运动跟踪之CMT算法
Posted eternity1118_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了运动跟踪之CMT算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
CMT(Clustering of Static-Adaptive Correspondences for Deformable Object Tracking),是一套比较新的跟踪算法,诞生于2014年,原名叫Consensus-based Tracking and Matching of Keypoints for Object Tracking ,当时在计算机视觉应用(Application of Computer Vision)的冬季会议上获得了最佳论文奖,随后于2015年发表在了CVPR上:论文地址。
CMT是一个非常好用且效果超好的跟踪算法,可以跟踪任何场景任何物体;这是一种基于特征的跟踪方法,并且使用了经典的光流法作为算法的一部分。这篇文章不打算分析CMT的代码,因为他的code很容易找到(Github),网上也有很多分析它的code的文章,这篇博客的目的打算结合原论文分析下CMT的主要思想。
--初始化
step1:(交互)选择待跟踪的物体框PR,计算矩形框中心;
step2:灰度化frame,提取fast特征点,并分离出前景和背景部分的特征点;
step3:创建前景类,即特征点的索引;
step4:将fast特征点生成BRISK特征描述子;
step5:将前景特征点进行归一化;
step6:利用归一化的前景点初始化匹配器(BruteForce-Hamming),生成前景类标签,匹配库;
step7:利用归一化的前景点初始化一致器,生成矩形框内任意点对之间的距离和角度矩阵;
step8:创建初始的有效类和有效点,即前景点的坐标和step6中生成的类标签;
--光流法获取第一部分跟踪点
step1:利用forward-backward 跟踪,提高准确度;
step2:剔除跟踪失败的点;
--全局匹配获取第二部分跟踪点
即全图像与矩形框匹配,这部分的工作对应于论文中的‘3.1 Static-Adaptive Correspondences’;其中code中的thr_dist对应于论文中的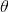 ,thr_ratio对应于论文中的
,thr_ratio对应于论文中的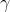 ;
;
--对两部分跟踪点进行数据融合
即找到两部分中都跟踪到的点,保留下来;
--估计尺度和旋转,进行凝聚聚类
这部分的工作对应于论文中的‘3.2 Correspondence Clustering’;
step1:估计尺度变化;
step2:估计旋转变化;
step3:利用尺度和旋转生成变换矩阵H,即论文中的变换矩阵H;
step4:寻找得到的各特征点之间的一致性,方法是让每一个点为中心投票,这部分的目的是为了使匹配更加准确;
此部分,论文是基于这样一个假设:与目标相关的点肯定都包含在最大的聚类中,于是我们的目的就是通过计算vote点之间的非相似度D(对应于论文中的D)来进行投票,最后得到最大的聚类;其中,code中使用的thr_cutoff对应于论文中的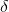 ,这个参数控制着可容忍的物体的形变程度,当其值较小时,往往会导致将所有的点都划为外点outliers,当其值较大时,往往能够识别更多的点为内点inliers,当值为0时,则表示物体为完全刚性;
,这个参数控制着可容忍的物体的形变程度,当其值较小时,往往会导致将所有的点都划为外点outliers,当其值较大时,往往能够识别更多的点为内点inliers,当值为0时,则表示物体为完全刚性;
注:聚类这部分,论文中作者是调用了一个聚类的库fastcluster来完成实现的;
--利用融合得到的点进行局部匹配;
即矩形框与矩形框匹配,这部分的工作目的是为了去歧义,即为了解决那些完全一样的点或是具有相同描述子的点匹配难的问题,它对应于论文中的‘3.3 Disambiguation of Correspondences’;
--再次进行数据融合
--更新输出的跟踪矩形框
--将该矩形框以及矩形框内的内点作为下一帧的输入,循环
可以发现,CMT的核心就在于以下几个公式:
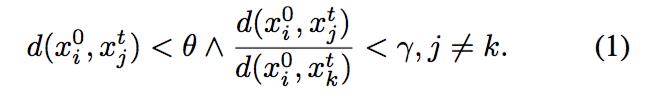
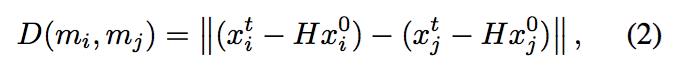
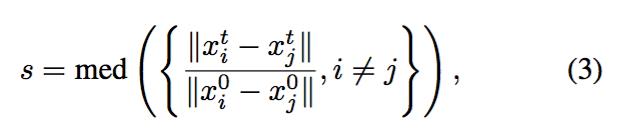
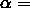
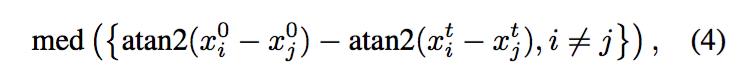
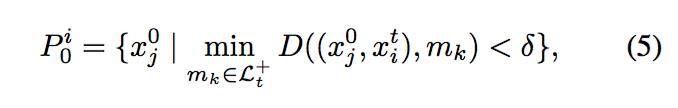
最后,为了更清晰,我将重新注释好的代码附上,应该就好理解了;
//初始化
void CMT::initialize(const Mat im_gray, const cv::Rect rect)
{
//Remember initial size 存储跟踪区域的初始大小
size_initial = rect.size();
//Remember initial image 存储初始灰度图像
im_prev = im_gray;
//Compute center of rect 计算跟踪区域的中心位置
Point2f center = Point2f(rect.x + rect.width/2.0, rect.y + rect.height/2.0);
//Initialize detector and descriptor 初始化检测器FAST和描述子提取器BRISK
detector = cv::FastFeatureDetector::create();
// descriptor = cv::DescriptorExtractor::create(str_descriptor);
descriptor = cv::BRISK::create();
//Get initial keypoints in whole image and compute their descriptors
///优化
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector->detect(im_gray, keypoints); // 检测初始全图像的所有关键点
//Divide keypoints into foreground and background keypoints according to selection 分离出前景和背景的关键点,前景即跟踪框内
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_fg;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_bg;
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); i++)
{
KeyPoint k = keypoints[i];
Point2f pt = k.pt;
if (pt.x > rect.x && pt.y > rect.y && pt.x < rect.br().x && pt.y < rect.br().y)
{
keypoints_fg.push_back(k);
}
else
{
keypoints_bg.push_back(k);
}
}
//Create foreground classes 创建前景类,就是矩形框中特征点的索引
vector<int> classes_fg;
classes_fg.reserve(keypoints_fg.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints_fg.size(); i++)
{
classes_fg.push_back((int)i);
}
//Compute foreground/background features 计算前景和背景的特征描述子
Mat descs_fg;
Mat descs_bg;
descriptor->compute(im_gray, keypoints_fg, descs_fg);
descriptor->compute(im_gray, keypoints_bg, descs_bg);
//Only now is the right time to convert keypoints to points, as compute() might remove some keypoints 将关键点转换为点存储
vector<Point2f> points_fg;
vector<Point2f> points_bg;
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints_fg.size(); i++)
{
points_fg.push_back(keypoints_fg[i].pt);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints_bg.size(); i++)
{
points_bg.push_back(keypoints_bg[i].pt);
}
