MFC串口调试工具教程
Posted herr_edoc
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MFC串口调试工具教程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
MFC串口调试软件教程
一、测试环境:Windows XP,VC++6.0
二、步骤
Step1:打开VC++6.0集成开发环境,新建基于对话框(Dialog based)的MFCAppWizard(exe)应用程序。其它设置默认即可。
Step2:在主对话框中添加需要的控件。如图1,在箭头所指窗口(控件)拖动空间到主对话框。这里串口调试软件只需要红框内所示的控件即可,其他可以根据需要自行添加。右键点击控件 ->选择属性可以自行设置控件显示的文本,例如图1中的“打开”按钮、“端口号”静态文本等。另外,为了增强变量的可读性,建议将每个控件的ID改成有意义的名字。例如,将发送按钮的控件ID改为“IDC_BUTTON_SEND”。
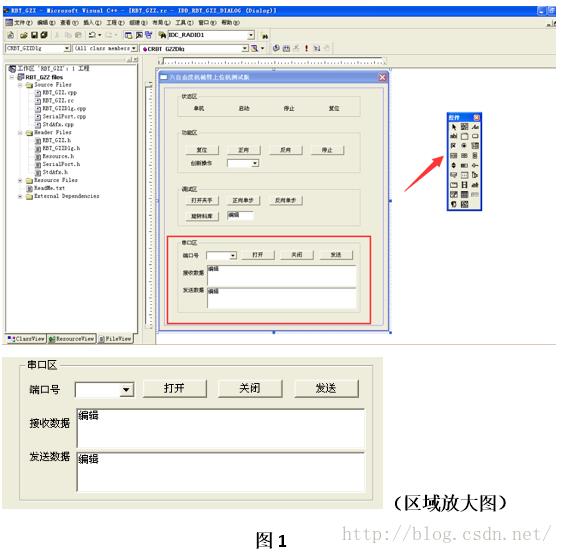
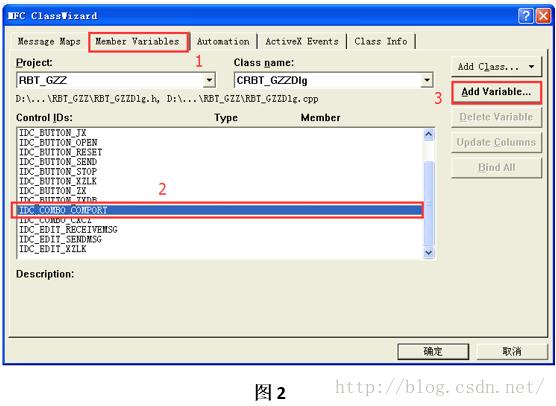
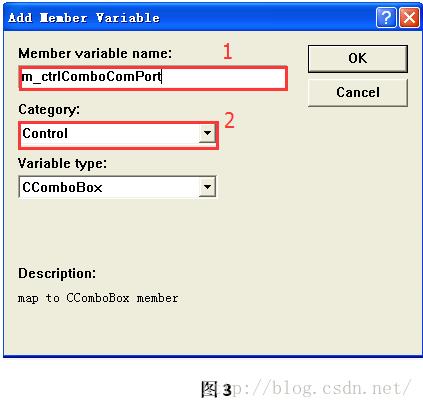
Step3:接下来需要为个别控件添加变量,以便于在程序中读取控件状态或者获得对控件的控制。例如,对“端口号”右边的组合下拉框(Combo)添加变量。右键点击组合框(Combo) ->选择建立类向导,则会出现如图2所示界面。按照图2中1->2->3步骤操作。点击确定出现图3界面。按照图3中1->2步骤操作,确定则成功添加control类型的变量m_ctrlComboComPort。
接下来,依次为接收数据和发送数据旁的编辑框添加Cstring类型的变量m_strEditReceiveMsg和m_strEditSendMsg
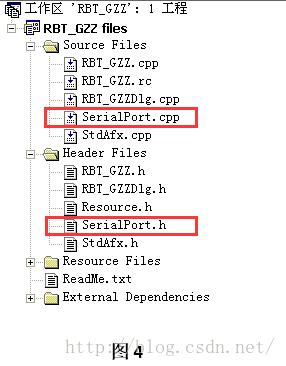
Step4:为了将CserialPort类添加到工程中,需要添加“SerialPort.h”和”SerialPort.cpp”文件。将文件添加到工程所在的文件夹中,然后,点击菜单栏上的工程 ->添加到工程 ->文件,选择这两个文件。添加结果如图4所示。
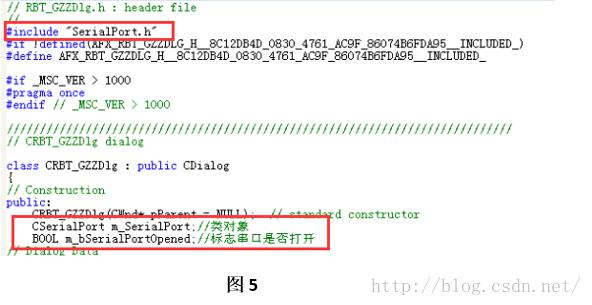
Step5:在对话框头文件(这里是“RBT_GZZDlg.h”)添加头文件声明(#include “CserialPort.h”)和类对象声明(CserialPort m_SerialPort)以及变量名声明(BOOLm_bSSerialPortOpened串口打开标志位)。如图5所示。
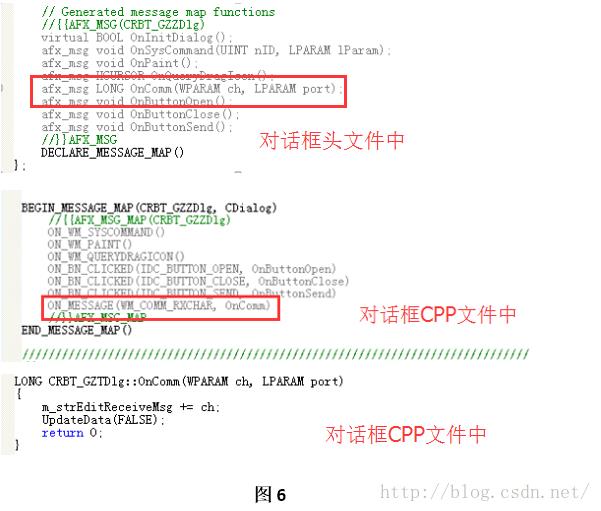
