数码相框(LCDI2C)
Posted 清浅づ流年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数码相框(LCDI2C)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:项目介绍
该项目最终实现的功能很简单,手指在触摸屏左滑(下一张图片),右滑(上一张图片)
1.1软硬件资源
硬件:pc机,ARM Cortex-A9开发板
软件:linux 操作系统
1.3项目流程
本项目主要分为三大模块:
一:LCD驱动编写
二:I2C驱动编写
三:使用I2C读取触摸屏上的数据,判断是向左或者向右,再控制lcd进行图片的显示
大体流程图如下所示: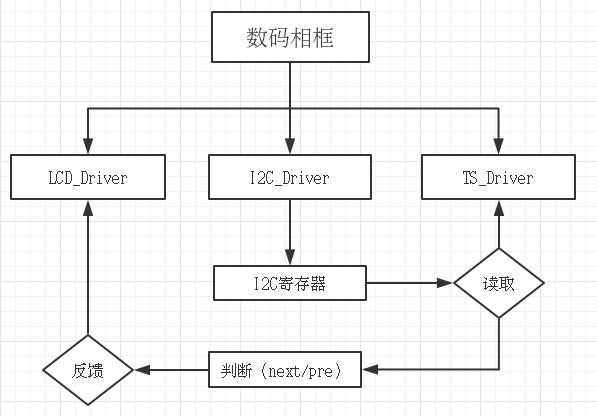
二:项目环境搭建
2.1安装交叉环境编译器 4.5.1,dnw软件
2.2烧写uboot
三:LCD裸板驱动的编写
在编写lcd驱动前先看一下电路图:
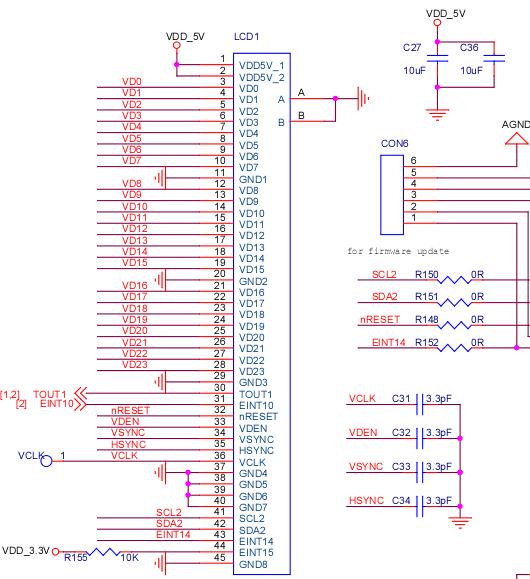
可以观察到 LCD1由45根线来控制,主要配置的寄存器是24根RGB以及TOU1 EINT10 以及VDEN VYNC HSYNC VCLK驱动;
在核心板中找到网标,找出相应的寄存器;
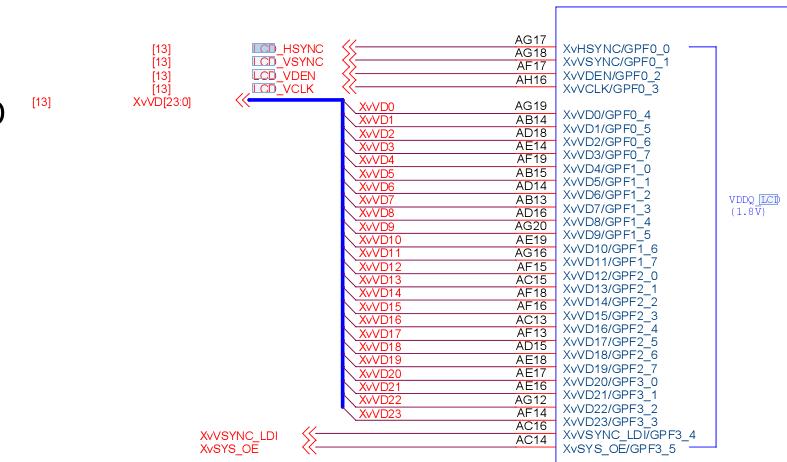
编写lcd可大致分为如下几步:
第一步:配置 OUT1 EINT10 以及24根RGB
第二步:看时序图配置相关寄存器
第三步:配置窗口寄存器
3.1 lcd控制器
Exynos4412的LCD控制器可以通过编程支持不同LCD屏的要求,例如行和列像素数,数据总线宽度,接口时序和刷新频率等。
LCD控制器的主要作用,是将定位在系统存储器中的显示缓冲区中的LCD图像数据传送到外部LCD驱动器,并产生必要的控制信号,
例如RGB_VSYNC,RGB_HSYNC, RGB_VCLK等
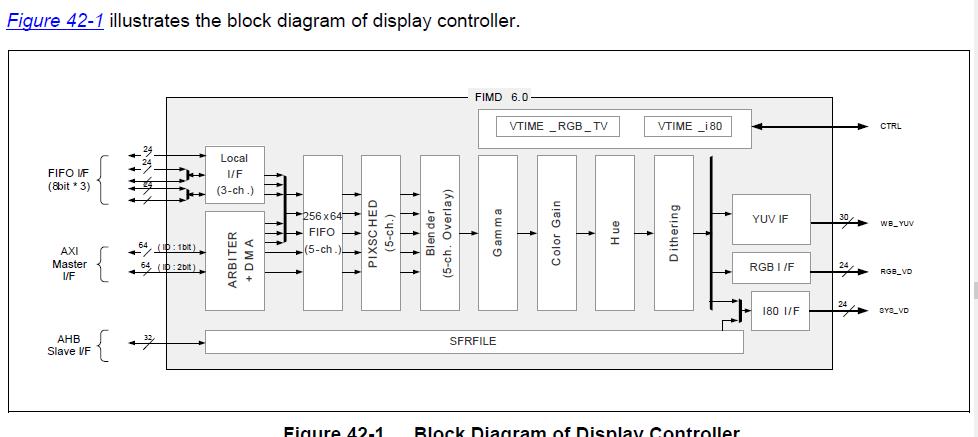
由上图可知:LCD控制器的构成主要由VSFR,VDMA,VPRCS , VTIME和视频时钟产生器几个模块组成;
(1)VSFR由121个可编程控制器组,一套gammaLUT寄存器组(包括64个寄存器),一套i80命令寄存器组(包括12个寄存器)和5块256*32调色板存储器组成,主要用于对lcd控制器进行配置。
(2)VDMA是LCD专用的DMA传输通道,可以自动从系统总线上获取视频数据传送到VPRCS,无需CPU干涉。
(3)VPRCS收到数据后组成特定的格式(如16bpp或24bpp),然后通过数据接口(RGB_VD, VEN_VD, V656_VD or SYS_VD)传送到外部LCD屏上。
(4)VTIME模块由可编程逻辑组成,负责不同lcd驱动器的接口时序控制需求。VTIME模块产生 RGB_VSYNC, RGB_HSYNC, RGB_VCLK, RGB_VDEN,VEN_VSYNC等信号。
3.2 lcd接口信号
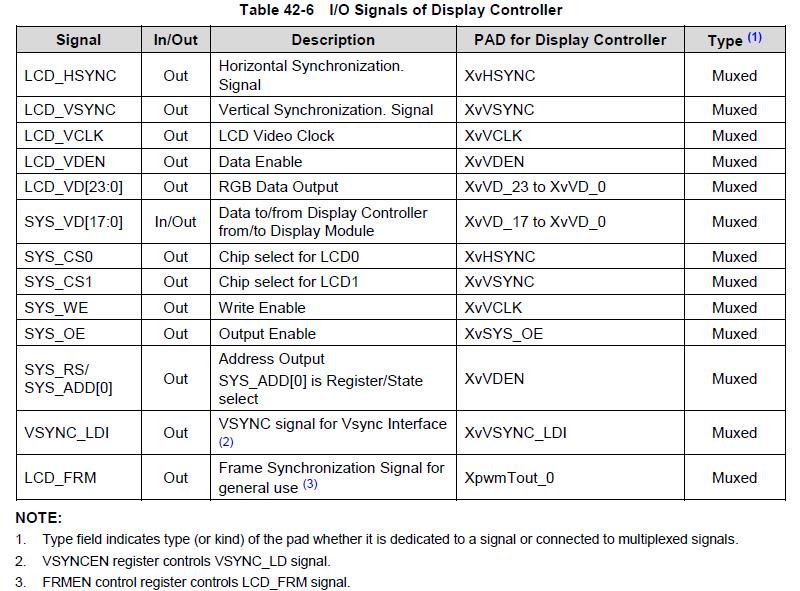
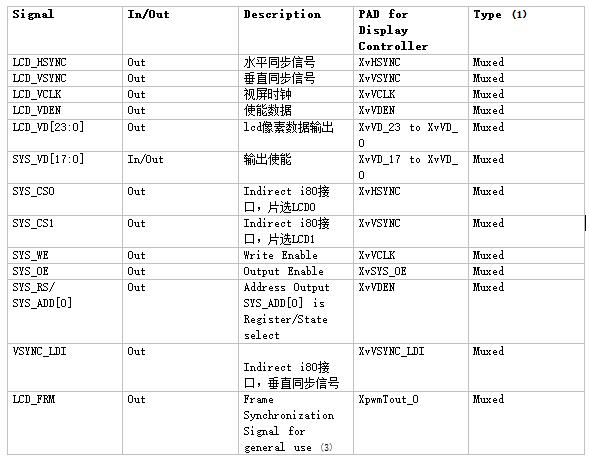
其中主要的RGB接口信号:
(1)LCD_HSYNC:行同步信号,表示一行数据的开始,LCD控制器在整个水平线(整行)数据移入LCD驱动器后,插入一个LCD_HSYNC信号;
(2)LCD_VSYNC: 帧同步信号,表示一帧数据的开始,LCD控制器在一个完整帧显示完成后立即插入一个LCD_VSYNC信号,开始新一帧的显示;VSYNC信号出现的频率表示一秒钟内能显示多少帧图像,称为“显示器的频率”
(3)LCD_VCLK:像素时钟信号,表示正在传输一个像素的数据;
(4)LCD_VDEN:数据使能信号;
(5) LCD_VD[23:0]: LCD像素数据输出端口
3.3、RGB信号的时序
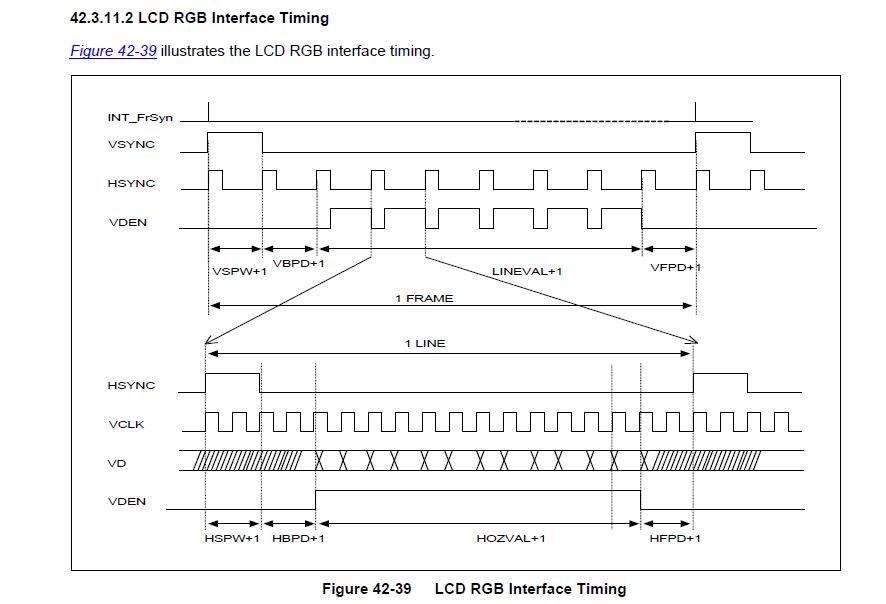
(1)、相关参数说明
VBPD(vertical back porch):表示在一帧图像开始时,垂直同步信号以后的无效的行数。
VFBD(vertical front porch):表示在一帧图像结束后,垂直同步信号以前的无效的行数。
VSPW(vertical sync pulse width):表示垂直同步脉冲的宽度,用行数计算。
HBPD(horizontal back porch):表示从水平同步信号开始到一行的有效数据开始之间的VCLK的个数。
HFPD(horizontal front porth):表示一行的有效数据结束到下一个水平同步信号开始之间的VCLK的个数。
HSPW(horizontal sync pulse width):表示水平同步信号的宽度,用VCLK计算。
(2)、帧的传输过程
VSYNC信号有效时,表示一帧数据的开始,信号宽度为(VSPW +1)个HSYNC信号周期,即(VSPW +1)个无效行;
VSYNC信号脉冲之后,总共还要经过(VBPD+ 1)个HSYNC信号周期,有效的行数据才出现; 所以,在VSYNC信号有效之后,还要经过(VSPW +1 + VBPD + 1)个无效的行;
随即发出(LINEVAL+ 1)行的有效数据;
最后是(VFPD + 1)个无效的行。
(3)、行中像素数据的传输过程