//Create normalized points 创建归一化的点,即计算前景的关键点到前景矩形框中心的相对位置作为归一化的点的坐标
vector<Point2f> points_normalized;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_fg.size(); i++)
{
points_normalized.push_back(points_fg[i] - center);
}
//Initialize matcher 初始化匹配器,生成类标签,匹配库
matcher.initialize(points_normalized, descs_fg, classes_fg, descs_bg, center);
//Initialize consensus 初始化一致器,生成矩形框内任意点对之间的距离和角度
consensus.initialize(points_normalized);
//Create initial set of active keypoints 创建初始的有效点和有效类,即前景关键点的坐标
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints_fg.size(); i++)
{
points_active.push_back(keypoints_fg[i].pt);
classes_active = classes_fg;
}
}
//帧处理
void CMT::processFrame(cv::Mat im_gray)
{
//Track keypoints
vector<Point2f> points_tracked;
vector<unsigned char> status;
//第一部分特征点
// 利用光流法得到部分跟踪点。
tracker.track(im_prev, im_gray, points_active, points_tracked, status);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_tracked.size() << " tracked points.";
//keep only successful classes剔除跟踪失败的点
vector<int> classes_tracked;
for (size_t i = 0; i < classes_active.size(); i++)
{
if (status[i])
{
classes_tracked.push_back(classes_active[i]);
}
}
//第二部分特征点
//Detect keypoints, compute descriptors 计算当前图像的关键点
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector->detect(im_gray, keypoints);
// 计算当前图像特征点的描述
Mat descriptors;
descriptor->compute(im_gray, keypoints, descriptors);
//Match keypoints globally 利用数据库全局匹配特征点,计算出匹配好的的特征点和类
//**********全局匹配(3.1 Static-Adaptive Correspondences)*****************
vector<Point2f> points_matched_global;
vector<int> classes_matched_global;
matcher.matchGlobal(keypoints, descriptors, points_matched_global, classes_matched_global);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_matched_global.size() << " points matched globally.";
//Fuse tracked and globally matched points
//融合跟踪和全局匹配的点
//*********************第一次数据融合***********************************
vector<Point2f> points_fused;
vector<int> classes_fused;
fusion.preferFirst(points_tracked, classes_tracked, points_matched_global, classes_matched_global,
points_fused, classes_fused);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_fused.size() << " points fused.";
// 估计旋转和尺度 ,
//*****************聚类 (3.2 Correspondence Clustering)*************************
//Estimate scale and rotation from the fused points
//这里的scale和rotation就是论文中的变换矩阵H
float scale;
float rotation;
consensus.estimateScaleRotation(points_fused, classes_fused, scale, rotation);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << "scale " << scale << ", " << "rotation " << rotation;
//Find inliers and the center of their votes
//计算一致性,获取inliers和中心
Point2f center;
vector<Point2f> points_inlier;
vector<int> classes_inlier;
consensus.findConsensus(points_fused, classes_fused, scale, rotation,
center, points_inlier, classes_inlier);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_inlier.size() << " inlier points.";
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << "center " << center;
//Match keypoints locally 局部匹配
//*************************去歧义 (3.3 Disambiguation of Correspondences)*********************
vector<Point2f> points_matched_local;
vector<int> classes_matched_local;
matcher.matchLocal(keypoints, descriptors, center, scale, rotation, points_matched_local, classes_matched_local);
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_matched_local.size() << " points matched locally.";
//Clear active points
points_active.clear();
classes_active.clear();
//Fuse locally matched points and inliers
// 融合局部匹配的点和inliers
//*********************第二次数据融合***********************************
fusion.preferFirst(points_matched_local, classes_matched_local, points_inlier, classes_inlier, points_active, classes_active);
// points_active = points_fused;
// classes_active = classes_fused;
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << points_active.size() << " final fused points.";
//TODO: Use theta to suppress result
// 计算出新的跟踪窗口
//更新输出矩形框
bb_rot = RotatedRect(center, size_initial * scale, rotation/CV_PI * 180);
//Remember current image 更新上一帧图像
im_prev = im_gray;
//FILE_LOG(logDEBUG) << "CMT::processFrame() return";
}
以上是关于运动跟踪之CMT算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章