图像中区域生长算法的详解和实现
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图像中区域生长算法的详解和实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
区域生长算法的基本思想是将有相似性质的像素点合并到一起。对每一个区域要先指定一个种子点作为生长的起点,然后将种子点周围领域的像素点和种子点进行对比,将具有相似性质的点合并起来继续向外生长,直到没有满足条件的像素被包括进来为止。这样一个区域的生长就完成了。这个过程中有几个关键的问题:
1 给定种子点(种子点如何选取?)
种子点的选取很多时候都采用人工交互的方法实现,也有用其他方式的,比如寻找物体并提取物体内部点或者利用其它算法找到的特征点作为种子点。
2 确定在生长过程中能将相邻像素包括进来的准则
这个准则很重要:例如包括灰度值的差值;彩色图像的颜色;梯度特征,包括梯度的方向和幅值特征。该点周围的区域特征,例如harr特征,也就是区域像素和特征。
举个例子:发在PAMI上的LSD直线检测算法中的关键一步就是找line support regions.这个区域的查找就是利用区域生长法则,生长的条件就是梯度的方向角度。
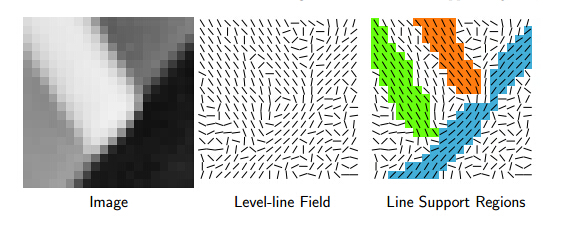
上图第一张图是原始图像,第二张图就是计算梯度角度,第三章图就是根据梯度角度区域生长的结果,相同颜色就是一个区域生长结果
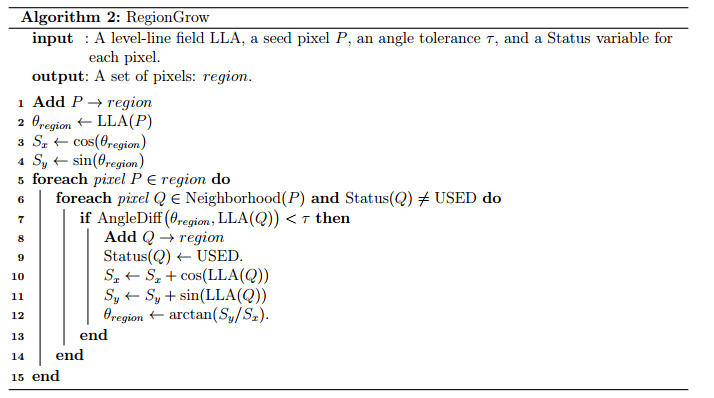
这个是论文中区域生长的伪代码。
上图就是Harr特征,这个特征很有用,由于是区域特征,在图像干扰很大的时候,能对感兴趣的区域进行有效的提取。当然也可以作为生长的准则。
3 生长的停止条件
算法实现的步骤:
1> 创建一个空白的图像(全黑);
2> 将种子点存入vector(或者stack)中,vector中存储待生长的种子点;
3> 依次弹出种子点,一般从尾部弹出,也就是后进先出,并判断种子点如周围8领域的关系(生长规则),相似的点则作为下次生长的种子点;
4> vector中不存在种子点后就停止生长。
上代码:
 View Code
View Code

1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <stack> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 using namespace cv; 8 9 10 11 void regiongrowth(IplImage* &inputimg,IplImage* &outputimg,CvPoint pt,int th) 12 { 13 14 CvPoint ptGrowing;//待生长点的位置 15 int nGrowLabel=0;//是否被标记 16 int nScrValue=0;//生长起始点的灰度值 17 int nCurValue=0;//当前生长点的灰度值 18 19 IplImage* Dstimg=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(inputimg),8,1); 20 if (Dstimg==NULL) 21 { 22 printf("image read error too"); 23 return; 24 } 25 cvZero(Dstimg); 26 27 int DIR[8][2]={{-1,-1}, {0,-1}, {1,-1}, {1,0}, {1,1}, {0,1}, {-1,1}, {-1,0}}; 28 29 vector<CvPoint>vcGrowpt;//生长点的堆栈 30 vcGrowpt.push_back(pt);//将初始生长点压入堆栈 31 32 //标记初始生长点 33 Dstimg->imageData[pt.x+pt.y*Dstimg->widthStep]=255; 34 nScrValue=inputimg->imageData[pt.x+pt.y*inputimg->widthStep]; 35 36 37 while(!vcGrowpt.empty()) 38 { 39 CvPoint curpt=vcGrowpt.back();//在堆栈中取出一个生长点 40 vcGrowpt.pop_back(); 41 42 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) 43 { 44 ptGrowing.x=curpt.x+DIR[i][0]; 45 ptGrowing.y=curpt.y+DIR[i][1]; 46 //检查边缘点 47 