HSYNC信号有效时,表示一行数据的开始,信号宽度为(HSPW+ 1)个VCLK信号周期,即(HSPW +1)个无效像素;
HSYNC信号脉冲之后,还要经过(HBPD +1)个VCLK信号周期,有效的像素数据才出现;
随后发出(HOZVAL+1)个像素的有效数据;
最后是(HFPD +1)个无效的像素。
(4)、将VSYNC、HSYNC、VCLK等信号的时间参数设置好之后,并将帧内存的地址告诉LCD控制器,它即可自动地发起DMA传输从帧内存中得到图像数据,最终在上述信号的控制下RGB数据出现在数据总线VD[23:0]上。用户只需要把要显示的图像数据写入帧内存中。
3.4、lcd相关寄存器设置说明
(1)设置LCD的RGB接口,只需要将其设置为2即可。同时将其IO口设置成为内部上拉,且将其驱动能力设置为最强代码如下:
GPF0CON = 0x22222222;
GPF1CON = 0x22222222;
GPF2CON = 0x22222222;
GPF3CON &= ~(0xffff);
GPF3CON |= 0x2222;
/*max driver strength*/
GPF0DRV = 0xfffffff;
GPF1DRV = 0xfffffff;
GPF2DRV = 0xfffffff;
GPF3DRV &= ~0xff;
GPF3DRV |= 0xff;
(2)设置LCD相关时钟寄存器
这一步主要设置选择LCD时钟输入源为MPLL,且不对其进行分频,同时设置LCDBLK_CFG使其使用FIMD接口,且设置LCDBLK_CFG2使其PWM输出使能;
(4)设置VIDCONx,设置接口类型,时钟分频,极性以及使能LCD控制器等
VIDCON0:这一个寄存器主要设置接口类型和时钟分频,这里仅仅设置了其时钟分频值,由于我们的MPLL为800MHZ,所以这里设置值,根据手册进行计算,要得到33.3MHZ左右的像素时钟;
VIDCON0 = (1 << 17)|(23 <<6)|3;
VIDCON1:主要设置时钟信号,需不需要翻转,以及触发方式;
VIDTCONx:用来设置时序和长宽等参数,这里就主要设置VBPD(vertical back porch)、 VFBD(vertical frontporch)、VSPW(vertical sync pulse width)、HBPD(horizontal backporch)、 HFPD(horizontal sync pulse width)等参数
VIDTCON0取值过程,VIDTCON0设置帧同步时序。
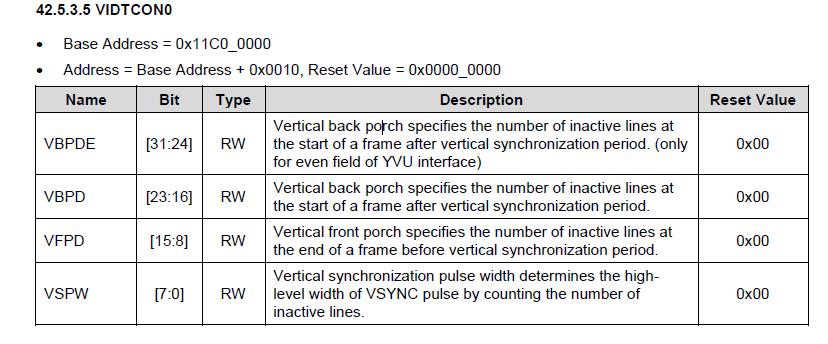
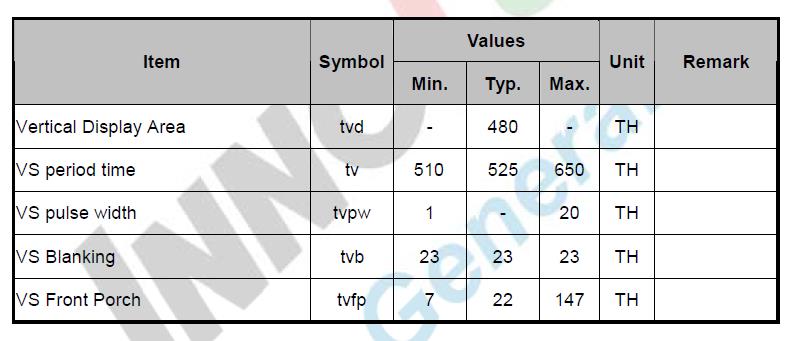
VIDTCON0 = (22 << 16) | (21 << 8) | (0);
VIDTCON1取值过程,VIDTCON1设置像素同步时序。
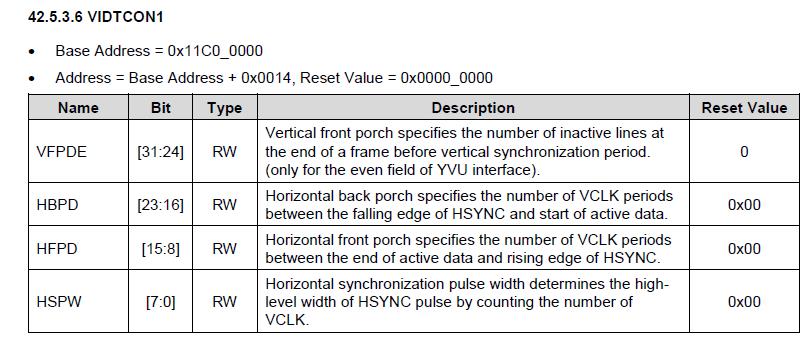
VIDTCON1 = (35 << 16) | (209 << 8) | (9);
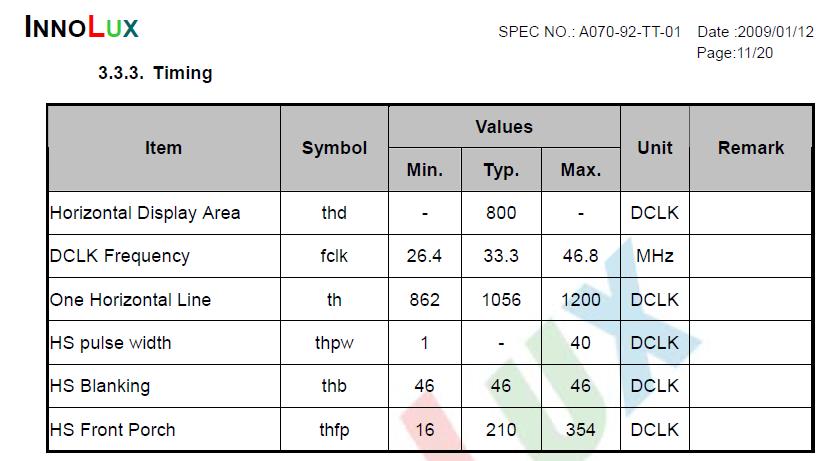
VIDTCON2
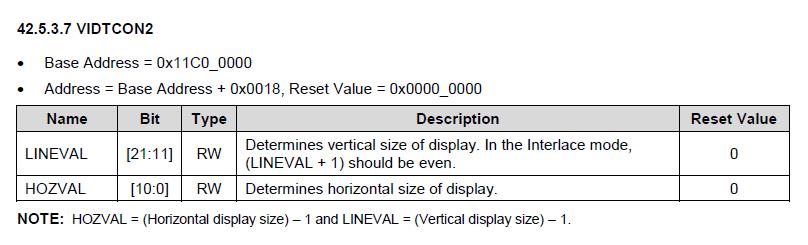
VIDTCON2 = (479 << 11) | 799;
(5)设置WINCON0寄存器,即设置数据格式。
Exynos4412的LCD控制器有overlay功能,它支持5个window。这里只使用window0,设置其代码RGB模式为24bit(A888)且使能window0;
WINCON0 = (1 << 22) | (1 << 15) | (11 << 2) | 1;
(6)设置VID0SD0A/B/C,即设置Window0的坐标系
配置VIDW00ADD0B0和VIDW00ADD1B0,设置framebuffer的地址;
(7)配置SHADOWCON和WINCHMAP2、选择使能DMA通道0。由于我们使用的是Window0,所以需要使能DMA通道0;
(8)最后设置VIDCON0低两位使能LCD
VIDCON0 |= 1 | (1 << 1);
下面是Tiny4412 LCD裸板驱动具体代码:

1 #define LCD_BASE 0x11C00000 2 3 #define VIDCON0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0000)) 4 #define VIDCON1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0004)) 5 #define VIDCON2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0008)) 6 #define VIDCON3 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x000C)) 7 #define VIDTCON0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0010)) 8 #define VIDTCON1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0014)) 9 #define