所有节点对最短路径
Posted FounderWatts
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了所有节点对最短路径相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一些约定:用d(i,j)表示节点i到节点j的最短路径,w(i,j)表示节点i到节点j的权重;
对于n个节点的图,采用邻接矩阵的方式输入输出,输出及中间结果的矩阵也是n*n的矩阵,第i行j列表示从i到j的当前最短路径
我们这里讲解三个算法,第一个是利用传统的动态规划,第二个也是个动态规划算法,但是基于一种观察结果,他就是warshall算法,第三个算法是将问题转换为没有负数权重的图,再对每个节点调用Dijkstra算法,他就是Johnson算法。
注意:通常情况下我们只用warshall算法,其他两个算法一个效率太低,一个写起来太麻烦。
动态规划求所有节点对最短路径
适用条件:
没有负环(可有负权重)
动态规划步骤:
1.分析最优解的结构
(最短路径结构)
根据最短路径的最优子结构性质,有d(i,j) = d(i,k) + w(k,j)
2.递归定义最优解的值
(所有节点对最短路径问题的递归解)
首先要获取递归求解的对象表达式
这里采取最短路径的边数作为递归的计数对象,因为图中没有负环,所以对于边数大于n-1的最短路径计算也就没有意义(因为n-1条边已经能够将所有节点连接,一旦大于n-1条边则会形成环,并且所有的环都是正权重,所以会使结果变大),因此我们递归时控制边数m使其m>0 && m < n。m=1时,即为输入的邻接矩阵M。
在递归时,我们计算边数为m的最短路径时,将m-1的最短路径与d(i,j) = d(i,k) + w(k,j)进行比较,取最小值。因为k=j时,即为m-1的最短路径,因此问题简化为循环遍历k求d(i,j) = d(i,k) + w(k,j)的最小值。如下图公式:
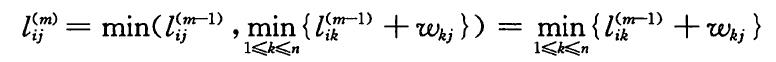
3.自底向上计算最优解的值
(自底向上计算最短路径权重)
因为含有m条边的距离是在m-1条边的基础上计算出来的,所以从含有一条边开始,自底向上求值,按照第二步所述编写代码,详见具体代码。
4.从计算出的最优解的值上构建最优解
按照正常步骤,按部就班的每次递归m++;这样最终的时间复杂度为O(n^4)。但我们要的是最终m=n-1的结果,而对中间结果不感兴趣,因此我们可以使m每次增加一倍。m>n-1时的结果与n-1时的结果相同,最终的时间复杂度被压缩到O(n^3 lgn)。(详见具体代码)
具体代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Founder
*
*/
public class Main{
private static final int INFINITE = 1000000000;
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] matrix = initialize();
print(getPairsPath(matrix));
}
public static int[][] initialize(){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
int[][] data = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
data[i][j] = input.nextInt();
return data;
}
public static int[][] extendPath(int[][] matrix){
int[][] newMatrix = new int[matrix.length][matrix.length];
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < matrix.length; ++j){
newMatrix[i][j] = INFINITE;
for(int k = 0; k < matrix.length; ++k)
if(matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j] < newMatrix[i][j]){
newMatrix[i][j] = matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j];
}
}
return newMatrix;
}
public static int[][] getPairsPath(int[][] matrix){
int m = matrix.length;
int i = 1;//i代表路径边数
while(i < m - 1){
matrix = extendPath(matrix);
m *= 2;
}
return matrix;
}
public static void print(int[][] matrix){
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < matrix.length; ++j){
if(matrix[i][j] != INFINITE && i != j){
System.out.println("From " + i + " to " + j + " the cost is:" + matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
}测试用例:
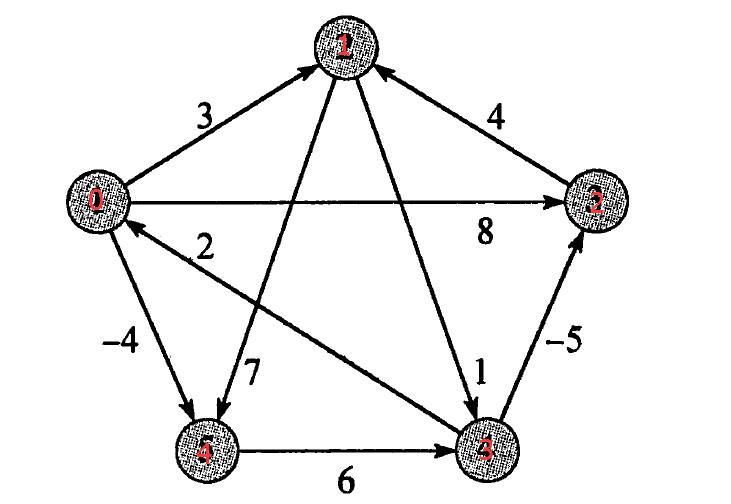
输入:
5
0 3 8 1000000000 -4
1000000000 0 1000000000 1 7
1000000000 4 0 1000000000 1000000000
2 1000000000 -5 0 1000000000
1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 6 0输出:
From 0 to 1 the cost is:1
From 0 to 2 the cost is:-3
From 0 to 3 the cost is:2
From 0 to 4 the cost is:-4
From 1 to 0 the cost is:3
From 1 to 2 the cost is:-4
From 1 to 3 the cost is:1
From 1 to 4 the cost is:-1
From 2 to 0 the cost is:7
From 2 to 1 the cost is:4
From 2 to 3 the cost is:5
From 2 to 4 the cost is:3
From 3 to 0 the cost is:2
From 3 to 1 the cost is:-1
From 3 to 2 the cost is:-5
From 3 to 4 the cost is:-2
From 4 to 0 the cost is:8
From 4 to 1 the cost is:5
From 4 to 2 the cost is:1
From 4 to 3 the cost is:6Floyd-Warshall 算法
适用条件:
没有负环(可有负权重)
原理讲解:
warshall算法非常伟大,它的时间复杂度可以达到O(V^3),而warshall算法的实现,也是基于以下现象的观察:
对于中间节点取自(1,2,3,…,k)的最短路径,它是由中间节点取自(1,2,3,…,k-1)的最短路径构成的。
基于这个观察,我们可以有以下递归式:
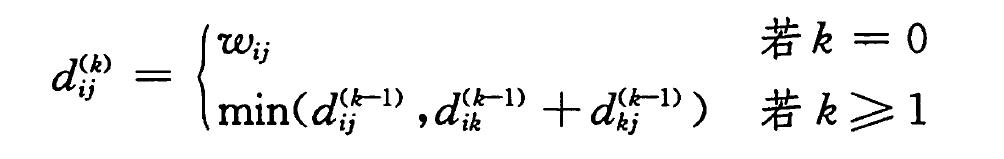
算法步骤:
1.初始化存储权重的矩阵和前驱结点矩阵
2.自底向上进行动态规划,k从0到matrix.length,判断if(matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j] < matrix[i][j])来创建新的数据矩阵和前驱矩阵;
