数据结构与算法--栈与队列
Posted huster-田浪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构与算法--栈与队列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
栈和队列
栈和队列都是比较常用的数据结构。栈的应用非常的广泛,比如说,递归函数的实现就是借助于栈保存相关的数据。操作系统中每个线程也会使用栈来保存函数调用涉及到的一些参数和其他变量等。栈最大的一个特点就是先进后出(FILO—First-In/Last-Out)。
队列和栈不同的是,队列是一种先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)的数据结构。
对应的STL中都有实现了的方法。
栈的相关方法:
| 入栈,s.push(x) 出栈,s.pop() 访问栈顶,s.top() 判断栈空,s.empty() 访问栈中的元素个数,s.size() |
队列的方法与栈大同小异,列举如下:
| 入队,q.push(x) 出队,q.pop() 访问队首元素,q.front()、访问队尾元素,q.back() 判断队列空,q.empty() 访问队列中的元素个数,q.size() |
注意,两者的pop()方法,仅仅删除栈顶和队列首元素,并不返回,如需截获元素,在pop()方法之前使用top()或者front()方法。
栈的主要机制可以用数组来实现,也可以用链表来实现,下面用数组来实现栈的基本操作:
1 public class ArrayStack { 2 private long[] a; 3 private int size; //栈数组的大小 4 private int top; //栈顶 5 6 public ArrayStack(int maxSize) { 7 this.size = maxSize; 8 this.a = new long[size]; 9 this.top = -1; //表示空栈 10 } 11 12 public void push(long value) {//入栈 13 if(isFull()) { 14 System.out.println("栈已满!"); 15 return; 16 } 17 a[++top] = value; 18 } 19 20 public long peek() {//返回栈顶内容,但不删除 21 if(isEmpty()) { 22 System.out.println("栈中没有数据"); 23 return 0; 24 } 25 return a[top]; 26 } 27 28 public long pop() { //弹出栈顶内容,删除 29 if(isEmpty()) { 30 System.out.println("栈中没有数据!"); 31 return 0; 32 } 33 return a[top--]; 34 } 35 36 public int size() { 37 return top + 1; 38 } 39 40 public boolean isEmpty() { 41 return (top == -1); 42 } 43 44 public boolean isFull() { 45 return (top == size -1); 46 } 47 48 public void display() { 49 for(int i = top; i >= 0; i--) { 50 System.out.print(a[i] + " "); 51 } 52 System.out.println(""); 53 } 54 }
数据项入栈和出栈的时间复杂度均为O(1)。这也就是说,栈操作所消耗的时间不依赖于栈中数据项的个数,因此操作时间很短。栈不需要比较和移动操作。
队列也可以用数组来实现,不过这里有个问题,当数组下标满了后就不能再添加了,但是数组前面由于已经删除队列头的数据了,导致空。所以队列我们可以用循环数组来实现,见下面的代码:
1 public class RoundQueue { 2 private long[] a; 3 private int size; //数组大小 4 private int nItems; //实际存储数量 5 private int front; //头 6 private int rear; //尾 7 8 public RoundQueue(int maxSize) { 9 this.size = maxSize; 10 a = new long[size]; 11 front = 0; 12 rear = -1; 13 nItems = 0; 14 } 15 16 public void insert(long value) { 17 if(isFull()){ 18 System.out.println("队列已满"); 19 return; 20 } 21 rear = ++rear % size; 22 a[rear] = value; //尾指针满了就循环到0处,这句相当于下面注释内容 23 nItems++; 24 /* if(rear == size-1){ 25 rear = -1; 26 } 27 a[++rear] = value; 28 */ 29 } 30 31 public long remove() { 32 if(isEmpty()) { 33 System.out.println("队列为空!"); 34 return 0; 35 } 36 nItems--; 37 front = front % size; 38 return a[front++]; 39 } 40 41 public void display() { 42 if(isEmpty()) { 43 System.out.println("队列为空!"); 44 return; 45 } 46 int item = front; 47 for(int i = 0; i < nItems; i++) { 48 System.out.print(a[item++ % size] + " "); 49 } 50 System.out.println(""); 51 } 52 53 public long peek() { 54 if(isEmpty()) { 55 System.out.println("队列为空!"); 56 return 0; 57 } 58 return a[front]; 59 } 60 61 public boolean isFull() { 62 return (nItems == size); 63 } 64 65 public boolean isEmpty() { 66 return (nItems == 0); 67 } 68 69 public int size() { 70 return nItems; 71 } 72 }
和栈一样,队列中插入数据项和删除数据项的时间复杂度均为O(1)。
还有个优先级队列,优先级队列是比栈和队列更专用的数据结构。优先级队列与上面普通的队列相比,主要区别在于队列中的元素是有序的,关键字最小(或者最大)的数据项总在队头。数据项插入的时候会按照顺序插入到合适的位置以确保队列的顺序。优先级队列的内部实现可以用数组或者一种特别的树——堆来实现