VIDTCON2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0018)) 10 #define VIDTCON3 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x001C)) 11 #define WINCON0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0020)) 12 #define WINCON1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0024)) 13 #define WINCON2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0028)) 14 #define WINCON3 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x002C)) 15 #define WINCON4 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0030)) 16 #define SHADOWCON (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0034)) 17 #define WINCHMAP2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x003C)) 18 #define VIDOSD0A (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0040)) 19 #define VIDOSD0B (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0044)) 20 #define VIDOSD0C (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0048)) 21 #define VIDOSD1A (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0050)) 22 #define VIDOSD1B (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0054)) 23 #define VIDOSD1C (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0058)) 24 #define VIDOSD1D (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x005C)) 25 #define VIDOSD2A (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0060)) 26 #define VIDOSD2B (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0064)) 27 #define VIDOSD2C (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0068)) 28 #define VIDOSD2D (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x006C)) 29 #define VIDOSD3A (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0070)) 30 #define VIDOSD3B (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0074)) 31 #define VIDOSD3C (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0078)) 32 #define VIDOSD4A (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0080)) 33 #define VIDOSD4B (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0084)) 34 #define VIDOSD4C (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0088)) 35 #define VIDW00ADD0B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00A0)) 36 #define VIDW00ADD0B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00A4)) 37 #define VIDW00ADD0B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20A0)) 38 #define