深入理解sudo
Posted 潇潇、寒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入理解sudo相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
[root@cairui ~]# cat /etc/sudoers ## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as ## the root user, without needing the root password. #sudoers允许特定的用户去执行各种命令以rot的身份,不需要root密码。 ## ## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections ## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular ## users or groups. ## ## This file must be edited with the \'visudo\' command. ## Host Aliases ## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using ## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead. # Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2 # Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2 ## User Aliases ## These aren\'t often necessary, as you can use regular groups ## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname ## rather than USERALIAS # User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem ## Command Aliases ## These are groups of related commands... ## Networking # Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient, /usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig, /sbin/mii-tool ## Installation and management of software # Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum ## Services # Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig ## Updating the locate database # Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/bin/updatedb ## Storage # Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount ## Delegating permissions # Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp ## Processes # Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall ## Drivers # Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe # Defaults specification # # Refuse to run if unable to disable echo on the tty. # Defaults !visiblepw # # Preserving HOME has security implications since many programs # use it when searching for configuration files. Note that HOME # is already set when the the env_reset option is enabled, so # this option is only effective for configurations where either # env_reset is disabled or HOME is present in the env_keep list. # Defaults always_set_home Defaults env_reset Defaults env_keep = "COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE INPUTRC KDEDIR LS_COLORS" Defaults env_keep += "MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES" Defaults env_keep += "LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY" # # Adding HOME to env_keep may enable a user to run unrestricted # commands via sudo. # # Defaults env_keep += "HOME" Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin ## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on ## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple ## systems). ## Syntax: ## ## user MACHINE=COMMANDS ## ## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it. ## ## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Allows members of the \'sys\' group to run networking, software, ## service management apps and more. # %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS ## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands # %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Same thing without a password # %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL ## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the ## cdrom as root # %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom ## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system # %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now ## Read drop-in files from /etc/sudoers.d (the # here does not mean a comment) #includedir /etc/sudoers.d
注意:修改完(visudo)之后,需要visudo -c检查一下是否有错误。
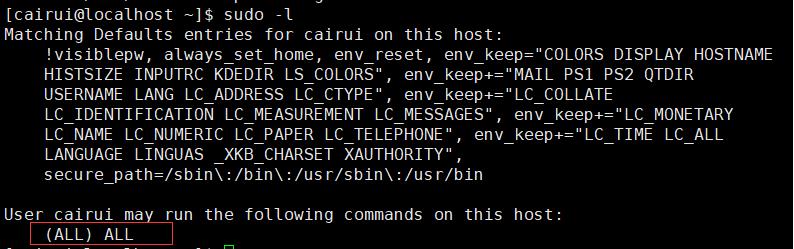
sudo -l查看用户拥有的权限。

1、sudoers配置文件别名介绍
(1)Host Aliases(主机别名)
生产环境中一般不会设置主机别名,一般主机别名不太常用
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #第一个ALL就是主机别名的应用位置
(2)User Aliases(用户别名)
如果表示用户组那么前面加%
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #root就是用户别名的应用位置
User_Aliases ADMINS = jsmith,mikem
(3)Runas_Alias别名
此别名是指定“用户身份”,即sudo允许切换到的用户
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #第二个ALL就是用户别名的应用位置
Runas_Alias OP = root
(4)Cmnd_Alias(命令别名)
就是定义一个别名,它可以包含一堆命令的内容(一组相关命令的集合)
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modpro
2、sudo日志审计
(1)生产环境中日志方案
a、syslog全部操作日志审计,这种方法信息量大,不便查看
b、sudo日志配置syslog服务进行日志审查
c、堡垒机日志审查
d、bash安装监视器,记录用户使用操作
(2)配合sudo日志审计
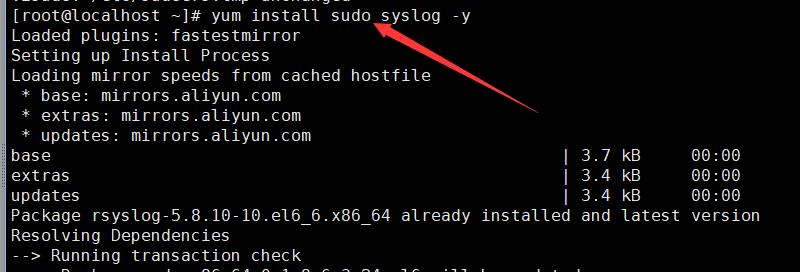
安装sudo与syslog服务
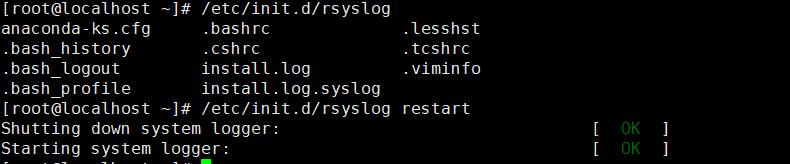
配置服务
创建日志保存目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/log/
查看服务器版本,6.x为/etc/rsyslog.conf,5.x版本为syslog.conf


上述为rsyslog的配置文件

上述为sudoers的配置文件
测试结果:
[root@localhost ~]# su - cairui [cairui@localhost ~]$ sudo visudo [sudo] password for cairui: visudo: /etc/sudoers.tmp unchanged [cairui@localhost ~]$ cd /tmp/ [cairui@localhost tmp]$ touch 123.txt [cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo ll sudo: ll: command not found [cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo ls -ll total 0 -rw-rw-r-- 1 cairui cairui 0 Feb 12 09:41 123.txt -rw-------. 1 root root 0 Feb 9 09:57 yum.log [cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo cat /var/log/sudo.log Feb 12 09:41:19 : cairui : TTY=pts/0 ; PWD=/home/cairui ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/sbin/visudo Feb 12 09:41:47 : cairui : TTY=pts/0 ; PWD=/tmp ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/bin/ls -ll Feb 12 09:42:12 : cairui : TTY=pts/0 ; PWD=/tmp ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/bin/cat /var/log/sudo.log
以上是关于深入理解sudo的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章