Task运行过程分析1
Posted lfdanding
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Task运行过程分析1相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、Task运行过程概述
在MapReduce计算框架中,一个应用程序被划分成Map和Reduce两个计算阶段,它们分别由一个或者多个Map Task和Reduce Task组成。其中,每个Map Task处理输入数据集合中的一片数据(InputSplit),并将产生的若干个数据片段写到本地磁盘上,而Reduce Task则从每个Map Task上远程拷贝相应的数据片段,经分组聚集和归约后,将结果写到HDFS上作为最终结果,如下图所示:
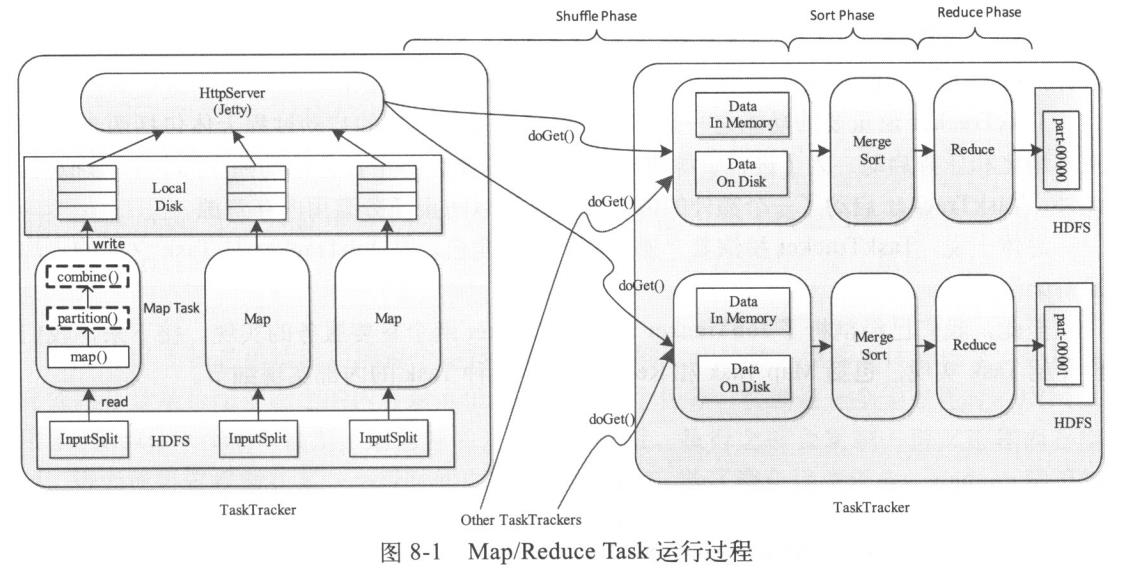
总体上看,Map Task与Reduce Task之间的数据传输采用了pull模型。为了能够容错,Map Task将中间计算结果存放到本地磁盘上,而Reduce Task则通过Http请求从各个Map Task端拖取(pull)相应的输入数据。为了更好地支持大量Reduce Task并发从Map Task端拷贝数据,Hadoop采用了Jetty Server作为HTTP Server处理并发数据读请求。
对于Map Task而言,它的执行过程可概述为:首先,通过用户提供的InputFormat将对应的InputSplit解析成一系列key/value,并依次交给用户编写的map()函数处理;接着按照指定的Partitioner对数据分片,以确定每个key/value将交给哪个Reduce Task处理;之后将数据交给用户定义的Combiner进行一次本地规约(用户没有定义则直接跳过);最后将处理结果保存到本地磁盘上。
对于Reduce Task而言,由于它的输入数据来自各个Map Task,因此首先需要通过HTTP请求从各个已经运行完成的Map Task上拷贝对应的数据分片,待所有数据拷贝完成后,再以key为关键字对所有数据进行排序,通过排序,key 相同的记录聚集到一起形成若干分组,然后将每组数据交给用户编写的reduce()函数处理,并将数据结果直接写到HDFS上作为最终输出结果。
这里插一句,当我在想这个流程的时候,有几个问题一直困扰着我。。。
Map Task如何启动的?