3.根据遍历完的结果,输出答案。
具体代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
private static final int INFINITE = 1000000000;
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] matrix = initialize();
int[][] parent = new int[matrix.length][matrix.length];
for(int i = 0; i < parent.length; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < parent.length; ++j){
if(i == j)
parent[i][j] = 0;
else{
if(matrix[i][j] != INFINITE)
parent[i][j] = i;
else
parent[i][j] = -1;
}
}
printPath(floyd_warshall(matrix,parent),parent);
}
public static int[][] initialize(){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
int[][] data = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
data[i][j] = input.nextInt();
return data;
}
public static int[][] floyd_warshall(int[][] matrix,int[][] parent){
for(int k = 0; k < matrix.length; ++k){
int[][] newMatrix = new int[matrix.length][matrix.length];
int[][] newParent = new int[parent.length][parent.length];
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < matrix.length; ++j){
if(matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j] < matrix[i][j]){
newMatrix[i][j] = matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j];
newParent[i][j] = parent[k][j];
}else{
newMatrix[i][j] = matrix[i][j];
newParent[i][j] = parent[i][j];
}
}
matrix = newMatrix;
for(int m = 0; m < parent.length; ++m)
for(int n = 0; n < parent.length; ++n)
parent[m][n] = newParent[m][n];
}
return matrix;
}
public static void printPath(int[][] matrix,int[][] parent){
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < matrix.length; ++j){
if(matrix[i][j] != INFINITE && i != j){
System.out.print("From " + i + " to " + j + " the cost is:" + matrix[i][j]
+ "\\nThe path is: " + j +" ");
int temp = j;
while((temp = parent[i][temp]) != i)
System.out.print("<< " + temp + " ");
System.out.println("<< " + i + " ");
}
}
}
}测试用例:

输入:
5
0 3 8 1000000000 -4
1000000000 0 1000000000 1 7
1000000000 4 0 1000000000 1000000000
2 1000000000 -5 0 1000000000
1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 6 0输出:
From 0 to 1 the cost is:1
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 2 the cost is:-3
The path is: 2 << 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 3 the cost is:2
The path is: 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 4 the cost is:-4
The path is: 4 << 0
From 1 to 0 the cost is:3
The path is: 0 << 3 << 1
From 1 to 2 the cost is:-4
The path is: 2 << 3 << 1
From 1 to 3 the cost is:1
The path is: 3 << 1
From 1 to 4 the cost is:-1
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3 << 1
From 2 to 0 the cost is:7
The path is: 0 << 3 << 1 << 2
From 2 to 1 the cost is:4
The path is: 1 << 2
From 2 to 3 the cost is:5
The path is: 3 << 1 << 2
From 2 to 4 the cost is:3
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3 << 1 << 2
From 3 to 0 the cost is:2
The path is: 0 << 3
From 3 to 1 the cost is:-1
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3
From 3 to 2 the cost is:-5
The path is: 2 << 3
From 3 to 4 the cost is:-2
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3
From 4 to 0 the cost is:8
The path is: 0 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 1 the cost is:5
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 2 the cost is:1
The path is: 2 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 3 the cost is:6
The path is: 3 << 4 拓展
根据warshall算法求闭包:
只需将输入的矩阵变为:相连为1,不相连为0
判断条件:matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j] < matrix[i][j] 变为:matrix[i][j] |(matrix[i][k] & matrix[k][j])
