http://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6059914.html
http://blog.csdn.net/zldeng19840111/article/details/6703104
http://www.importnew.com/26049.html
http://www.importnew.com/19685.html
HashMap
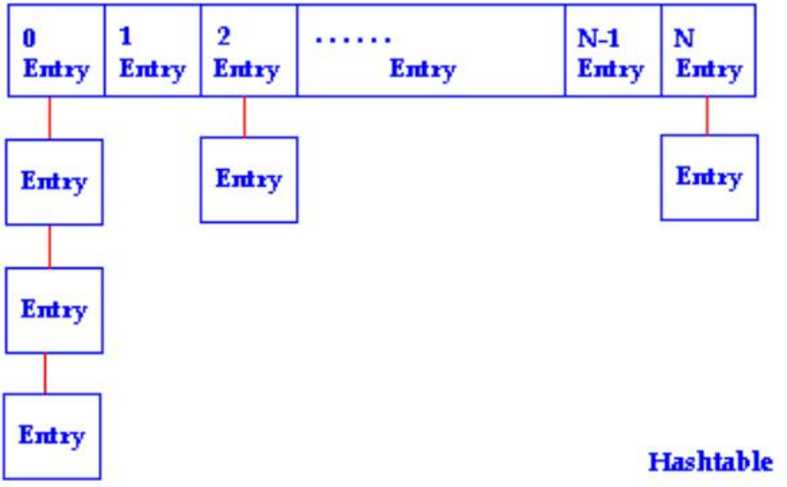
hashmap本质数组+链表+红黑树(链地址法,解决hash冲突问题)。根据key取得hash值,然后计算出数组下标,如果多个key对应到同一个下标,就用链表串起来,新插入的在前面。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity) //最多容纳的Entry数,如果当前元素个数多于这个就要扩容
}
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; //扩充空表
//&:两个数都转为二进制,然后从高位开始比较,如果两个数都为1则为1,否则为0。取最小
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //p取hash链头,并判断是否已存在hash链
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //赋值-新hash链
else {
//存在hash链,hash链中key值不唯一
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //p同key
e = p; //取原值
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //红黑树
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) { //从表链中取数据e:p的下一个;判断是否有p以外(其他k)的Node
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //插入新值
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // 8-1
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
/** TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/超过数量装换list为tree
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //e同key
break;
p = e; //为迭代
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
/** modCount
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/fail-fast 机制是java集合(Collection)中的一种错误机制。当多个线程对同一个集合的内容进行操作时,就可能会产生fail-fast事件。
//if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (++size > threshold) resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
HashMap是线程不安全的:在多线程的环境下,其他的元素也在同时进行put操作,如果hash值相同,可能出现同时在同一数组下用链表表示,造成闭环,导致在get时会出现死循环。
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}