service‘;
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { TvShow } from ‘../../models/tv-show‘;
import { Subscription } from ‘rxjs/Subscription‘;
import { ToastrService } from ‘ngx-toastr‘;
import { PhotoService } from ‘../../services/photo.service‘;
import { Photo } from ‘../../models/photo‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import ‘rxjs/add/observable/forkJoin‘;
@Component({
selector: ‘app-tv-show-detail‘,
templateUrl: ‘./tv-show-detail.component.html‘,
styleUrls: [‘./tv-show-detail.component.css‘]
})
export class TvShowDetailComponent implements OnInit {
tvShowId: number;
@ViewChild(‘fileInput‘) fileInput: ElementRef;
model: TvShow = new TvShow();
busy: Subscription;
photoes: Photo[] = [];
constructor(
private tvShowService: TvShowService,
private router: Router,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private toastr: ToastrService,
private photoService: PhotoService
) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.route.paramMap.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => {
this.tvShowId = +params.get(‘id‘);
return Observable.forkJoin<TvShow, Photo[]>(
this.tvShowService.getById(this.tvShowId),
this.photoService.getPhotoes(this.tvShowId)
);
}).subscribe(([tvShow, photoes]) => {
this.model = tvShow;
this.photoes = photoes;
});
}
upload() {
const ele = this.fileInput.nativeElement;
this.photoService.upload(this.tvShowId, ele.files[0]).subscribe(photo => {
this.photoes.push(photo);
});
}
}
这部分比较简单, 注意同时发送多个请求可以使用forkJoin.
看看效果:
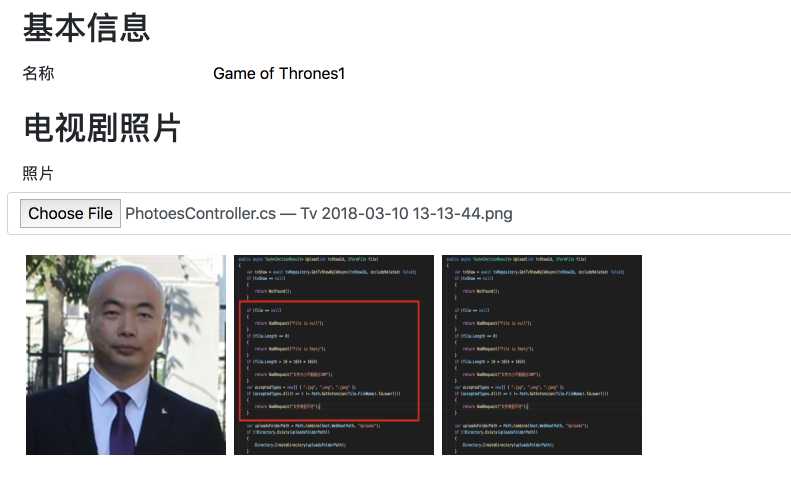
如果照片没有显示出来, 可能是asp.net core没有启用静态文件到支持, 在Startup.cs添加这句话即可:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using AutoMapper; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using Tv.Database; namespace Tv { public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddAutoMapper(); // services.AddDbContext<TvContext>(opt => opt.UseSqlServer(Configuration["ConnectionStrings:Default"])); services.AddDbContext<TvContext>(opt => opt.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))); services.AddScoped<ITvRepository, TvRepository>(); services.AddScoped<IPhotoRepository, PhotoRepository>(); services.AddScoped<IUnitOfWork, UnitOfWork>(); services.AddMvc(); } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseMvc(); } } }
很好. 即使是刚添加完到照片也会即时显示出来.
上传进度显示.