Map Task的输入从哪里来?
Reduce Task如何知道自己处理哪些数据?
自己查阅了相关资料,也有一些自己的理解,如果不正确,希望指出来。。。
1、首先Map Task如何启动
实际上,TaskTracker初始化时,会初始化并启动两个TaskLauncher类型的线程,mapLauncher,reduceLauncher。在TaskTracker从JobTracher获取到任务后,对应的会把任务添加到两个TaskLauncher的Queue中。
在org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java中的initialize()函数中初始化并启动这两个线程
mapLauncher = new TaskLauncher(TaskType.MAP, maxMapSlots);
reduceLauncher = new TaskLauncher(TaskType.REDUCE, maxReduceSlots);
mapLauncher.start();
reduceLauncher.start();TaskLauncher是一个线程,一直检查tasksToLaunch列表中是否有任务,有的情况下取出执行。
TaskLauncher是org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java的一个内部类。。。
class TaskLauncher extends Thread {
private IntWritable numFreeSlots;
private final int maxSlots;
private List<TaskInProgress> tasksToLaunch;
public TaskLauncher(TaskType taskType, int numSlots) {
this.maxSlots = numSlots;
this.numFreeSlots = new IntWritable(numSlots);
this.tasksToLaunch = new LinkedList<TaskInProgress>();
setDaemon(true);
setName("TaskLauncher for " + taskType + " tasks");
}
public void addToTaskQueue(LaunchTaskAction action) {
synchronized (tasksToLaunch) {
TaskInProgress tip = registerTask(action, this);
tasksToLaunch.add(tip);
tasksToLaunch.notifyAll();
}
}
public void cleanTaskQueue() {
tasksToLaunch.clear();
}
public void addFreeSlots(int numSlots) {
synchronized (numFreeSlots) {
numFreeSlots.set(numFreeSlots.get() + numSlots);
assert (numFreeSlots.get() <= maxSlots);
LOG.info("addFreeSlot : current free slots : " + numFreeSlots.get());
numFreeSlots.notifyAll();
}
}
void notifySlots() {
synchronized (numFreeSlots) {
numFreeSlots.notifyAll();
}
}
int getNumWaitingTasksToLaunch() {
synchronized (tasksToLaunch) {
return tasksToLaunch.size();
}
}
public void run() {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
try {
TaskInProgress tip;
Task task;
synchronized (tasksToLaunch) {
while (tasksToLaunch.isEmpty()) {
tasksToLaunch.wait();
}
//get the TIP
tip = tasksToLaunch.remove(0);
task = tip.getTask();
LOG.info("Trying to launch : " + tip.getTask().getTaskID() +
" which needs " + task.getNumSlotsRequired() + " slots");
}
//wait for free slots to run
synchronized (numFreeSlots) {
boolean canLaunch = true;
while (numFreeSlots.get() < task.getNumSlotsRequired()) {
//Make sure that there is no kill task action for this task!
//We are not locking tip here, because it would reverse the
//locking order!
//Also, Lock for the tip is not required here! because :
// 1. runState of TaskStatus is volatile
// 2. Any notification is not missed because notification is
// synchronized on numFreeSlots. So, while we are doing the check,
// if the tip is half way through the kill(), we don't miss
// notification for the following wait().
if (!tip.canBeLaunched()) {
//got killed externally while still in the launcher queue
LOG.info("Not blocking slots for " + task.getTaskID()
+ " as it got killed externally. Task's state is "
+ tip.getRunState());
canLaunch = false;
break;
}
LOG.info("TaskLauncher : Waiting for " + task.getNumSlotsRequired() +
" to launch " + task.getTaskID() + ", currently we have " +
numFreeSlots.get() + " free slots");
numFreeSlots.wait();
}
if (!canLaunch) {
continue;
}
LOG.info("In TaskLauncher, current free slots : " + numFreeSlots.get()+
" and trying to launch "+tip.getTask().getTaskID() +
" which needs " + task.getNumSlotsRequired() + " slots");
numFreeSlots.set(numFreeSlots.get() - task.getNumSlotsRequired());
assert (numFreeSlots.get() >= 0);
}
synchronized (tip) {
//to make sure that there is no kill task action for this
if (!tip.canBeLaunched()) {
//got killed externally while still in the launcher queue
LOG.info("Not launching task " + task.getTaskID() + " as it got"
+ " killed externally. Task's state is " + tip.getRunState());
addFreeSlots(task.getNumSlotsRequired());
continue;
}
tip.slotTaken = true;
}
//got a free slot. launch the task
startNewTask(tip);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return; // ALL DONE
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOG.error("TaskLauncher error " +
StringUtils.stringifyException(th));
}
}
}
}调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java中的startNewTask方法
/**
* Start a new task.
