数据结构之堆
Posted 爱跑步的星仔
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构之堆相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
堆是一种树,由它实现的优先级队列的插入和删除的时间复杂度都是O(logN)。而有序数组尽管删除最大数据项的时间复杂度为O(1),但是插入需要O(N)时间。当速度非常重要,且有很多插入操作时,可以选择堆来实现优先级队列。
ps:这里的“堆”是指一种特殊的二叉树,不要与java和C++等编程语言里的“堆”混淆,后者指程序员用new能得到的计算机内存的可用部分。
堆是有如下特点的二叉树:
1)是完全二叉树,也就是说,除了树的最后一层节点不需要是满的,其他的每一层从左到右都完全是满的。
2)它常常用一个数组实现(神不神奇,用数组而不是由引用连接起来的各个节点来存储二叉树)。
3)堆中的每一个节点都满足堆的条件,也就是说每一个节点的关键字都大于(或等于)这个节点的子节点的关键字(假设最大的节点在根上)。

弱序性:堆和二叉搜索树相比是弱序的,在二叉搜索树中所有节点的左子孙的关键字都小于右子孙的关键字。这说明在一个二叉搜索树中通过一个简单的算法就可以按序遍历节点,但是在堆中按序遍历节点是困难的,这是因为堆的组织规则(堆的条件)比二叉搜索树的组织规则弱。对于堆来说,只要求沿着从根到叶子的每一条路径,节点都是按降序排列的。除了有共享节点的路径,路径之间都是相互独立的。
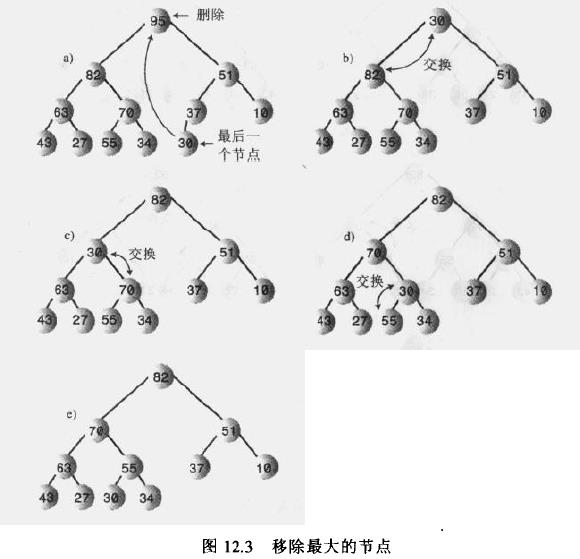
移除:移除是指删除关键字最大的节点。这个节点总是根节点,所以移除是很容易的。根在堆数组中的索引总是0。问题是一旦移除了根节点,树就不是完全的了,数组中就有了一个空的数据单元,简单“填洞”的方法把数组中所有数据都向前移动一个单元,但是还有快得多的方法。下面是移除最大节点的步骤:
1)移走根;
2)把最后一个节点移动到根的位置(最后一个节点是树最底层的最右端的数据项,它对应于数组中的最后一个填入的数据单元);
3)一直向下筛选这个节点,直到它在一个大于它的节点之下,小于它的节点之上为止,其中向下筛选指的是在被筛目标节点的每个暂时停留的位置上,向下筛选的算法都要检查哪一个子节点更大,然后目标节点和较大的子节点交换位置。。
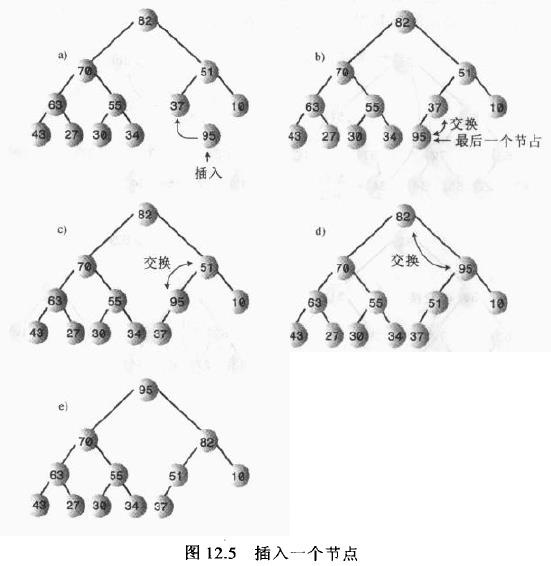
插入节点步骤:
1)节点初始时插入到数组最后第一个空着的单元中,数组容量大小增一。
2)向上筛选新节点,知道它在一个大于它的节点之下,在一个小于它的节点之上。其中向上筛选指的是目标节点与其父节点比较。
用数组表示堆的要点:若数组中节点的索引为x,则它的父节点的下标为(x-1)/2,它的左子节点的下标为2*x+1,它的右子节点的下标为2*x+2。
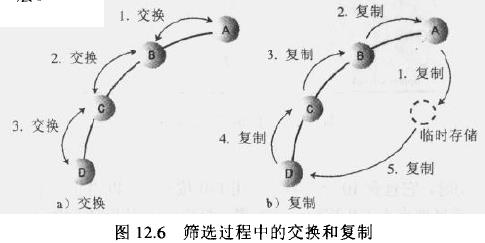
不是真的交换:上面两张图展示了向下筛选和向上筛选的过程中节点交换位置的情况。换位是在概念上理解插入和删除最简单的方法,并且实际上某些堆的实现也确实使用了换位。下图中三次换位后,节点A停在了D的位置,并且节点B、C和D都会向上移动一层。但是一次交换需要三次复制,因此在下图的三次交换中就需要九次复制,通过在筛选的算法中使用复制取代交换,可以减少所需的复制次数。例如:暂时保存节点A,然后B覆盖A,C覆盖B,D覆盖C,最后,再从临时存储中取出A复制到以前D的位置上,这样就把复制的次数从九次较少到了五次。
节点类:

package heap;
public class Node {
//关键字
private int keyword;
Node(int keyword){
this.keyword = keyword;
}
/**
* @return the keyword
*/
public int getKeyword() {
return keyword;
}
/**
* @param keyword the keyword to set
*/
public void setKeyword(int keyword) {
this.keyword = keyword;
}
}
堆类:

package heap;
//堆,数组实现
public class Heap {
//数组
private Node[] nodeArray;
private int maxSize;
private int currentSize;
//构造函数
Heap(int maxSize){
this.nodeArray = new Node[maxSize];
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.currentSize = 0;
}
//插入
public boolean insert(int keyword){
if(currentSize == maxSize)
return false;
Node newNode = new Node(keyword);
nodeArray[currentSize] = newNode;
//向上
trickleUp(currentSize++);
return true;
}
//移除
public Node remove(){
if(currentSize == 0)
return null;
Node returnNode = nodeArray[0];
nodeArray[0] = nodeArray[--currentSize];
//向下
trickleDown(0);
return returnNode;
}
//向上筛选
public void trickleUp(int current){
Node tempNode = this.nodeArray[current];
//父节点下标
int parent = (current-1)/2;
while(current>0 && nodeArray[parent].getKeyword()<tempNode.getKeyword() ){
nodeArray[current] = nodeArray[parent];
current = parent;
parent = (parent-1)/2;
}
nodeArray[current] = tempNode;
}
//向下筛选
public void trickleDown(int current){
int largeChild;
Node tempNode = nodeArray[current];
//左子节点下标
int leftIndex = 2*current+1;
//右子节点下标
int rightIndex = 2*current+2;
while(leftIndex < currentSize){
if(rightIndex < currentSize && nodeArray[leftIndex].getKeyword() < nodeArray[rightIndex].getKeyword()){
largeChild = rightIndex;
}else{
largeChild = leftIndex;
}
if(tempNode.getKeyword() <= nodeArray[largeChild].getKeyword()){
nodeArray[current] = nodeArray[largeChild];
current = largeChild;
leftIndex = 2*current+1;
rightIndex = 2*current+2;
}else{
break;
}
}
nodeArray[current] = tempNode;
}
//遍历
public void show(){
for(int i = 0;i<currentSize;i++)
System.out.print(nodeArray[i].getKeyword()+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
优先级队列类:

package heap;
public class PriorityQueue {
private Heap heap;
//构造函数
PriorityQueue(int maxSize){
this.heap = new Heap(maxSize);
}
public boolean insert(int keyword){
return this.heap.insert(keyword);
}
public Node remove(){
return this.heap.remove();
}
public void show(){
this.heap.show();
}
}
测试类:
package heap;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue(10);
pq.insert(2);
pq.insert(9);
pq.insert(3);
pq.insert(7);
pq.insert(8);
pq.insert(1);
pq.show();
pq.remove();
pq.show();
}
}
结果:

上面的代码没有改变队列优先级的方法,一个简单的实现方法是下面这种,这里提供了下标作为参数,但是难点在于如何查找更改优先级的节点,在实际的应用中,需要另外有查找适当节点的机制,因为在堆中通常易于访问的节点只有关键字最大的那个节点。
//更改关键字(优先级)
public boolean change(int index,int newValue){
if(index < 0|| index >= currentSize){
return false;
}
int oldValue = nodeArray[index].getKeyword();
nodeArray[index].setKeyword(newValue);
if(oldValue > newValue){
trickleDown(index);
}else if(oldValue < newValue){
trickleUp(index);
}
return true;
}
堆排序:堆数据结构的效率使它引出了一种出奇简单但却很有效率的排序算法,基本思想是在堆中初入全部无序的数据项,然后重复用remove()方法,就可以按序移除所有的数据项。
package heap;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue(10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
pq.insert((int)(Math.random()*100));
pq.show();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.print(pq.remove().getKeyword()+" ");
}
}
结果:

效率:因为insert()和remove()方法操作的时间复杂度都是O(logN),并且每个方法必须都要执行N次,所以整个排序操作需要O(N*logN)时间。
下面介绍如何将普通的数组转化为堆数组。
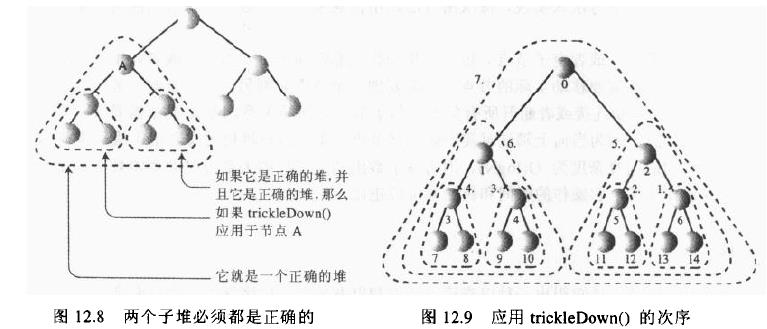
由两个正确的子堆形成一个正确的堆:如果有一个不遵守堆有序条件的项占据了根的位置,而它的两个子堆却都是正确的堆,对根进行trickleDown()方法也能狗创建一个正确的堆。这就产生了一种把无序数组变成堆数组的方法:从数组末端的节点开始,然后上行直到(下标为0的)根的各个节点都应用此方法。在每一步应用方法时,该节点下面的子堆都是正确的堆,就这样,在对根应用了trickleDown()方法后,无序的数组转化成了堆。不过,需要注意的是,对于叶子结点来说,已经是正确的堆了。所以可以从N/2-1开始,而不是从N-1开始。例如,右下图中15个节点,从节点6开始筛选。
代码:
package heap;
//堆,数组实现
public class ArrayIntoHeap {
//数组
private Node[] nodeArray;
private int maxSize;
private int currentSize;
//构造函数
ArrayIntoHeap(int maxSize){
this.nodeArray = new Node[maxSize];
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.currentSize = 0;
}
public void insertIntoArray(int value){
if(currentSize < maxSize)
this.nodeArray[currentSize++] = new Node(value);
}
//移除
public Node remove(){
if(currentSize == 0)
return null;
Node returnNode = nodeArray[0];
nodeArray[0] = nodeArray[--currentSize];
//向下
trickleDown(0);
return returnNode;
}
public void sort(){
for(int i=currentSize/2-1;i>=0;i--){
trickleDown(i);
}
}
//向下筛选
public void trickleDown(int current){
int largeChild;
Node tempNode = nodeArray[current];
//左子节点下标
int leftIndex = 2*current+1;
//右子节点下标
int rightIndex = 2*current+2;
while(leftIndex < currentSize){
if(rightIndex < currentSize && nodeArray[leftIndex].getKeyword() < nodeArray[rightIndex].getKeyword()){
largeChild = rightIndex;
}else{
largeChild = leftIndex;
}
if(tempNode.getKeyword() <= nodeArray[largeChild].getKeyword()){
nodeArray[current] = nodeArray[largeChild];
current = largeChild;
leftIndex = 2*current+1;
rightIndex = 2*current+2;
}else{
break;
}
}
nodeArray[current] = tempNode;
}
//遍历
public void show(){
for(int i = 0;i<currentSize;i++)
System.out.print(nodeArray[i].getKeyword()+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
测试类:
package heap;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
ArrayIntoHeap heap = new ArrayIntoHeap(10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
heap.insertIntoArray((int)(Math.random()*100));
System.out.print("无序数组:");
heap.show();
heap.sort();
System.out.print("堆数组:");
heap.show();
System.out.print("堆排序:");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.print(heap.remove().getKeyword()+" ");
}
}
结果:

以上是关于数据结构之堆的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