Step6:在对话框头文件(本工程是“RBT_GZZDlg.h”)添加串口字符接受消息(WM_COM_RXCHAR)的响应函数声明afx_msg LONG OnCom(WPARAM ch, LPARAM port),并在对话框CPP(本工程是“RBT_GZZDlg.cpp”)文件中进行WM_COM_RXCHAR消息映射和函数的实现代码。如图6所示。
Step7:接下来对“打开”按钮、“关闭”按钮和“发送“按钮添加响应函数。双击”打开“按钮,出现生成函数提示框,点击确定进入函数(本工程是void CRBT_GZZDlg::OnButtonOpen())。该函数主要是实现获取串口号、设置串口通信的参数功能。
类似操作添加void CRBT_GZZDlg::OnButtonClose()和voidCRBT_GZZDlg::OnButtonSend()函数。关闭函数主要就是关闭串口;发送函数先获取编辑框内的数据,然后以字符串或者十六进制格式发送数据,具体由编程决定。本工程发送十六进制,所以添加了Str2Hex函数和HexChar函数对数据进行处理。
如图7、8所示为本工程添加的函数。


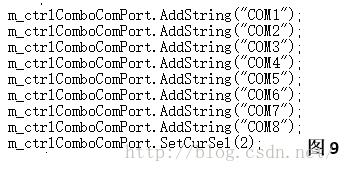
需要注意的是”打开“按钮响应函数中从组合框获取串口号(intnPort=m_ctrlComboComPort.GetCurel()+1),所以需要在对话框CPP文件中的初始化函数(BOOL CEx2Dlg::OnInitDialog())中添加如图9所示初始化函数。
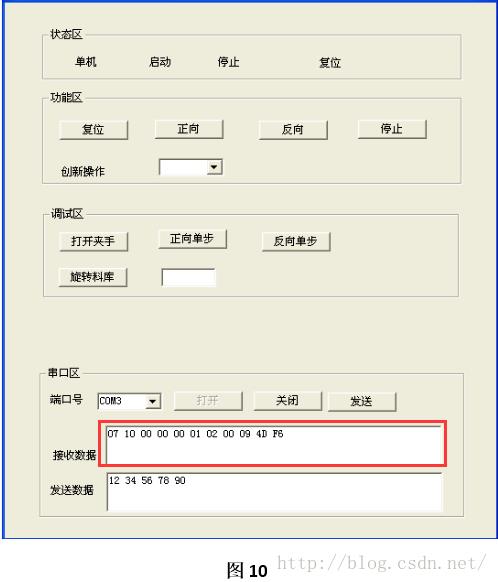
Step8:编译 -> 执行。如图10所示,开始执行后,点击”打开“按钮,串口开始接收数据。
三、常见问题
1.无法添加控件(cannot add new member)
解决方法:先把工程关闭,然后删除*.clw文件,重新打开工程,打开ClassWizard(CTRL+W可以打开),输入先前删除的文件的文件名(*.clw)。点击添加按钮(ADD),然后确定。这样便可以添加控件了。
(参考网址:http://m.2cto.com/kf/201212/173233.html)
2.编译没有问题,无法执行(Could not execute:Bad executable format(Win32 error 193))。如图11所示。
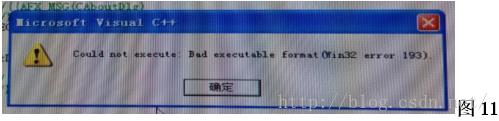
解决方法:这个是VC++经常出现的问题。Error193是操作系统错误,通常是生成的exe文件损坏或者格式错误。网上的解答最多的是”在工程设置里将Link选项设置正确就行了“,但是,这个方法并不是万能的。
我发现的一种出现这种错误的原因是向工程添加的文件的日期与系统日期不一致,通常是在”未来时“,所以可以先检查所添加的文件的日期。如果是该错误,则在工程中打开该文件,然后,修改一下重新保存即可。最后,点击Clean –> Rebuild ->执行。错误消失。