* All exceptions are handled locally, so that we don't mess up the
* task tracker.
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
void startNewTask(final TaskInProgress tip) throws InterruptedException {
Thread launchThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
RunningJob rjob = localizeJob(tip);
tip.getTask().setJobFile(rjob.getLocalizedJobConf().toString());
// Localization is done. Neither rjob.jobConf nor rjob.ugi can be null
launchTaskForJob(tip, new JobConf(rjob.getJobConf()), rjob);
} catch (Throwable e) {
String msg = ("Error initializing " + tip.getTask().getTaskID() +
":\\n" + StringUtils.stringifyException(e));
LOG.warn(msg);
tip.reportDiagnosticInfo(msg);
try {
tip.kill(true);
tip.cleanup(false, true);
} catch (IOException ie2) {
LOG.info("Error cleaning up " + tip.getTask().getTaskID(), ie2);
} catch (InterruptedException ie2) {
LOG.info("Error cleaning up " + tip.getTask().getTaskID(), ie2);
}
if (e instanceof Error) {
LOG.error("TaskLauncher error " +
StringUtils.stringifyException(e));
}
}
}
});
launchThread.start();
}由于用户应用程序相关文件(比如jar包,字典文件等)可能很大,这使得任务花费较长时间从HDFS上下载这些数据,如果TaskTracker串行启动各个任务,势必会延长任务的启动时间。为了解决该问题,TaskTracker采用多线程启动任务,即为每个任务单独启动一个线程,简化代码如下:
void startNewTask(final TaskInProgress tip){
Thread launchThread = new Thread(new Runnable()){
public void run(){
...
RunningJob rjob = localizeJob(tip) ;//作业本地化
tip.getTask().setJobFile(rjob.getLocalizedJobConf().toString());
// Localization is done. Neither rjob.jobConf nor rjob.ugi can be null
launchTaskForJob(tip, new JobConf(rjob.getJobConf()), rjob);
...
}
}
}调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java中的localizeJob方法,初始化job目录
// intialize the job directory
RunningJob localizeJob(TaskInProgress tip)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Task t = tip.getTask();
JobID jobId = t.getJobID();
RunningJob rjob = addTaskToJob(jobId, tip);
InetSocketAddress ttAddr = getTaskTrackerReportAddress();
try {
synchronized (rjob) {
if (!rjob.localized) {
while (rjob.localizing) {
rjob.wait();
}
if (!rjob.localized) {
//this thread is localizing the job
rjob.localizing = true;
}
}
}
if (!rjob.localized) {
Path localJobConfPath = initializeJob(t, rjob, ttAddr);
JobConf localJobConf = new JobConf(localJobConfPath);
//to be doubly sure, overwrite the user in the config with the one the TT
//thinks it is
localJobConf.setUser(t.getUser());
//also reset the #tasks per jvm
resetNumTasksPerJvm(localJobConf);
//set the base jobconf path in rjob; all tasks will use
//this as the base path when they run
synchronized (rjob) {
rjob.localizedJobConf = localJobConfPath;
rjob.jobConf = localJobConf;
rjob.keepJobFiles = ((localJobConf.getKeepTaskFilesPattern() != null) ||
localJobConf.getKeepFailedTaskFiles());
rjob.localized = true;
}
}
} finally {
synchronized (rjob) {
if (rjob.localizing) {
rjob.localizing = false;
rjob.notifyAll();
}
}
}
synchronized (runningJobs) {
runningJobs.notify(); //notify the fetcher thread
}
return rjob;
}为了防止同一个作业的多个任务同时进行作业本地化,TaskTracker需要对相关数据结构加锁。一种常见的加锁方法是:
RunningJob rjob ;
...//对rjob赋值
synchronized(job){//获取rjob锁
initializeJob(rjob) ;//作业本地化。如果作业文件很大,则该函数运行时间很长,这导致rjob锁长时间不释放
