树的子结构——18
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了树的子结构——18相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
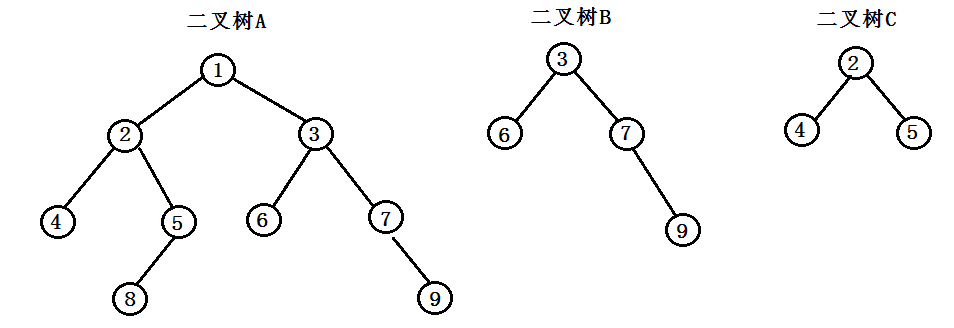
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。如图:二叉树B就是二叉树A的一棵子树,而二叉树C不是二叉树A的子树。
上图可以发现,判断一棵树是不是另一棵树的子树,可以从一棵树的根结点开始遍历,直到找到另一棵树的根结点开始,就依次比较两棵树的左右子树,再次直到比较到两棵树的叶子结点为止,如果中途有任意一个结点不等,那么树B就不是另一棵A的子树,否则,就是其子树,可以用递归来实现;
程序设计如下:
#include <iostream> #include <assert.h> #include <string.h> using namespace std; struct BinaryTreeNode//树结点结构体 { int _val; BinaryTreeNode* _Lchild; BinaryTreeNode* _Rchild; BinaryTreeNode(int val)//构造函数 :_val(val) ,_Lchild(NULL) ,_Rchild(NULL) {} }; BinaryTreeNode* _CreatTree(const int *arr, size_t& index, size_t size)//创建二叉树 { if((arr[index] != ‘#‘) && (index < size)) { BinaryTreeNode *root = new BinaryTreeNode(arr[index]); root->_Lchild = _CreatTree(arr, ++index, size); root->_Rchild = _CreatTree(arr, ++index, size); return root; } else return NULL; }; BinaryTreeNode* CreatTree(const int *arr, size_t size) { assert(arr && size); size_t index = 0; return _CreatTree(arr, index, size); } bool Judge(BinaryTreeNode* father, BinaryTreeNode* child)//递归判断子树是否存在 { //如果父子都到了叶子结点,说明当前子树是相等的 //如果任意结点不相等,则一定不是子树 //如果一棵树到达了叶子结点而另一棵还没有到达叶子结点,那么一定不是子树 if((father == NULL) && (child == NULL)) return true; else if((father != NULL) && (child != NULL)) { if(father->_val != child->_val) return false; } else return false; //返回结果应该是左右结点都完全相等 bool ret = Judge(father->_Lchild, child->_Lchild) && Judge(father->_Rchild, child->_Rchild); return ret; } //在父类书中寻找与要判断子树根结点相等的结点 bool JudgeChildTree(BinaryTreeNode* father, BinaryTreeNode* child) { bool ret = false; //如果其中一棵树为空,则子树不在当前父类树中 if((father == NULL) || (child == NULL)) return ret; //如果当前结点等于要判断子树的根结点,则进行完全比较 if(father->_val == child->_val) ret = Judge(father, child); //当结果不为真的时候,才进行继续寻找,否则说明判断成功,就不再继续遍历 if(!ret) ret = JudgeChildTree(father->_Lchild, child); if(!ret) ret = JudgeChildTree(father->_Rchild, child); return ret; } void PrevOrder(BinaryTreeNode *root)//前序遍历打印树结点 { if(root != NULL) { cout<<root->_val<<"->"; PrevOrder(root->_Lchild); PrevOrder(root->_Rchild); } } void DestoryTree(BinaryTreeNode *root)//销毁树 { if(root != NULL) { delete root; DestoryTree(root->_Lchild); DestoryTree(root->_Rchild); } } int main() { int arr1[] = {1,2,4,‘#‘,‘#‘,5,8,‘#‘,‘#‘,‘#‘,3,6,‘#‘,‘#‘,7,‘#‘,9,‘#‘,‘#‘}; int arr2[] = {3,6,‘#‘,‘#‘,7,‘#‘,9,‘#‘,‘#‘}; int arr3[] = {2,4,‘#‘,‘#‘,5,‘#‘,‘#‘}; BinaryTreeNode *father = CreatTree(arr1, sizeof(arr1)/sizeof(arr1[0])); BinaryTreeNode *child1 = CreatTree(arr2, sizeof(arr2)/sizeof(arr2[0])); BinaryTreeNode *child2 = CreatTree(arr3, sizeof(arr3)/sizeof(arr3[0])); PrevOrder(father); cout<<"NULL"<<endl; PrevOrder(child1); cout<<"NULL"<<endl; PrevOrder(child2); cout<<"NULL"<<endl; bool ret = JudgeChildTree(father, child1); cout<<ret<<endl; ret = JudgeChildTree(father, child2); cout<<ret<<endl; DestoryTree(father); DestoryTree(child1); DestoryTree(child2); return 0; }
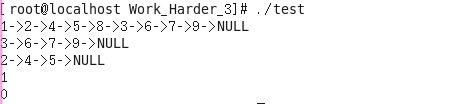
运行程序:
《完》
本文出自 “敲完代码好睡觉zzz” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://2627lounuo.blog.51cto.com/10696599/1774469
以上是关于树的子结构——18的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章