如果上述方法仍不奏效的话,则点击Clean,然后直接点击执行(即那个红色的感叹号),不要点击Build或者Rebuild。错误消失。四、相关文件(来自书本《串口通信编程实践》电子工业出版社,请勿用于商业用途)
1.”SerialPort.h”
/*
** FILENAME CSerialPort.h
**
** PURPOSE This class can read, write and watch one serial port.
** It sends messages to its owner when something happends on the port
** The class creates a thread for reading and writing so the main
** program is not blocked.
**
** CREATION DATE 15-09-1997
** LAST MODIFICATION 12-11-1997
**
** AUTHOR Remon Spekreijse
**
**
*/
#ifndef __SERIALPORT_H__
#define __SERIALPORT_H__
#define WM_COMM_BREAK_DETECTED WM_USER+1 // A break was detected on input.
#define WM_COMM_CTS_DETECTED WM_USER+2 // The CTS (clear-to-send) signal changed state.
#define WM_COMM_DSR_DETECTED WM_USER+3 // The DSR (data-set-ready) signal changed state.
#define WM_COMM_ERR_DETECTED WM_USER+4 // A line-status error occurred. Line-status errors are CE_FRAME, CE_OVERRUN, and CE_RXPARITY.
#define WM_COMM_RING_DETECTED WM_USER+5 // A ring indicator was detected.
#define WM_COMM_RLSD_DETECTED WM_USER+6 // The RLSD (receive-line-signal-detect) signal changed state.
#define WM_COMM_RXCHAR WM_USER+7 // A character was received and placed in the input buffer.