}在以上实现方案中,作业本地化过程会一直占用rjob锁,这导致很多其他需要该锁的线程或者函数不得不等待。
为了避免作业本地化过程中长时间占用rjob锁,TaskTracker为每个正在运行的作业维护了两个
变量:localizing和localized,分别表示正在进行作业本地化和已经完成作业本地化。通过对这两个变量的控制可避免作业本地化时对RunningJob对象加锁,且能够保证只有作业的第一个任务进行作业本地化:
synchronized (rjob) {
if (!rjob.localized) { //该作业尚未完成本地化工作
while (rjob.localizing) {//另为一个任务正在进行作业本地化
rjob.wait();
}
if (!rjob.localized) {//没有任务进行作业本地化
//this thread is localizing the job
rjob.localizing = true;//让当前任务对该作业进行本地化
}
}
}
if (!rjob.localized) {//运行到此,说明当前没有任务进行作业本地化
initializeJob(rjob); //进行作业本地化工作
}org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java中的startNewTask方法调用了org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java中的launchTaskForJob方法
protected void launchTaskForJob(TaskInProgress tip, JobConf jobConf,
RunningJob rjob) throws IOException {
synchronized (tip) {
jobConf.set(JobConf.MAPRED_LOCAL_DIR_PROPERTY,
localStorage.getDirsString());
tip.setJobConf(jobConf);
tip.setUGI(rjob.ugi);
tip.launchTask(rjob);
}
}调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskTracker.java的launchTask方法
/**
* Kick off the task execution
*/
public synchronized void launchTask(RunningJob rjob) throws IOException {
if (this.taskStatus.getRunState() == TaskStatus.State.UNASSIGNED ||
this.taskStatus.getRunState() == TaskStatus.State.FAILED_UNCLEAN ||
this.taskStatus.getRunState() == TaskStatus.State.KILLED_UNCLEAN) {
localizeTask(task);
if (this.taskStatus.getRunState() == TaskStatus.State.UNASSIGNED) {
this.taskStatus.setRunState(TaskStatus.State.RUNNING);
}
setTaskRunner(task.createRunner(TaskTracker.this, this, rjob));
this.runner.start();
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.taskStatus.setStartTime(now);
this.lastProgressReport = now;
} else {
LOG.info("Not launching task: " + task.getTaskID() +
" since it's state is " + this.taskStatus.getRunState());
}
}调用了org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Task.java中的CreateRunner方法。Task是个抽象类,两个子类分别是MapTask和ReduceTask。先关注Map的CreateRunner方法。
在org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask.java中的CreateRunner方法
@Override
public TaskRunner createRunner(TaskTracker tracker,
TaskTracker.TaskInProgress tip,
TaskTracker.RunningJob rjob
) throws IOException {
return new MapTaskRunner(tip, tracker, this.conf, rjob);
}然后会启动MapTaskRunner所继承的run方法
@Override
public final void run() {
String errorInfo = "Child Error";
try {
//before preparing the job localize
//all the archives
TaskAttemptID taskid = t.getTaskID();
final LocalDirAllocator lDirAlloc = new LocalDirAllocator("mapred.local.dir");
//simply get the location of the workDir and pass it to the child. The
//child will do the actual dir creation
final File workDir =
new File(new Path(localdirs[rand.nextInt(localdirs.length)],
TaskTracker.getTaskWorkDir(t.getUser(), taskid.getJobID().toString(),
taskid.toString(),
t.isTaskCleanupTask())).toString());
String user = tip.getUGI().getUserName();
// Set up the child task's configuration. After this call, no localization
// of files should happen in the TaskTracker's process space. Any changes to
// the conf object after this will NOT be reflected to the child.