首先创建一个修改photo service:
根据官方文档, 如果想要上传文件时显示进度, 那么应该使用HttpRequest, 并设置属性reportProgress为true:
import { Injectable } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { HttpHeaders, HttpClient, HttpRequest, HttpEvent, HttpEventType, HttpErrorResponse } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import { Photo } from ‘../models/photo‘;
@Injectable()
export class PhotoService {
constructor(
private http: HttpClient
) { }
upload(tvShowId: number, photo: File) {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append(‘file‘, photo);
// return this.http.post<Photo>(`/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`, formData);
const req = new HttpRequest(‘POST‘, `/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`, formData, {
reportProgress: true
});
return this.http.request<Photo>(req);
}
getPhotoes(tvShowId: number): Observable<Photo[]> {
return this.http.get<Photo[]>(`/api/tvshows/${tvShowId}/photoes`);
}
}
回到 tv-show-detail.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit, ElementRef, ViewChild } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { TvShowService } from ‘../../services/tv-show.service‘;
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { TvShow } from ‘../../models/tv-show‘;
import { Subscription } from ‘rxjs/Subscription‘;
import { ToastrService } from ‘ngx-toastr‘;
import { PhotoService } from ‘../../services/photo.service‘;
import { Photo } from ‘../../models/photo‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import ‘rxjs/add/observable/forkJoin‘;
import { HttpEvent, HttpEventType } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
import { HttpResponse } from ‘selenium-webdriver/http‘;
@Component({
selector: ‘app-tv-show-detail‘,
templateUrl: ‘./tv-show-detail.component.html‘,
styleUrls: [‘./tv-show-detail.component.css‘]
})
export class TvShowDetailComponent implements OnInit {
tvShowId: number;
@ViewChild(‘fileInput‘) fileInput: ElementRef;
model: TvShow = new TvShow();
busy: Subscription;
photoes: Photo[] = [];
constructor(
private tvShowService: TvShowService,
private router: Router,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private toastr: ToastrService,
private photoService: PhotoService
) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.route.paramMap.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => {
this.tvShowId = +params.get(‘id‘);
return Observable.forkJoin<TvShow, Photo[]>(
this.tvShowService.getById(this.tvShowId),
this.photoService.getPhotoes(this.tvShowId)
);
}).subscribe(([tvShow, photoes]) => {
this.model = tvShow;
this.photoes = photoes;
});
}
upload() {
const ele = this.fileInput.nativeElement;
const file = ele.files[0];
this.photoService.upload(this.tvShowId, file).subscribe((event: HttpEvent<any>) => {
switch (event.type) {
case HttpEventType.Sent:
console.log(`开始上传 "${file.name}", 大小是: ${file.size}.`);
break;
case HttpEventType.UploadProgress:
const percentDone = Math.round(100 * event.loaded / event.total);
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 的上传进度是 ${percentDone}%.`);
break;
case HttpEventType.Response:
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 上传成功!`);
this.toastr.success(`文件 "${file.name}" 上传成功!`);
this.photoes.push(<Photo>(event.body));
break;
default:
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 的事件类型: ${event.type}.`);
break;
}
});
}
}
这样, 上传文件时, 每个进度都会返回一个event, 我暂时就先把它打印到控制台.
看一下效果:
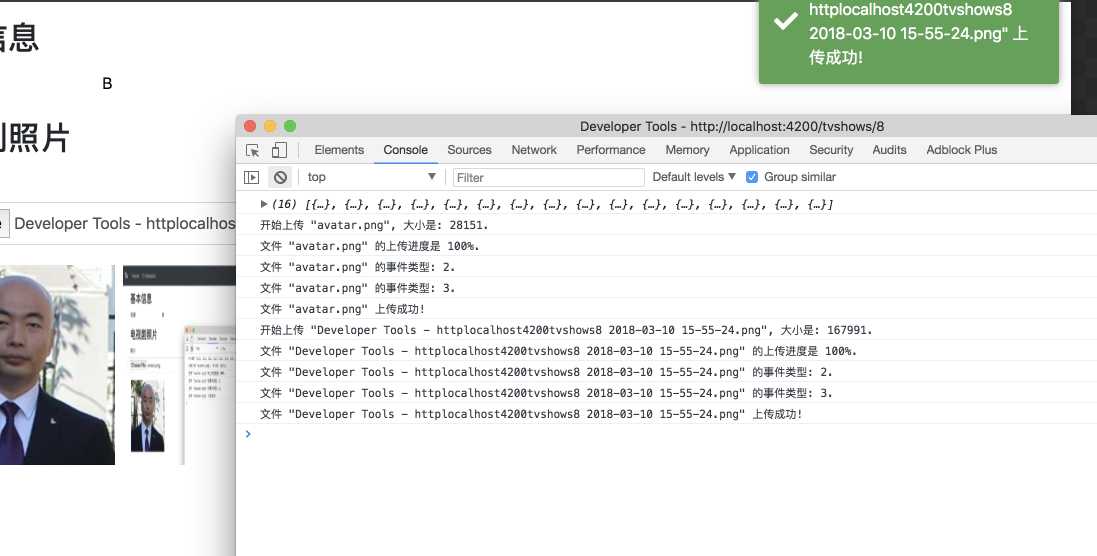
好的, 文件太小, 本地到速度又太快, 进度直接100%了.