#define WM_COMM_RXFLAG_DETECTED WM_USER+8 // The event character was received and placed in the input buffer.
#define WM_COMM_TXEMPTY_DETECTED WM_USER+9 // The last character in the output buffer was sent.
class CSerialPort
{
public:
// contruction and destruction
CSerialPort();
virtual ~CSerialPort();
// port initialisation
BOOL InitPort(CWnd* pPortOwner, UINT portnr = 1, UINT baud = 19200, char parity = 'N', UINT databits = 8, UINT stopsbits = 1, DWORD dwCommEvents = EV_RXCHAR | EV_CTS, UINT nBufferSize = 512);
// start/stop comm watching
BOOL StartMonitoring();
BOOL RestartMonitoring();
BOOL StopMonitoring();
DWORD GetWriteBufferSize();
DWORD GetCommEvents();
DCB GetDCB();
int m_nWriteSize;
void WriteToPort(char* string);
void WriteToPort(char* string, int n);
void WriteToPort(LPCTSTR string);
void WriteToPort(LPCTSTR string, int n);
protected:
// protected memberfunctions
void ProcessErrorMessage(char* ErrorText);
static UINT CommThread(LPVOID pParam);
static void ReceiveChar(CSerialPort* port, COMSTAT comstat);
static void WriteChar(CSerialPort* port);
// thread
CWinThread* m_Thread;
// synchronisation objects
CRITICAL_SECTION m_csCommunicationSync;
BOOL m_bThreadAlive;
// handles
HANDLE m_hShutdownEvent;
HANDLE m_hComm;
HANDLE m_hWriteEvent;
// Event array.
// One element is used for each event. There are two event handles for each port.
// A Write event and a receive character event which is located in the overlapped structure (m_ov.hEvent).
// There is a general shutdown when the port is closed.
HANDLE m_hEventArray[3];
// structures
OVERLAPPED m_ov;
COMMTIMEOUTS m_CommTimeouts;
DCB m_dcb;
// owner window
CWnd* m_pOwner;
// misc
UINT m_nPortNr;
char* m_szWriteBuffer;
DWORD m_dwCommEvents;
DWORD m_nWriteBufferSize;
};
#endif __SERIALPORT_H__
2.”SerialPort.cpp”
/*
** FILENAME CSerialPort.cpp
**
** PURPOSE This class can read, write and watch one serial port.
** It sends messages to its owner when something happends on the port
** The class creates a thread for reading and writing so the main
** program is not blocked.
**
** CREATION DATE 15-09-1997
** LAST MODIFICATION 12-11-1997
**
** AUTHOR Remon Spekreijse
**
**
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "SerialPort.h"
#include <assert.h>
//
// Constructor
//
CSerialPort::CSerialPort()
{
m_hComm = NULL;
// initialize overlapped structure members to zero
m_ov.Offset = 0;
m_ov.OffsetHigh = 0;
// create events
m_ov.hEvent = NULL;
m_hWriteEvent = NULL;
m_hShutdownEvent = NULL;
m_szWriteBuffer = NULL;
m_bThreadAlive = FALSE;
}
//
// Delete dynamic memory
//
CSerialPort::~CSerialPort()
{
do
{
SetEvent(m_hShutdownEvent);
} while (m_bThreadAlive);
TRACE("Thread ended\\n");
delete [] m_szWriteBuffer;
}
//
// Initialize the port. This can be port 1 to 4.