// setupChildTaskConfiguration(lDirAlloc);
if (!prepare()) {
return;
}
// Accumulates class paths for child.
List<String> classPaths = getClassPaths(conf, workDir,
taskDistributedCacheManager);
long logSize = TaskLog.getTaskLogLength(conf);
// Build exec child JVM args.
Vector<String> vargs = getVMArgs(taskid, workDir, classPaths, logSize);
tracker.addToMemoryManager(t.getTaskID(), t.isMapTask(), conf);
// set memory limit using ulimit if feasible and necessary ...
String setup = getVMSetupCmd();
// Set up the redirection of the task's stdout and stderr streams
File[] logFiles = prepareLogFiles(taskid, t.isTaskCleanupTask());
File stdout = logFiles[0];
File stderr = logFiles[1];
tracker.getTaskTrackerInstrumentation().reportTaskLaunch(taskid, stdout,
stderr);
Map<String, String> env = new HashMap<String, String>();
errorInfo = getVMEnvironment(errorInfo, user, workDir, conf, env, taskid,
logSize);
// flatten the env as a set of export commands
List <String> setupCmds = new ArrayList<String>();
for(Entry<String, String> entry : env.entrySet()) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("export ");
sb.append(entry.getKey());
sb.append("=\\"");
sb.append(entry.getValue());
sb.append("\\"");
setupCmds.add(sb.toString());
}
setupCmds.add(setup);
launchJvmAndWait(setupCmds, vargs, stdout, stderr, logSize, workDir);
tracker.getTaskTrackerInstrumentation().reportTaskEnd(t.getTaskID());
if (exitCodeSet) {
if (!killed && exitCode != 0) {
if (exitCode == 65) {
tracker.getTaskTrackerInstrumentation().taskFailedPing(t.getTaskID());
}
throw new IOException("Task process exit with nonzero status of " +
exitCode + ".");
}
}
} catch (FSError e) {
LOG.fatal("FSError", e);
try {
tracker.fsErrorInternal(t.getTaskID(), e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException ie) {
LOG.fatal(t.getTaskID()+" reporting FSError", ie);
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
LOG.warn(t.getTaskID() + " : " + errorInfo, throwable);
Throwable causeThrowable = new Throwable(errorInfo, throwable);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
causeThrowable.printStackTrace(new PrintStream(baos));
try {
tracker.reportDiagnosticInfoInternal(t.getTaskID(), baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn(t.getTaskID()+" Reporting Diagnostics", e);
}
} finally {
// It is safe to call TaskTracker.TaskInProgress.reportTaskFinished with
// *false* since the task has either
// a) SUCCEEDED - which means commit has been done
// b) FAILED - which means we do not need to commit
tip.reportTaskFinished(false);
}
}然后会调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskRunner.java继承下来的
void launchJvmAndWait(List <String> setup, Vector<String> vargs, File stdout,
File stderr, long logSize, File workDir)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
jvmManager.launchJvm(this, jvmManager.constructJvmEnv(setup, vargs, stdout,
stderr, logSize, workDir, conf));
synchronized (lock) {
while (!done) {
lock.wait();
}
}
}然后会调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JvmManager.java中的launch.Jvm方法
public boolean validateTipToJvm(TaskInProgress tip, JVMId jvmId) {
if (jvmId.isMapJVM()) {
return mapJvmManager.validateTipToJvm(tip, jvmId);
} else {
return reduceJvmManager.validateTipToJvm(tip, jvmId);
}
}然后会调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JvmManager.java中的reap.Jvm方法
private synchronized void reapJvm(
TaskRunner t, JvmEnv env) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (t.getTaskInProgress().wasKilled()) {
//the task was killed in-flight
//no need to do the rest of the operations
//如果task被杀死则直接返回
return;
}
boolean spawnNewJvm = false;
JobID jobId = t.getTask().getJobID();
//检查是否有空闲的槽,如果小于最大jvm数,则重新开启一个jvm,不让你从现有job的空闲jvm中选择一个,或者杀死另外job的空闲jvm
//Check whether there is a free slot to start a new JVM.