即可求出。
其中k代表路径有<=k+1条边时的相连情况。
用于稀疏图的Johnson算法
先判断是否存在line的权重为负
如果不存在 直接进行后面的步骤
否则{
在图G中添加一个额外的节点s,和s到其他各个节点的line,权重为0,形成新图G’
计算s到其他各个节点的最短距离(使用bellman-ford算法),使之为各个节点的权重
计算G’中各个line的新的权重,weight+u.length-v.length
将新的权重赋予到图G中
}
建立一个|V|*|V|的新的矩阵用于记录数据
对图G中的每个节点调用Dijkstra算法并记录
算法效率:O(V^2 lgV + VE)
适用条件:
没有负环(可有负权重)
具体代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author FounderWatts
* 输入方式:邻接链表
*/
public class Main {
public static final int INFINITE = 2000000000;
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph G = new Graph();
if(initialize(G)){
Graph newG = new Graph(G);
fixNewGraph(newG);
if(!bellman_ford(newG)){
System.out.println("图中含有负数环路,节点间不存在最短路径。");
return;
}
setNodesNewWeight(G,newG);
}
Graph[] Gs = new Graph[G.getNodes().size()];
for(int i = 0; i < G.getNodes().size(); ++i){
Gs[i] = new Graph(G);
Gs[i].getNodes().get(i).setLength(0);
dijkstra(Gs[i]);
}
print(Gs);
}
public static boolean initialize(Graph G){
boolean haveMinus = false;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
ArrayList<Node> nodes = G.getNodes();
ArrayList<Line> lines = G.getLines();
input.nextLine();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
Node node = new Node(i);
String str = input.nextLine();
if(!str.equals("")){
String[] strs = str.split(" ");
for(int j = 0; j < strs.length; ++j){
int endNo = Integer.parseInt(strs[j]);
int weight = Integer.parseInt(strs[++j]);
if(weight < 0) haveMinus = true;
Line line = new Line(i,endNo,weight);
lines.add(line);
node.addLine(line);
}
}
nodes.add(node);
}
return haveMinus;
}
public static void fixNewGraph(Graph newG){
ArrayList<Node> nodes = newG.getNodes();
ArrayList<Line> lines = newG.getLines();
Node s = new Node(nodes.size());
s.setLength(0);
for(int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); ++i){
Line line = new Line(nodes.size(),i,0);
s.addLine(line);
lines.add(line);
}
nodes.add(s);
}
public static void relax(Graph G,Line line){
Node u = G.getNodes().get(line.getStartNodeNo());
Node v = G.getNodes().get(line.getEndNodeNo());
if(u.getLength() + line.getWeight() < v.getLength()){
v.setLength(u.getLength() + line.getWeight());
v.setParent(u);
}
}
public static boolean bellman_ford(Graph G){
for(int i = 0; i < G.getNodes().size() - 1; ++i)
for(Line line:G.getLines())
relax(G,line);
for(Line line:G.getLines()){
Node u = G.getNodes().get(line.getStartNodeNo());
Node v = G.getNodes().get(line.getEndNodeNo());
if(u.getLength() + line.getWeight() < v.getLength())
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void setNodesNewWeight(Graph G,Graph newG){
for(Line line:G.getLines()){
int startWeight = newG.getNodes().get(line.getStartNodeNo()).getLength();
int endWeight = newG.getNodes().get(line.getEndNodeNo()).getLength();
G.getNodes().get(line.getStartNodeNo()).setWeight(startWeight);
G.getNodes().get(line.getEndNodeNo()).setWeight(endWeight);
line.setWeight(line.getWeight() + startWeight - endWeight);
}
}
public static void dijkstra(Graph G){
ArrayList<Node> restNode = new ArrayList<>(G.getNodes());
while(!restNode.isEmpty())
for(Line line:getLeastNode(restNode).getLinkLines())
relax(G, line);
}
public static Node getLeastNode(ArrayList<Node> restNode){
Node node = restNode.get(0);
for(Node item:restNode)
if(item.getLength() < node.getLength()){
node = item;
}
restNode.remove(node);
return node;
}
public static void print(Graph[] Gs){
for(int i = 0; i < Gs.length; ++i){
ArrayList<Node> nodes = Gs[i].getNodes();
for(int j = 0; j < nodes.size(); ++j){
if(i != j && nodes.get(j).getLength() != INFINITE){