VIDW01ADD0B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00A8)) 39 #define VIDW01ADD0B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00AC)) 40 #define VIDW01ADD0B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20A8)) 41 #define VIDW02ADD0B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00B0)) 42 #define VIDW02ADD0B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00B4)) 43 #define VIDW02ADD0B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20B0)) 44 #define VIDW03ADD0B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00B8)) 45 #define VIDW03ADD0B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00BC)) 46 #define VIDW03ADD0B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20B8)) 47 #define VIDW04ADD0B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00C0)) 48 #define VIDW04ADD0B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00C4)) 49 #define VIDW04ADD0B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20C0)) 50 #define VIDW00ADD1B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00D0)) 51 #define VIDW00ADD1B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00D4)) 52 #define VIDW00ADD1B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20D0)) 53 #define VIDW01ADD1B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00D8)) 54 #define VIDW01ADD1B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00DC)) 55 #define VIDW01ADD1B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20D8)) 56 #define VIDW02ADD1B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00E0)) 57 #define VIDW02ADD1B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00E4)) 58 #define VIDW02ADD1B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20E0)) 59 #define VIDW03ADD1B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00E8)) 60 #define VIDW03ADD1B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00EC)) 61 #define VIDW03ADD1B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20E8)) 62 #define VIDW04ADD1B0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00F0)) 63 #define VIDW04ADD1B1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x00F4)) 64 #define VIDW04ADD1B2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x20F0)) 65 #define VIDW00ADD2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0100)) 66 #define VIDW01ADD2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0104)) 