CS231n笔记 Lecture 11, Detection and Segmentation
Posted ichneumon
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了CS231n笔记 Lecture 11, Detection and Segmentation相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Other Computer Vision Tasks
- Semantic Segmentation. Pixel level, don\'t care about instances.
- Classification + Localization. Single object.
- Object Detection. Multiple object.
- Instance Segmentation. Multiple object.
Semantic Segmentation
Simple idea: sliding window, crop across the whole image, and ask what the center pixel is. Expensive.
Fully Convoltional (Naive) : let the network to learning all the pixels at once, keep the spacial size, convolutions at original image resolution, expensive.
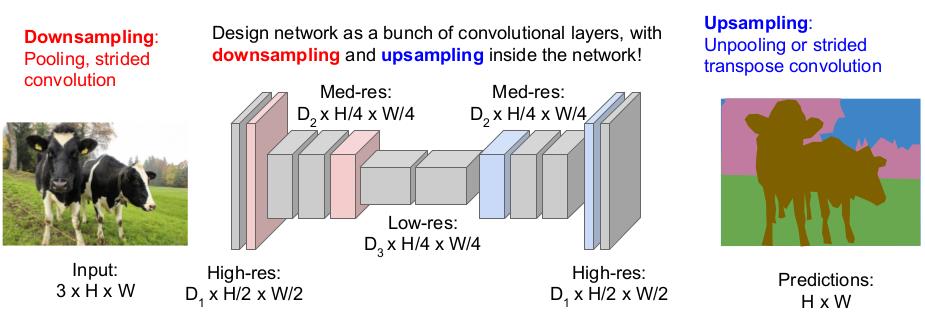
Fully convolutional: Design network as a bunch of convolutional layers, with downsampling and upsampling inside the network!
- Downsampling: Pooling, strided convolution
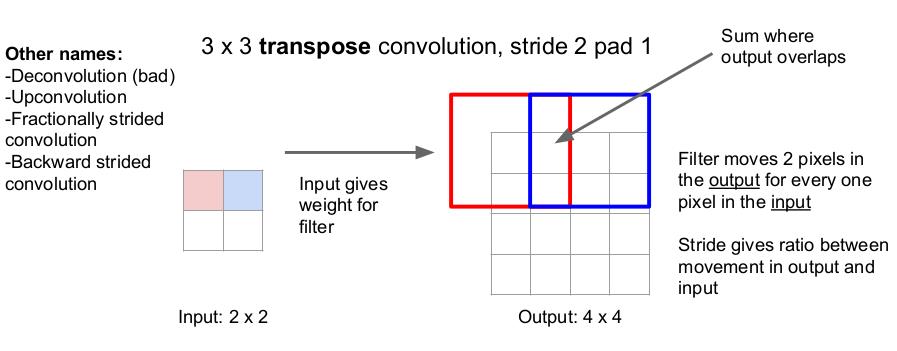
- Upsampling: Unpooling (nearest neighbor, bed of nails, max unpooling in symetrical NN), Transpose convolution (multiply the filter by the pixels on the input, use stride and pad to impose the value on the output).
Classification + Localization
Get class scores and box coordinates from the CNN, treat localization as a regression problem, we have 2 loss!
Aside: Human Pose Estimation, for different position, multitask loss.
Object Detection
Since we have different numbers of objects present, it\'s impossible to use regression. Naively, sliding window.
R-CNN: Based on tranditional techniques in CV, gives thousands proposal region, much better.
Fast R-CNN: Region crop after ConvNet.
Faster R-CNN: Proposal Region Network.
YOLO/SSD: base grids.
Instance Segmentation
Mask R-CNN
以上是关于CS231n笔记 Lecture 11, Detection and Segmentation的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章