//
BOOL CSerialPort::InitPort(CWnd* pPortOwner, // the owner (CWnd) of the port (receives message)
UINT portnr, // portnumber (1..4)
UINT baud, // baudrate
char parity, // parity
UINT databits, // databits
UINT stopbits, // stopbits
DWORD dwCommEvents, // EV_RXCHAR, EV_CTS etc
UINT writebuffersize) // size to the writebuffer
{
//assert(portnr > 0 && portnr < 5);
assert(pPortOwner != NULL);
// if the thread is alive: Kill
if (m_bThreadAlive)
{
do
{
SetEvent(m_hShutdownEvent);
} while (m_bThreadAlive);
TRACE("Thread ended\\n");
}
// create events
if (m_ov.hEvent != NULL)
ResetEvent(m_ov.hEvent);
m_ov.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, TRUE, FALSE, NULL);
if (m_hWriteEvent != NULL)
ResetEvent(m_hWriteEvent);
m_hWriteEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, TRUE, FALSE, NULL);
if (m_hShutdownEvent != NULL)
ResetEvent(m_hShutdownEvent);
m_hShutdownEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, TRUE, FALSE, NULL);
// initialize the event objects
m_hEventArray[0] = m_hShutdownEvent; // highest priority
m_hEventArray[1] = m_ov.hEvent;
m_hEventArray[2] = m_hWriteEvent;
// initialize critical section
InitializeCriticalSection(&m_csCommunicationSync);
// set buffersize for writing and save the owner
m_pOwner = pPortOwner;
if (m_szWriteBuffer != NULL)
delete [] m_szWriteBuffer;
m_szWriteBuffer = new char[writebuffersize];
m_nPortNr = portnr;
m_nWriteBufferSize = writebuffersize;
m_dwCommEvents = dwCommEvents;
BOOL bResult = FALSE;
char *szPort = new char[50];
char *szBaud = new char[50];
// now it critical!
EnterCriticalSection(&m_csCommunicationSync);
// if the port is already opened: close it
if (m_hComm != NULL)
{
CloseHandle(m_hComm);
m_hComm = NULL;
}
// prepare port strings
sprintf(szPort, "COM%d", portnr);
sprintf(szBaud, "baud=%d parity=%c data=%d stop=%d", baud, parity, databits, stopbits);
// get a handle to the port
m_hComm = CreateFile(szPort, // communication port string (COMX)
GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE, // read/write types
0, // comm devices must be opened with exclusive access
NULL, // no security attributes
OPEN_EXISTING, // comm devices must use OPEN_EXISTING
FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED, // Async I/O
0); // template must be 0 for comm devices
if (m_hComm == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
// port not found
delete [] szPort;
delete [] szBaud;
return FALSE;
}
// set the timeout values
m_CommTimeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = 1000;
// configure
if (SetCommTimeouts(m_hComm, &m_CommTimeouts))
{
if (SetCommMask(m_hComm, dwCommEvents))
{
if (GetCommState(m_hComm, &m_dcb))
{
m_dcb.fRtsControl = RTS_CONTROL_ENABLE; // set RTS bit high!
if (BuildCommDCB(szBaud, &m_dcb))
{
if (SetCommState(m_hComm, &m_dcb))
; // normal operation... continue
else
ProcessErrorMessage("SetCommState()");
}
else
ProcessErrorMessage("BuildCommDCB()");
}
else
ProcessErrorMessage("GetCommState()");
}
else
ProcessErrorMessage("SetCommMask()");
}
else
ProcessErrorMessage("SetCommTimeouts()");
delete [] szPort;
delete [] szBaud;
// flush the port
PurgeComm(m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR | PURGE_RXABORT | PURGE_TXABORT);
// release critical section
LeaveCriticalSection(&m_csCommunicationSync);
TRACE("Initialisation for communicationport %d completed.\\nUse Startmonitor to communicate.\\n", portnr);
return TRUE;
}
//
// The CommThread Function.
//
UINT CSerialPort::CommThread(LPVOID pParam)
{
// Cast the void pointer passed to the thread back to
// a pointer of CSerialPort class
CSerialPort *port = (CSerialPort*)pParam;
// Set the status variable in the dialog class to
// TRUE to indicate the thread is running.
port->m_bThreadAlive = TRUE;
// Misc. variables
DWORD BytesTransfered = 0;
DWORD Event = 0;
DWORD CommEvent = 0;
DWORD dwError = 0;
COMSTAT comstat;
BOOL bResult = TRUE;
// Clear comm buffers at startup
if (port->m_hComm) // check if the port is opened
PurgeComm(port->m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR | PURGE_RXABORT | PURGE_TXABORT);
// begin forever loop. This loop will run as long as the thread is alive.