67 #define VIDW02ADD2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0108)) 68 #define VIDW03ADD2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x010C)) 69 #define VIDW04ADD2 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0110)) 70 #define VIDINTCON0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0130)) 71 #define VIDINTCON1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0134)) 72 #define W1KEYCON0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0140)) 73 #define VIDW0ALPHA0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x021C)) 74 #define VIDW0ALPHA1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0220)) 75 #define VIDW1ALPHA0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0224)) 76 #define VIDW1ALPHA1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0228)) 77 #define VIDW2ALPHA0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x022C)) 78 #define VIDW2ALPHA1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0230)) 79 #define VIDW3ALPHA0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0234)) 80 #define VIDW3ALPHA1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0238)) 81 #define VIDW4ALPHA0 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x023C)) 82 #define VIDW4ALPHA1 (*(volatile unsigned int *)(LCD_BASE + 0x0240)) 83 84 #endif
1 #include "lcd.h" 2 #define RGB888(r, g, b) (((r) << 16) | ((g) << 8) | (b)) 3 4 void lcd_init(void); 5 void clean_screen(unsigned long *fb, int w, int h); 6 7 int main(void) 8 { 9 fb = ADDR0; 10 lcd_init(); 11 clean_screen(fb, 800, 480); 12 } 13 14 void clean_screen(unsigned long *fb, int w, int h) 15 { 16 int i, j; 17 for (i = 0; i < h; i ++) { 18 for (j = 0; j < w; j ++) { 19 fb[i * w + j] = RGB888(255, 0, 0); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 24 void lcd_init(void) 25 { 26 /* 27 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg138 pg141 pg144 pg147> * 28 * GPF0CON : [31:0] : 0x2 29 * GPF1CON : [31:0] : 0x2 30 * GPF2CON : [31:0] : 0x2 31 * GPF3CON : [31:0] : 0x2 32 * */ 33 34 //定义IO引脚功能为RGB接口 35 GPF0CON = 0x22222222; 36 GPF1CON = 0x22222222; 37 GPF2CON = 0x22222222; 38 GPF3CON &= ~(0xffff); 39 GPF3CON |= 0x2222; 40 41 //max driver strebgh---- 42 GPF0DRV = 0xffffffff; 43 GPF1DRV = 0xffffffff; 44 GPF2DRV = 0xffffffff; 45 GPF3DRV &= ~0xff; 46 GPF3DRV |= 0xff; 