System.out.print("From " + i + " to " + j + " the cost is:" + (nodes.get(j).getLength() - nodes.get(i).getWeight() + nodes.get(j).getWeight())
+ "\\nThe path is: " + j +" ");
Node parent = nodes.get(j);
while((parent = parent.getParent()) != null)
System.out.print("<< " + parent.getNo() + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
}
class Line{
private int startNodeNo;
private int endNodeNo;
private int weight;
public int getStartNodeNo() {
return startNodeNo;
}
public void setStartNodeNo(int startNodeNo) {
this.startNodeNo = startNodeNo;
}
public int getEndNodeNo() {
return endNodeNo;
}
public void setEndNodeNo(int endNodeNo) {
this.endNodeNo = endNodeNo;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public Line(int startNodeNo, int endNodeNo, int weight) {
super();
this.startNodeNo = startNodeNo;
this.endNodeNo = endNodeNo;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
class Node{
private int no;
private int length = Main.INFINITE;
private int weight = 0;
private Node parent = null;
private LinkedList<Line> linkLines;
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public Node getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public LinkedList<Line> getLinkLines() {
return linkLines;
}
public void setLinkLines(LinkedList<Line> linkLines) {
this.linkLines = linkLines;
}
public void addLine(Line line){
linkLines.add(line);
}
public Node(int no) {
super();
this.no = no;
linkLines = new LinkedList<>();
}
public Node(Node node) {
super();
this.no = node.no;
length = node.getLength();
parent = node.getParent();
linkLines = node.getLinkLines();
weight = node.getWeight();
}
}
class Graph{
private ArrayList<Node> nodes;
private ArrayList<Line> lines;
public ArrayList<Node> getNodes() {
return nodes;
}
public void setNodes(ArrayList<Node> nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
}
public ArrayList<Line> getLines() {
return lines;
}
public void setLines(ArrayList<Line> lines) {
this.lines = lines;
}
public Graph() {
super();
nodes = new ArrayList<>();
lines = new ArrayList<>();
}
public Graph(Graph graph) {
lines = new ArrayList<>(graph.getLines());
nodes = new ArrayList<>();
for(Node node:graph.getNodes())
nodes.add(new Node(node));
}
}测试用例:

输入:
5
1 3 2 8 4 -4
3 1 4 7
1 4
0 2 2 -5
3 6输出:
From 0 to 1 the cost is:1
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 2 the cost is:-3
The path is: 2 << 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 3 the cost is:2
The path is: 3 << 4 << 0
From 0 to 4 the cost is:-4
The path is: 4 << 0
From 1 to 0 the cost is:3
The path is: 0 << 3 << 1
From 1 to 2 the cost is:-4
The path is: 2 << 3 << 1
From 1 to 3 the cost is:1
The path is: 3 << 1
From 1 to 4 the cost is:-1
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3 << 1
From 2 to 0 the cost is:7
The path is: 0 << 3 << 1 << 2
From 2 to 1 the cost is:4
The path is: 1 << 2
From 2 to 3 the cost is:5
The path is: 3 << 1 << 2
From 2 to 4 the cost is:3
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3 << 1 << 2
From 3 to 0 the cost is:2
The path is: 0 << 3
From 3 to 1 the cost is:-1
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3
From 3 to 2 the cost is:-5
The path is: 2 << 3
From 3 to 4 the cost is:-2
The path is: 4 << 0 << 3
From 4 to 0 the cost is:8
The path is: 0 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 1 the cost is:5
The path is: 1 << 2 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 2 the cost is:1
The path is: 2 << 3 << 4
From 4 to 3 the cost is:6
The path is: 3 << 4 以上是关于所有节点对最短路径的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章