if(ptGrowing.x<0||ptGrowing.y<0||(ptGrowing.x>inputimg->width-1)||(ptGrowing.y>inputimg->height-1)) 48 continue; 49 nGrowLabel=Dstimg->imageData[ptGrowing.x+ptGrowing.y*Dstimg->widthStep]; 50 if (nGrowLabel==0)//表示还未标记过 51 { 52 nCurValue=inputimg->imageData[ptGrowing.x+ptGrowing.y*inputimg->widthStep]; 53 if(abs(nCurValue-nScrValue)<=th) 54 { 55 Dstimg->imageData[ptGrowing.x+ptGrowing.y*Dstimg->widthStep]=255; 56 vcGrowpt.push_back(ptGrowing); 57 58 } 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 64 } 65 cvCopy(Dstimg,outputimg); 66 cvReleaseImage(&Dstimg); 67 68 } 69 70 71 72 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 73 { 74 75 IplImage* sourceimage=cvLoadImage("H:\\programm\\test.jpg",0); 76 77 if (sourceimage==NULL) 78 { 79 printf("image read error"); 80 } 81 82 83 84 IplImage* outputimg=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(sourceimage),8,1); 85 IplImage* resultimg=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(sourceimage),8,1); 86 cvZero(resultimg); 87 cvCopy(sourceimage,outputimg); 88 regiongrowth(sourceimage,outputimg,cvPoint(392,282),12); 89 cvAdd(outputimg,resultimg,resultimg); 90 91 regiongrowth(sourceimage,outputimg,cvPoint(587,195),8); 92 cvAdd(outputimg,resultimg,resultimg); 93 94 regiongrowth(sourceimage,outputimg,cvPoint(707,356),8); 95 cvAdd(outputimg,resultimg,resultimg); 96 97 regiongrowth(sourceimage,outputimg,cvPoint(546,549),10); 98 cvAdd(outputimg,resultimg,resultimg); 99 100 regiongrowth(sourceimage,outputimg,cvPoint(310,435),10); 101 cvAdd(outputimg,resultimg,resultimg); 102 103 cvNamedWindow("source",0); 104 cvShowImage("source",sourceimage); 105 106 cvNamedWindow("result",0); 107 cvShowImage("result",resultimg); 108 cvWaitKey(0); 109 110 cvReleaseImage(&sourceimage); 111 cvReleaseImage(&outputimg); 112 cvReleaseImage(&resultimg); 113 system("pause"); 114 return 0; 115 }
这个代码实现结果,就是提取下面左图中的5个区域,右边为提取结果,由于用的是灰度差作为生长条件,效果一般般。
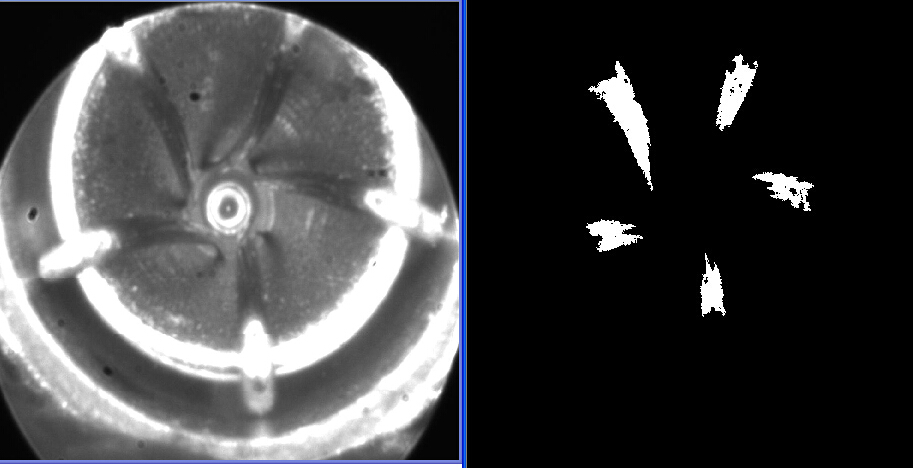
参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/robin__chou/article/details/50071313
以上是关于图像中区域生长算法的详解和实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