47 /* 48 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg526> 49 *CLK_DIV_LCD: 50 * [3:0]:FIMD0_RATIO 0 51 * SCLK_FIMD0 = MOUTFIMD0/(FIMD0_RATIO + 1) 52 * = MOUTFIMD0/1 = 800MHz 53 * MOUTFIMD0 == SCLKmpll_user_t == 800MHz <Exyons 4412 datasheet pg453> LCD0_BLK 54 * */ 55 56 CLK_DIV_LCD &= ~0xf; 57 /* 58 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg501> 59 *CLK_SRC_LCD0: 60 * [3:0]:FIMD0_SEL 0110 ===> SCLKmpll_user_t 选择时钟源为SCLKmpll_user_t 61 * 62 * */ 63 CLK_SRC_LCD0 &= ~0xf; 64 CLK_SRC_LCD0 |= 6; 65 //LCD0_SYS_PWR_REG == 7 Don\'t use 66 67 68 /*<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1799> 69 *Using the display controller data, you can select one of the above data paths by setting LCDBLK_CFG Register 70 *(0x1001_0210). For more information, refer to the "System Others" manual. 71 * 72 * 73 * <Exyons 4412 datasheet pg880> 74 * LCDBLK_CFG: 75 * [1] : FIMD of LBLK0 Bypass Selection 1 : FIMD Bypass 使用FIMD接口 76 * 77 * LCDBLK_CFG : 78 * [0]:MIE0_DISPON 1 : PWM outpupt enable 79 * 80 * 81 * */ 82 LCDBLK_CFG |= 1 << 1; //set FIMD 83 LCDBLK_CFG2 |= 1; 84 85 /* 86 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1869> 87 *VIDCON0: 88 * [13:6]: CLKVAL_F //设置lcd时钟分频系数 89 * 90 * VCLK == 33.3Mhz <S700-AT070TN92 pg14> DCLK Frequency ===> Type : 33.3Mhz 91 * VCLK = FIMD * SCLK/(CLKVAL+1) 92 * VCLK = 800000000 / (CLKVAL + 1) 93 * 33300000 = 800000000 /(CLKVAL + 1) 94 * CLKVAL + 1 = 24.02 95 * CLKVAL = 23 96 * */ 97 98 //设置接口类型及时钟分频 33.3MHZ (配置时钟分频系数) 99 VIDCON0 = (1 << 17) | (23 << 6) | 3; /*(1 << 17)非常重要 不配制会出现色差*/ 100 //VIDCON0 = (23 << 6) | 3; 101 /* 102 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1870 pg1848(时序)> <S700-AT070TN92 pg13(时序)> 103 *VIDTCON1: 104 * [5]:IVSYNC ===> 1 : Inverted(反转) 105 * [6]:IHSYNC ===> 1 : Inverted(反转) 106 * [7]:IVCLK ===> 1 : Fetches video data at VCLK rising edge (下降沿触发) 107 * [10:9]:FIXVCLK ====> 01 : VCLK running 108 * */ 109 /*VIDCON1主要设置像表时钟信号一直存在,且高电平有效, 110 而IHSYNC=1,极性反转IVSYNC=1,极性反转,这是由于S07的时序图中VSYNC和 111 HSYNC都是低脉冲有效,而Exynos4412芯片手册时序图,VSYNC 和HSYNC都是高脉冲有效 112 ,所以需要反转*/ 113 VIDCON1 = (1 << 9) | (1 << 7) | (1 << 5) | (1 << 6); //配置时序相关 114 115 /* 116 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1874 pg1848(时序)> <S700-AT070TN92 pg13(时序)> 117 *VIDTCON0: 118 * [23:16]: VBPD + 1 <------> tvpw (1 - 20) 13 119 * [15:8]: VFPD + 1 <------> tvfp 22 120 * [7:0]: VSPW + 1 <------> tvb - tvpw = 23 - 13 = 10 121 * */ 122 /*VIDTCONx用来设置时序和长宽等参数,这里就主要设置VBPD(vertical back porch)、 123 VFBD(vertical fro ntporch)、VSPW(vertical sync pulse width)、 124 HBPD(horizontal backporch)、 HFPD(horizontal sync pul se width)等参数*/ 125 VIDTCON0 = (10 << 16) | (21 << 8) | (12); //配置时序间隔时间 (VIDTCON0 VIDTCON1) 126 127 /*<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1874 pg1848(时序)> <S700-AT070TN92 pg13(时序)> 128 *VIDTCON1: 129 * [23:16]: HBPD + 1 <------> thpw (1 - 40) 36 130 * [15:8]: HFPD + 1 <------> thfp 210 131 * [7:0]: HSPW + 1 <------> thb - thpw = 46 - 36 = 10 132 */ 133 VIDTCON1 = (35 << 16) | (209 << 8) | (9); 134 135 /* 136 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1875> 137 * 138 *HOZVAL = (Horizontal display size) – 1 and LINEVAL = (Vertical display size) – 1. 139 * Horizontal(水平) display size : 800 140 *Vertical(垂直) display size : 480 141 * */ 142 VIDTCON2 = (479 << 11) | 799; 143 144 //win0 145 //#ifdef BPP565 146 /* 147 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1877> 148 *WINCON0: 149 * [16]:Specifies Half-Word swap control bit. 1 = Enables swap 150 * [5:2]: Selects Bits Per Pixel (BPP) mode for Window image : 0101 ===> 16BPP 151 * [1]:Enables/disables video output 1 = Enables 152 * 153 * */ 154 // WINCON0 = (1 << 16) | (5 << 2) | 1; 155 156 /* 157 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1895> 158 *VIDOSD0C:Specifies the Window Size (窗口尺寸 单位为word) 159 * 160 * 161 * */ 162 // VIDOSD0C = 480 * 800 >> 1; 163 //#else 164 /* 165 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1877> 166 *WINCON0: 167 * [5:2]: Selects Bits Per Pixel (BPP) mode for Window image : 1011 ===> 24BPP 168 * [1]:Enables/disables video output 1 = Enables 169 * 170 * */ 171 /*Exynos4412的LCD控制器有overlay功能,它支持5个window。 172 这里只使用window0,设置其代码RGB模式为24bit,(A888)且使能window0 173 */ 174 WINCON0 = (1 << 22) | (1 << 15) | (11 << 2) | 1;//配置窗口0颜色数据格式,使能视频数据输出 175 176 /* 177 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1895> 178 *VIDOSD0C:Specifies the Window Size (窗口尺寸 单位为word) 179 * 180 * 181 * */ 182 VIDOSD0C = 480 * 800; //windows size 183 //#endif 184 185 //SHADOWCON &= ~(1 << 5); Don\'t use 186 187 /* 188 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1891 pg1801> 189 *[0]: Enables Channel 0. 