那我改一下Chrome的设置, 打开Developer Tools的Network 选项, 然后点击这里:
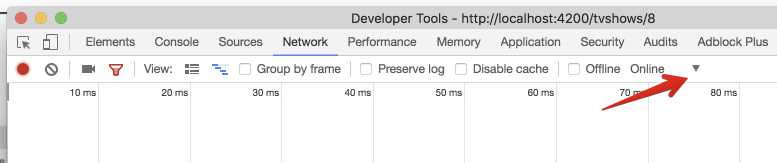
然后添加:
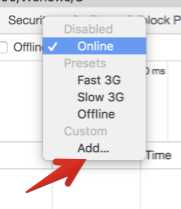
添加一个非常慢的网速限制:
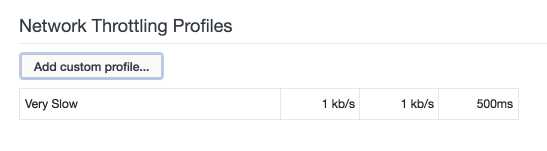
最后选取这个限制:
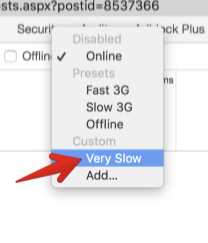
实际上, 选择Slow 3G就很慢了.
这时, 再上传一次试试效果:
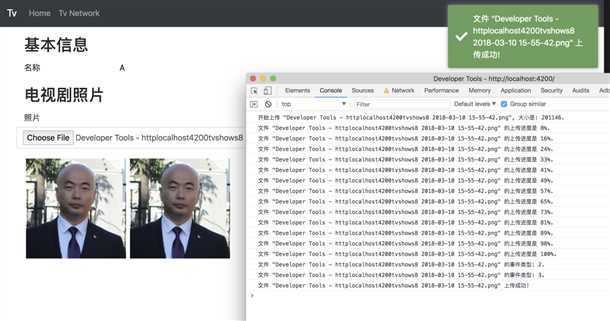
很好, 没问题.
接下来就是UI显示进度条的问题了, 很简单:
打开html:
<form> <h2>基本信息</h2> <div class="form-group row"> <label for="name" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">名称</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" readonly class="form-control-plaintext" id="name" value="{{model.name}}"> </div> </div> <h2>电视剧照片</h2> <div class="form-group row"> <label for="file" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">照片</label> <input type="file" name="file" id="file" class="form-control" #fileInput (change)="upload()"> </div> <div class="progress" *ngIf="progress"> <div class="progress-bar progress-bar-striped progress-bar-animated" role="progressbar" aria-valuenow="0" aria-valuemin="0" aria-valuemax="100" [style.width]="progress"></div> </div> <div> <img [src]="‘http://localhost:5000/Uploads/‘ + p.fileName" [alt]="p.fileName" *ngFor="let p of photoes" class="m-1" width="200" height="200" /> </div> </form>
打开tv-show-detail.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit, ElementRef, ViewChild } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { TvShowService } from ‘../../services/tv-show.service‘;
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { TvShow } from ‘../../models/tv-show‘;
import { Subscription } from ‘rxjs/Subscription‘;
import { ToastrService } from ‘ngx-toastr‘;
import { PhotoService } from ‘../../services/photo.service‘;
import { Photo } from ‘../../models/photo‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import ‘rxjs/add/observable/forkJoin‘;
import { HttpEvent, HttpEventType } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
import { HttpResponse } from ‘selenium-webdriver/http‘;
@Component({
selector: ‘app-tv-show-detail‘,
templateUrl: ‘./tv-show-detail.component.html‘,
styleUrls: [‘./tv-show-detail.component.css‘]
})
export class TvShowDetailComponent implements OnInit {
tvShowId: number;
@ViewChild(‘fileInput‘) fileInput: ElementRef;
model: TvShow = new TvShow();
busy: Subscription;
photoes: Photo[] = [];
progress: string;
constructor(
private tvShowService: TvShowService,
private router: Router,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private toastr: ToastrService,
private photoService: PhotoService
) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.route.paramMap.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => {
this.tvShowId = +params.get(‘id‘);
return Observable.forkJoin<TvShow, Photo[]>(
this.tvShowService.getById(this.tvShowId),
this.photoService.getPhotoes(this.tvShowId)
);
}).subscribe(([tvShow, photoes]) => {
this.model = tvShow;
this.photoes = photoes;
});
}
upload() {
const ele = this.fileInput.nativeElement;
const file = ele.files[0];
ele.value = ‘‘; // 上传图片后,把input的值清空.