//,or, Kill a (idle) JVM and launch a new one
//When this method is called, we *must*
// (1) spawn a new JVM (if we are below the max)
// (2) find an idle JVM (that belongs to the same job), or,
// (3) kill an idle JVM (from a different job)
// (the order of return is in the order above)
int numJvmsSpawned = jvmIdToRunner.size();
JvmRunner runnerToKill = null;
if (numJvmsSpawned >= maxJvms) {
//go through the list of JVMs for all jobs.
Iterator<Map.Entry<JVMId, JvmRunner>> jvmIter =
jvmIdToRunner.entrySet().iterator();
while (jvmIter.hasNext()) {
JvmRunner jvmRunner = jvmIter.next().getValue();
JobID jId = jvmRunner.jvmId.getJobId();
//look for a free JVM for this job; if one exists then just break
if (jId.equals(jobId) && !jvmRunner.isBusy() && !jvmRunner.ranAll()){
setRunningTaskForJvm(jvmRunner.jvmId, t); //reserve the JVM
LOG.info("No new JVM spawned for jobId/taskid: " +
jobId+"/"+t.getTask().getTaskID() +
". Attempting to reuse: " + jvmRunner.jvmId);
return;
}
//Cases when a JVM is killed:
// (1) the JVM under consideration belongs to the same job
// (passed in the argument). In this case, kill only when
// the JVM ran all the tasks it was scheduled to run (in terms
// of count).
// (2) the JVM under consideration belongs to a different job and is
// currently not busy
//But in both the above cases, we see if we can assign the current
//task to an idle JVM (hence we continue the loop even on a match)
if ((jId.equals(jobId) && jvmRunner.ranAll()) ||
(!jId.equals(jobId) && !jvmRunner.isBusy())) {
runnerToKill = jvmRunner;
spawnNewJvm = true;
}
}
} else {
spawnNewJvm = true;
}
if (spawnNewJvm) {
if (runnerToKill != null) {
LOG.info("Killing JVM: " + runnerToKill.jvmId);
killJvmRunner(runnerToKill);
}
spawnNewJvm(jobId, env, t);
return;
}
//*MUST* never reach this
try {
LOG.fatal("Inconsistent state!!! " +
"JVM Manager reached an unstable state " +
"while reaping a JVM for task: " + t.getTask().getTaskID()+
" " + getDetails() + ". Aborting. ");
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.fatal(e);
} finally {
System.exit(-1);
}
}
然后调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JvmManager.java的spawnNewJvm方法
private void spawnNewJvm(JobID jobId, JvmEnv env,
TaskRunner t) {
JvmRunner jvmRunner = new JvmRunner(env, jobId, t.getTask());
jvmIdToRunner.put(jvmRunner.jvmId, jvmRunner);
//spawn the JVM in a new thread. Note that there will be very little
//extra overhead of launching the new thread for a new JVM since
//most of the cost is involved in launching the process. Moreover,
//since we are going to be using the JVM for running many tasks,
//the thread launch cost becomes trivial when amortized over all
//tasks. Doing it this way also keeps code simple.
jvmRunner.setDaemon(true);
jvmRunner.setName("JVM Runner " + jvmRunner.jvmId + " spawned.");
setRunningTaskForJvm(jvmRunner.jvmId, t);
LOG.info(jvmRunner.getName());
jvmRunner.start();
}然后调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JvmManager.java的内部JvmRunner线程的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runChild(env);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
return;
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Caught IOException in JVMRunner", e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.error("Caught Throwable in JVMRunner. Aborting TaskTracker.", e);
System.exit(1);
} finally {
jvmFinished();
}
}然后调用org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JvmManager.java的runChild方法
public void runChild(JvmEnv env) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
int exitCode = 0;
try {
env.vargs.add(Integer.toString(jvmId.getId()));
TaskRunner runner = jvmToRunningTask.get(jvmId);
if (runner != null) {
Task task = runner.getTask();
//Launch the task controller to run task JVM
String user = task.getUser();
TaskAttemptID taskAttemptId = task.getTaskID();
String taskAttemptIdStr = task.isTaskCleanupTask() ?