1 = Enables 190 * */ 191 /*配置SHADOWCON和WINCHMAP2、选择使能DMA通道0, 192 由于我们使用的是Window0,所以需要使能DMA通道0 193 */ 194 SHADOWCON |= 1; //选择相应通道 195 196 197 /* 198 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1894 pg1801> 199 *[18:16] Selects Channel 0\'s channel. ===> 001 = Window 0 200 *[2:0] Selects Window 0\'s channel. ===> 001 = Channel 0 201 * 202 * 203 * */ 204 WINCHMAP2 &= ~(7 << 16);//选择通道与窗口 205 WINCHMAP2 |= 1 << 16; 206 WINCHMAP2 &= ~7; 207 WINCHMAP2 |= 1; 208 209 /* 210 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1895> 211 *VIDOSD0A: LCD左上角坐标 212 *VIDOSD0B: LCD右下角坐标 213 */ 214 215 VIDOSD0A = 0; 216 VIDOSD0B = (799 << 11) | 479; 217 218 /* 219 *<Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1902> 220 * VIDW00ADD0B0 : window0 frame buffer 起始地址 221 * VIDW00ADD1B0 : window0 frame buffer 结束地址 222 * */ 223 VIDW00ADD0B0 = FRAMEBUFFER00; 224 VIDW00ADD1B0 = FRAMEBUFFER00 + VIDOSD0C * 4; 225 VIDW00ADD2 = 800; 226 /* 227 * <Exyons 4412 datasheet pg1869> 228 * Display On: ENVID and ENVID_F are set to "1". 229 * [0]:ENVID ===> 1 = Enables 230 * [1]:ENVID_F ===> 1 = Enables 231 * */ 232 }
页面频率计算公式:

1 Frame_Rate = 1/[{(VSPW + 1) + (VBPD + 1) + (LIINEVAL + 1) + (VFPD + 1)} * {(HSPW + 1) + ( HBPD + 1) + (HFPD + 1) + (HOZVAL + 1)} * {(CLKVAL + 1)/(Frequency of Clock source)}] 2 3 50 = 1 / [{10 + 13 + 480 + 22} * {20 + 26 + 800 + 210} * X / 800M] 4 50 = 1 / [525 * 1056 * X / 800M] 5 1 = 50 * 525 * 1056 * X / 800M 6 800M = 50 * 525 * 1056 * X 7 X = 800M / (50 * 525 * 1056) 8 X = 800M / 27720000 9 X = 28.8
四:I2C裸板驱动驱动编写
4.1 I2C总线介绍
I2C总线有两条总线线路,一条是串行数据线(SDA),一条是串行时钟线(SCL)。SDA负责数据传输,SCL负责数据传输的时钟同步。I2C设备通过这两条总线连接到处理器的I2C总线控制器上。I2C总线最主要的特点就是其简单性、有效性以及支持多主控,其中任何能进行发送和接收的的设备都可以成为主控设备。主控设备能控制信号的传输和时钟平率,当然,在同一时间内只能有一个主控设备占用总线;
与其他总线相比,I2C总线有很多重要的特点:
主要特点:
(1)每一个连接到总线的设备都可以通过唯一的设备地址单独访问
(2)串行的8位双向数据传输,位速率在标准模式下可达到100kb/s;快速模式下可以达到400kb/s;告诉模式下可以达到3.4Mb/s
(3)总线长度最长7.6m左右
(4)片上滤波器可以增加抗干扰能力,保证数据的完成传输
(5)连接到一条I2C总线上的设备数量只受到最大电容400pF的限制
(6)它是一个多主机系统,在一条总线上可以同时有多个主机存在,通过冲突检测方式和延时等待防止数据不被破坏。同一时间只能有一个主机占用总线
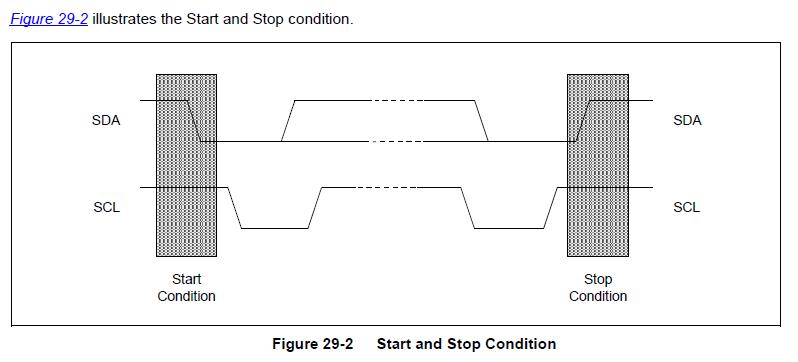
IIC总线在传输数据的过程中有3种类型的信号:开始信号、结束信号、和应答信号
开始信号(S): 当SCL为高电平时,SDA由高电平向低电平跳变,表示将要开始传输数据
结束信号(P):当SCL为高电平时,SDA由低电平向高电平跳变,表示结束传输数据
响应信号(ACK): 从机接收到8位数据后,在第9个周期,拉低SDA电平,表示已经收到数据。这个信号称为应答信号
如下图:
主机:IIC总线中发送命令的设备,对于ARM处理器来说,主机就是IIC控制器以上是关于数码相框(LCDI2C)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