for (;;)
{
// Make a call to WaitCommEvent(). This call will return immediatly
// because our port was created as an async port (FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED
// and an m_OverlappedStructerlapped structure specified). This call will cause the
// m_OverlappedStructerlapped element m_OverlappedStruct.hEvent, which is part of the m_hEventArray to
// be placed in a non-signeled state if there are no bytes available to be read,
// or to a signeled state if there are bytes available. If this event handle
// is set to the non-signeled state, it will be set to signeled when a
// character arrives at the port.
// we do this for each port!
bResult = WaitCommEvent(port->m_hComm, &Event, &port->m_ov);
if (!bResult)
{
// If WaitCommEvent() returns FALSE, process the last error to determin
// the reason..
switch (dwError = GetLastError())
{
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
{
// This is a normal return value if there are no bytes
// to read at the port.
// Do nothing and continue
break;
}
case 87:
{
// Under Windows NT, this value is returned for some reason.
// I have not investigated why, but it is also a valid reply
// Also do nothing and continue.
break;
}
default:
{
// All other error codes indicate a serious error has
// occured. Process this error.
port->ProcessErrorMessage("WaitCommEvent()");
break;
}
}
}
else
{
// If WaitCommEvent() returns TRUE, check to be sure there are
// actually bytes in the buffer to read.
//
// If you are reading more than one byte at a time from the buffer
// (which this program does not do) you will have the situation occur
// where the first byte to arrive will cause the WaitForMultipleObjects()
// function to stop waiting. The WaitForMultipleObjects() function
// resets the event handle in m_OverlappedStruct.hEvent to the non-signelead state
// as it returns.
//
// If in the time between the reset of this event and the call to
// ReadFile() more bytes arrive, the m_OverlappedStruct.hEvent handle will be set again
// to the signeled state. When the call to ReadFile() occurs, it will
// read all of the bytes from the buffer, and the program will
// loop back around to WaitCommEvent().
//
// At this point you will be in the situation where m_OverlappedStruct.hEvent is set,
// but there are no bytes available to read. If you proceed and call
// ReadFile(), it will return immediatly due to the async port setup, but
// GetOverlappedResults() will not return until the next character arrives.
//
// It is not desirable for the GetOverlappedResults() function to be in
// this state. The thread shutdown event (event 0) and the WriteFile()
// event (Event2) will not work if the thread is blocked by GetOverlappedResults().
//
// The solution to this is to check the buffer with a call to ClearCommError().
// This call will reset the event handle, and if there are no bytes to read
// we can loop back through WaitCommEvent() again, then proceed.
// If there are really bytes to read, do nothing and proceed.
bResult = ClearCommError(port->m_hComm, &dwError, &comstat);
if (comstat.cbInQue == 0)
continue;
} // end if bResult
// Main wait function. This function will normally block the thread
// until one of nine events occur that require action.
Event = WaitForMultipleObjects(3, port->m_hEventArray, FALSE, INFINITE);
switch (Event)
{
case 0:
{
// Shutdown event. This is event zero so it will be
// the higest priority and be serviced first.
port->m_bThreadAlive = FALSE;
// Kill this thread. break is not needed, but makes me feel better.
AfxEndThread(100);
break;
}
case 1: // read event
{
GetCommMask(port->m_hComm, &CommEvent);
if (CommEvent & EV_CTS)
::SendMessage(port->m_pOwner->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_CTS_DETECTED, (WPARAM) 0, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
if (CommEvent & EV_RXFLAG)
::SendMessage(port->m_pOwner->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_RXFLAG_DETECTED, (WPARAM) 0, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
if (CommEvent & EV_BREAK)
::SendMessage(port->m_pOwner->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_BREAK_DETECTED, (WPARAM) 0, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
if (CommEvent & EV_ERR)
::SendMessage(port->m_pOwner->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_ERR_DETECTED, (WPARAM) 0, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
if (CommEvent & EV_RING)
::SendMessage(port->m_pOwner->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_RING_DETECTED, (WPARAM) 0, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
if (CommEvent & EV_RXCHAR)
// Receive character event from port.