this.photoService.upload(this.tvShowId, file).subscribe((event: HttpEvent<any>) => {
switch (event.type) {
case HttpEventType.Sent:
console.log(`开始上传 "${file.name}", 大小是: ${file.size}.`);
break;
case HttpEventType.UploadProgress:
const percentDone = Math.round(100 * event.loaded / event.total);
this.progress = `${percentDone}%`;
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 的上传进度是 ${percentDone}%.`);
break;
case HttpEventType.Response:
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 上传成功!`);
this.toastr.success(`文件 "${file.name}" 上传成功!`);
this.photoes.push(<Photo>(event.body));
this.progress = null;
break;
default:
console.log(`文件 "${file.name}" 的事件类型: ${event.type}.`);
break;
}
});
}
}
试试效果:
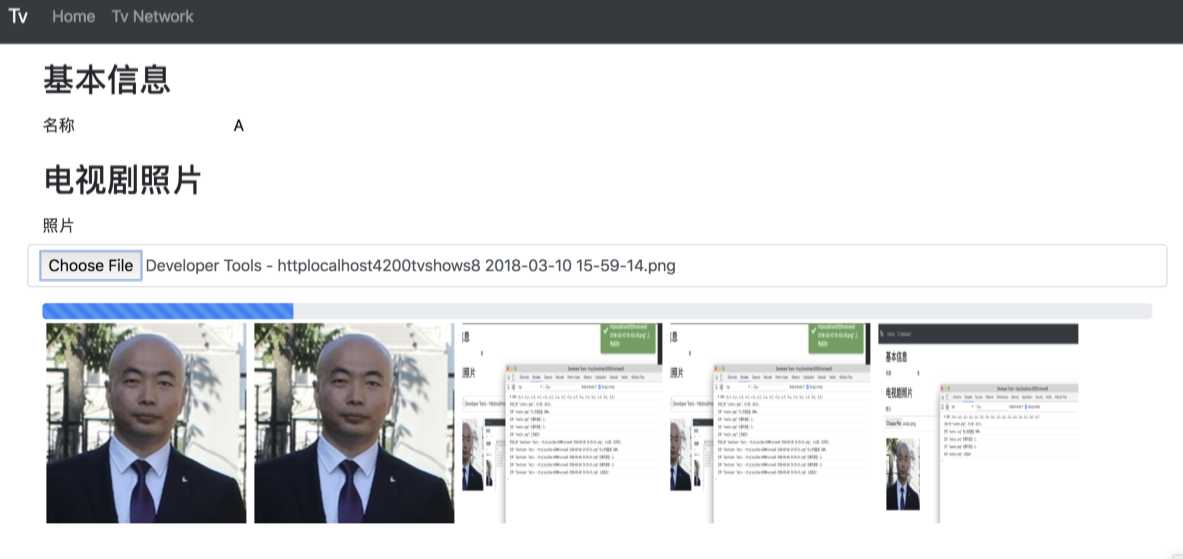
OK, 没问题!
今天就写到这吧.