(taskAttemptId.toString() + TaskTracker.TASK_CLEANUP_SUFFIX) :
taskAttemptId.toString();
exitCode = tracker.getTaskController().launchTask(user,
jvmId.jobId.toString(), taskAttemptIdStr, env.setup,
env.vargs, env.workDir, env.stdout.toString(),
env.stderr.toString());
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// do nothing
// error and output are appropriately redirected
} finally { // handle the exit code
// although the process has exited before we get here,
// make sure the entire process group has also been killed.
kill();
updateOnJvmExit(jvmId, exitCode);
LOG.info("JVM : " + jvmId + " exited with exit code " + exitCode
+ ". Number of tasks it ran: " + numTasksRan);
deleteWorkDir(tracker, firstTask);
}
}然后调用了org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TaskController.java中的launchTask方法
TaskController是一个抽象类,org.apache.hadoop.mapred.DefaultTaskController.java是它的一个实现类
/**
* Create all of the directories for the task and launches the child jvm.
* @param user the user name
* @param attemptId the attempt id
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public int launchTask(String user,
String jobId,
String attemptId,
List<String> setup,
List<String> jvmArguments,
File currentWorkDirectory,
String stdout,
String stderr) throws IOException {
ShellCommandExecutor shExec = null;
try {
FileSystem localFs = FileSystem.getLocal(getConf());
//create the attempt dirs
new Localizer(localFs,
getConf().getStrings(JobConf.MAPRED_LOCAL_DIR_PROPERTY)).
initializeAttemptDirs(user, jobId, attemptId);
// create the working-directory of the task
if (!currentWorkDirectory.mkdir()) {
throw new IOException("Mkdirs failed to create "
+ currentWorkDirectory.toString());
}
//mkdir the loglocation
String logLocation = TaskLog.getAttemptDir(jobId, attemptId).toString();
if (!localFs.mkdirs(new Path(logLocation))) {
throw new IOException("Mkdirs failed to create "
+ logLocation);
}
//read the configuration for the job
FileSystem rawFs = FileSystem.getLocal(getConf()).getRaw();
long logSize = 0; //TODO MAPREDUCE-1100
// get the JVM command line.
String cmdLine =
TaskLog.buildCommandLine(setup, jvmArguments,
new File(stdout), new File(stderr), logSize, true);
// write the command to a file in the
// task specific cache directory
// TODO copy to user dir
Path p = new Path(allocator.getLocalPathForWrite(
TaskTracker.getPrivateDirTaskScriptLocation(user, jobId, attemptId),
getConf()), COMMAND_FILE);
String commandFile = writeCommand(cmdLine, rawFs, p);
rawFs.setPermission(p, TaskController.TASK_LAUNCH_SCRIPT_PERMISSION);
/*
* MAPREDUCE-2374: if another thread fork(2)ed a child process during the
* window when writeCommand (above) had taskjvm.sh open for write, that
* child process might still have a writeable fd open to the script.
*
* If we run the script with "bash -c /path/to/taskjvm.sh", then bash
* would try to execve(2) the script and get ETXTBSY. Instead, just have
* bash interpret the script with "bash /path/to/taskjvm.sh".
*/
shExec = new ShellCommandExecutor(new String[]{
"bash", commandFile},
currentWorkDirectory);
shExec.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (shExec == null) {
return -1;
}
int exitCode = shExec.getExitCode();
LOG.warn("Exit code from task is : " + exitCode);
LOG.info("Output from DefaultTaskController's launchTask follows:");
logOutput(shExec.getOutput());
return exitCode;
}
return 0;
}在launchTask中,会将任务启动命令写到shell脚本taskjvm.sh中,并运行该脚本。
脚本会运行org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Child类运行任务。
这篇文章实在是太长了,接下来后续更新。。。
以上是关于Task运行过程分析1的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章