ReceiveChar(port, comstat);
break;
}
case 2: // write event
{
// Write character event from port
WriteChar(port);
break;
}
} // end switch
} // close forever loop
return 0;
}
//
// start comm watching
//
BOOL CSerialPort::StartMonitoring()
{
if (!(m_Thread = AfxBeginThread(CommThread, this)))
return FALSE;
TRACE("Thread started\\n");
return TRUE;
}
//
// Restart the comm thread
//
BOOL CSerialPort::RestartMonitoring()
{
TRACE("Thread resumed\\n");
m_Thread->ResumeThread();
return TRUE;
}
//
// Suspend the comm thread
//
BOOL CSerialPort::StopMonitoring()
{
TRACE("Thread suspended\\n");
m_Thread->SuspendThread();
return TRUE;
}
//
// If there is a error, give the right message
//
void CSerialPort::ProcessErrorMessage(char* ErrorText)
{
char *Temp = new char[200];
LPVOID lpMsgBuf;
FormatMessage(
FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM,
NULL,
GetLastError(),
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), // Default language
(LPTSTR) &lpMsgBuf,
0,
NULL
);
sprintf(Temp, "WARNING: %s Failed with the following error: \\n%s\\nPort: %d\\n", (char*)ErrorText, lpMsgBuf, m_nPortNr);
MessageBox(NULL, Temp, "Application Error", MB_ICONSTOP);
LocalFree(lpMsgBuf);
delete[] Temp;
}
//
// Write a character.
//
void CSerialPort::WriteChar(CSerialPort* port)
{
BOOL bWrite = TRUE;
BOOL bResult = TRUE;
DWORD BytesSent = 0;
ResetEvent(port->m_hWriteEvent);
// Gain ownership of the critical section
EnterCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
if (bWrite)
{
// Initailize variables
port->m_ov.Offset = 0;
port->m_ov.OffsetHigh = 0;
// Clear buffer
PurgeComm(port->m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR | PURGE_RXABORT | PURGE_TXABORT);
bResult = WriteFile(port->m_hComm, // Handle to COMM Port
port->m_szWriteBuffer, // Pointer to message buffer in calling finction
port->m_nWriteSize, // Length of message to send//strlen((char*)port->m_szWriteBuffer)
&BytesSent, // Where to store the number of bytes sent
&port->m_ov); // Overlapped structure
// deal with any error codes
if (!bResult)
{
DWORD dwError = GetLastError();
switch (dwError)
{
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
{
// continue to GetOverlappedResults()
BytesSent = 0;
bWrite = FALSE;
break;
}
default:
{
// all other error codes
port->ProcessErrorMessage("WriteFile()");
}
}
}
else
{
LeaveCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
}
} // end if(bWrite)
if (!bWrite)
{
bWrite = TRUE;
bResult = GetOverlappedResult(port->m_hComm, // Handle to COMM port
&port->m_ov, // Overlapped structure
&BytesSent, // Stores number of bytes sent
TRUE); // Wait flag
LeaveCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
// deal with the error code
if (!bResult)
{
port->ProcessErrorMessage("GetOverlappedResults() in WriteFile()");
}
} // end if (!bWrite)
// Verify that the data size send equals what we tried to send
//if (BytesSent != strlen((char*)port->m_szWriteBuffer))
if (BytesSent != port->m_nWriteSize)
{
TRACE("WARNING: WriteFile() error.. Bytes Sent: %d; Message Length: %d\\n", BytesSent, strlen((char*)port->m_szWriteBuffer));
}
}
//
// Character received. Inform the owner
//
void CSerialPort::ReceiveChar(CSerialPort* port, COMSTAT comstat)
{
BOOL bRead = TRUE;
BOOL bResult = TRUE;
DWORD dwError = 0;
DWORD BytesRead = 0;
unsigned char RXBuff;
for (;;)
{
// Gain ownership of the comm port critical section.