1 public class PriorityQueue { 2 private long[] a; 3 private int size; 4 private int nItems;//元素个数 5 6 public PriorityQueue(int maxSize) { 7 size = maxSize; 8 nItems = 0; 9 a = new long[size]; 10 } 11 12 public void insert(long value) { 13 if(isFull()){ 14 System.out.println("队列已满!"); 15 return; 16 } 17 int j; 18 if(nItems == 0) { //空队列直接添加 19 a[nItems++] = value; 20 } 21 else{//将数组中的数字依照下标按照从大到小排列 22 for(j = nItems-1; j >= 0; j--) { 23 if(value > a[j]){ 24 a[j+1] = a[j]; 25 } 26 else { 27 break; 28 } 29 } 30 a[j+1] = value; 31 nItems++; 32 } 33 } 34 35 public long remove() { 36 if(isEmpty()){ 37 System.out.println("队列为空!"); 38 return 0; 39 } 40 return a[--nItems]; 41 } 42 43 public long peekMin() { 44 return a[nItems-1]; 45 } 46 47 public boolean isFull() { 48 return (nItems == size); 49 } 50 51 public boolean isEmpty() { 52 return (nItems == 0); 53 } 54 55 public int size() { 56 return nItems; 57 } 58 59 public void display() { 60 for(int i = nItems-1; i >= 0; i--) { 61 System.out.print(a[i] + " "); 62 } 63 System.out.println(" "); 64 } 65 }
这里实现的优先级队列中,插入操作需要O(N)的时间,而删除操作则需要O(1)的时间。
面试题1:
用两个栈实现队列,请实现两个函数appendTail和deleteHead,完成在队列尾部插入结点和在队列首部删除结点的功能。模板定义如下:
1 template <typename T> class CQueue
2 {
3 public:
4 CQueue(void);
5 ~CQueue(void);
6
7 // 在队列末尾添加一个结点
8 void appendTail(const T& node);
9
10 // 删除队列的头结点
11 T deleteHead();
12
13 private:
14 stack<T> stack1;
15 stack<T> stack2;
16 };
分析:
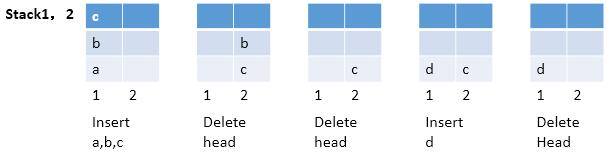
这道题是要求通过两个“先进后出”的操作完成“先进先出”的功能。下面这个例子比较形象的给出了实现的过程。
起初的时候,两个栈都为空,那么只要有元素来,那么默认插入到第一个栈。这是,如果要求删除一个元素,那么元素已经不在栈顶,在第一个栈中肯定无法直接删除了,此时我们发现第二个栈还没有派上用场,这里用到了,把第一个栈中的元素压入到第二个栈中,可以发现原来在第一个栈中栈底的元素已经出现在第二个栈的栈顶上,所以删除的功能就实现了。如果这个时候,“队列”里还有元素,我们还可以继续出队,而且,现在要出队的元素就在第二个栈的栈顶,所以直接出栈即可。
分析到现在,下面给出总结:如果栈2不为空,同时又需要出队,那么顺其自然直接弹出即可。如果栈2为空,那么从栈1中逐个弹出压入,那么完整的实现了先进先出的功能。
具体的流程和代码实现如下:
1 template<typename T> void CQueue<T>::appendTail(const T& element)
2 {
3 stack1.push(element);
4 }
5
6 template<typename T> T CQueue<T>::deleteHead()
7 {
8 if(stack2.size()<= 0)
9 {
10 while(stack1.size()>0)
11 {
12 T& data = stack1.top();
13 stack1.pop();
14 stack2.push(data);
15 }
16 }
17
18 if(stack2.size() == 0)
19 throw new exception("queue is empty");
20
21 T head = stack2.top();
22 stack2.pop();
23
24 return head;
25 }
面试题2:
用两个队列实现栈。
分析:
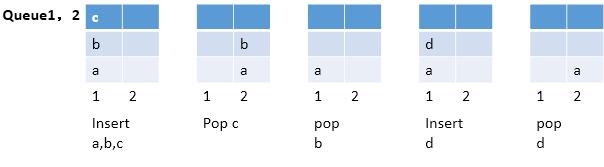
结合下图,我们分析一下具体的流程,搞清楚了相关的流程,那么对应的操作就明晰了。
起初的时候,两个队列都是空的,那么当“栈”要压入一个元素,我们就默认将该元素压入到队列1中。接下来继续压入剩余的元素。
接下来考虑,如果我们想要弹出一个元素如何操作。栈中要求出栈的为栈顶元素,那么即为最后插入的元素,但是该元素在队列的尾部,必须要求前面的元素出队后才能访问,说到这里,你也就发现思路的:出队前面的元素,到另一个队列中,那么就可以在原队列中弹出唯一的元素了。
现在我们再考虑另一个情况,队列里面还有元素,“栈”又进来了新的元素,那么就将新元素,压入到存在元素的那一个队列中,剩余的操作,上面已经提到了,一样的操作,看图也许就清晰多了。
1 template <typename T> class CStack
2 {
3 public:
4 CStack(void);
5 ~CStack(void);
6
7 // 在队列末尾添加一个结点
8 void Input(const T& );
9
10 // 删除队列的头结点
11 T Output();
12
13 private:
14 queue<T> queue1;
15 queue<T> queue2;
16 };
1 template<typename T> void CStack<T>::Input(const T& t){
2 if(queue1.empty()&&queue2.empty())
3 queue1.push(t);
4 else
5 if(!queue1.empty())
6 queue1.push(t);
7 else
8 queue2.push(t);
9 }
10
11 template<typename T> T CStack<T>::Output(){
12 T t;
13 if(queue1.empty()&&queue2.empty())
14 retutn NULL;
15 else
16 if(queue1.empty()){
17 while(queue2.size()!=1){
18 queue1.push(queue2.front());
19 queue2.pop();
20 }
21 t=queue2.front();
22 queue2.pop();
23 }
24 else
25 {
26 while(queue1.size()!=1){
27 queue2.push(queue1.front());
28 queue1.pop();
29 }
30 t=queue1.front();
31 queue1.pop();
32 }
33 return t;
34 }
35
以上是关于数据结构与算法--栈与队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