// This process guarantees no other part of this program
// is using the port object.
EnterCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
// ClearCommError() will update the COMSTAT structure and
// clear any other errors.
bResult = ClearCommError(port->m_hComm, &dwError, &comstat);
LeaveCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
// start forever loop. I use this type of loop because I
// do not know at runtime how many loops this will have to
// run. My solution is to start a forever loop and to
// break out of it when I have processed all of the
// data available. Be careful with this approach and
// be sure your loop will exit.
// My reasons for this are not as clear in this sample
// as it is in my production code, but I have found this
// solutiion to be the most efficient way to do this.
if (comstat.cbInQue == 0)
{
// break out when all bytes have been read
break;
}
EnterCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
if (bRead)
{
bResult = ReadFile(port->m_hComm, // Handle to COMM port
&RXBuff, // RX Buffer Pointer
1, // Read one byte
&BytesRead, // Stores number of bytes read
&port->m_ov); // pointer to the m_ov structure
// deal with the error code
if (!bResult)
{
switch (dwError = GetLastError())
{
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
{
// asynchronous i/o is still in progress
// Proceed on to GetOverlappedResults();
bRead = FALSE;
break;
}
default:
{
// Another error has occured. Process this error.
port->ProcessErrorMessage("ReadFile()");
break;
}
}
}
else
{
// ReadFile() returned complete. It is not necessary to call GetOverlappedResults()
bRead = TRUE;
}
} // close if (bRead)
if (!bRead)
{
bRead = TRUE;
bResult = GetOverlappedResult(port->m_hComm, // Handle to COMM port
&port->m_ov, // Overlapped structure
&BytesRead, // Stores number of bytes read
TRUE); // Wait flag
// deal with the error code
if (!bResult)
{
port->ProcessErrorMessage("GetOverlappedResults() in ReadFile()");
}
} // close if (!bRead)
LeaveCriticalSection(&port->m_csCommunicationSync);
// notify parent that a byte was received
::SendMessage((port->m_pOwner)->m_hWnd, WM_COMM_RXCHAR, (WPARAM) RXBuff, (LPARAM) port->m_nPortNr);
} // end forever loop
}
//
// Write a string to the port
//
void CSerialPort::WriteToPort(char* string)
{
assert(m_hComm != 0);
memset(m_szWriteBuffer, 0, sizeof(m_szWriteBuffer));
strcpy(m_szWriteBuffer, string);
m_nWriteSize=strlen(string);
// set event for write
SetEvent(m_hWriteEvent);
}
void CSerialPort::WriteToPort(char* string, int n)
{
assert(m_hComm != 0);
memset(m_szWriteBuffer, 0, sizeof(m_szWriteBuffer));
memcpy(m_szWriteBuffer, string, n);
m_nWriteSize=n;
// set event for write
SetEvent(m_hWriteEvent);
}
void CSerialPort::WriteToPort(LPCTSTR string)
{
assert(m_hComm != 0);
memset(m_szWriteBuffer, 0, sizeof(m_szWriteBuffer));
strcpy(m_szWriteBuffer, string);
m_nWriteSize=strlen(string);
// set event for write
SetEvent(m_hWriteEvent);
}
void CSerialPort::WriteToPort(LPCTSTR string, int n)
{
assert(m_hComm != 0);
memset(m_szWriteBuffer, 0, sizeof(m_szWriteBuffer));
memcpy(m_szWriteBuffer, string, n);
m_nWriteSize=n;
// set event for write
SetEvent(m_hWriteEvent);
}
//
// Return the device control block
//
DCB CSerialPort::GetDCB()
{
return m_dcb;
}
//
// Return the communication event masks
//
DWORD CSerialPort::GetCommEvents()
{
return m_dwCommEvents;
}
//
// Return the output buffer size
//
DWORD CSerialPort::GetWriteBufferSize()
{
return m_nWriteBufferSize;
}
以上是关于MFC串口调试工具教程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章