ConcurrentHashMap 解读
Posted xmz_java
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ConcurrentHashMap 解读相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

初始化:
问题:如何当且仅只有一个线程初始化table
1 private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; 3 while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { 4 if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) 5 Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin 6 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { 7 try { 8 if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { 9 int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; 10 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 11 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; 12 table = tab = nt; 13 sc = n - (n >>> 2); 14 } 15 } finally { 16 sizeCtl = sc; 17 } 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 return tab; 22 }
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table; private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
1、第3行 判断当前系统的table是否为空,这里用volatile 修饰table,对于各个线程都是可见的
2、第4行 判断sizeCtl 是否小于零,因为在初始化的过程中,会把sizeCtl设置成-1,所以如果小于零,说明当前有其他线程正在进行初始化,所以直接让出cpu时间
3、第6行 如果上一步的判断不小于零,那么这一步就要把sizeCtl设置成-1,这里用Unsafe类保证了仅只有一个线程能修改sizeCtl的值从0到-1
4、9-13行 初始化table
5、第16行 将sizeCtl 值设置为12
取值
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; 3 int h = spread(key.hashCode()); 4 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 5 (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) { 6 if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { 7 if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) 8 return e.val; 9 } 10 else if (eh < 0) 11 return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; 12 while ((e = e.next) != null) { 13 if (e.hash == h && 14 ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) 15 return e.val; 16 } 17 } 18 return null; 19 }
static final int spread(int h) { return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS; }
1. 第2行 定义一堆变量下面用
2. 第3行调整hash值分布的方法,类似于HashMap中的hash(Object key)方法,通过位运算来使key分布更均匀
3. 第4-5行判断 table 是否有值,如果有值 根据第三行计算出来的结果 计算出key在tab中的Node位置,取得Node中的first node
4. 第6-9行 hash值比对判断 如果刚刚取得的first node的hash值和当前key的hash值相同,那么就开始获取值
5. 第10-11 如果刚刚取的node的hash值小于0,那么这个node是个红黑树,进入到红黑树里面查询
6.第12-17 如果以上条件都不对,那么就开始遍历查询
扩容:
1.扩容的时机
1.链表新增节点后,所在链表的节点数会达到阈值,转变成红黑树,在转变之前会对数组长度做一次判断,如果数组的长度小于64,则会用调用tryPresize方法把数组长度扩大到原来的两倍,并触发transfer方法,重新调整节点的位置
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
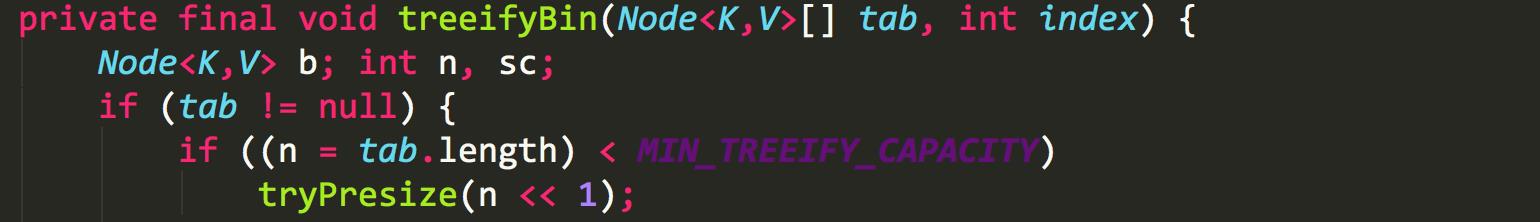
2.新增节点之后,会调用addCount方法记录元素个数,并检查是否需要进行扩容,当数组元素个数达到阈值时,会触发transfer方法,重新调整节点的位置
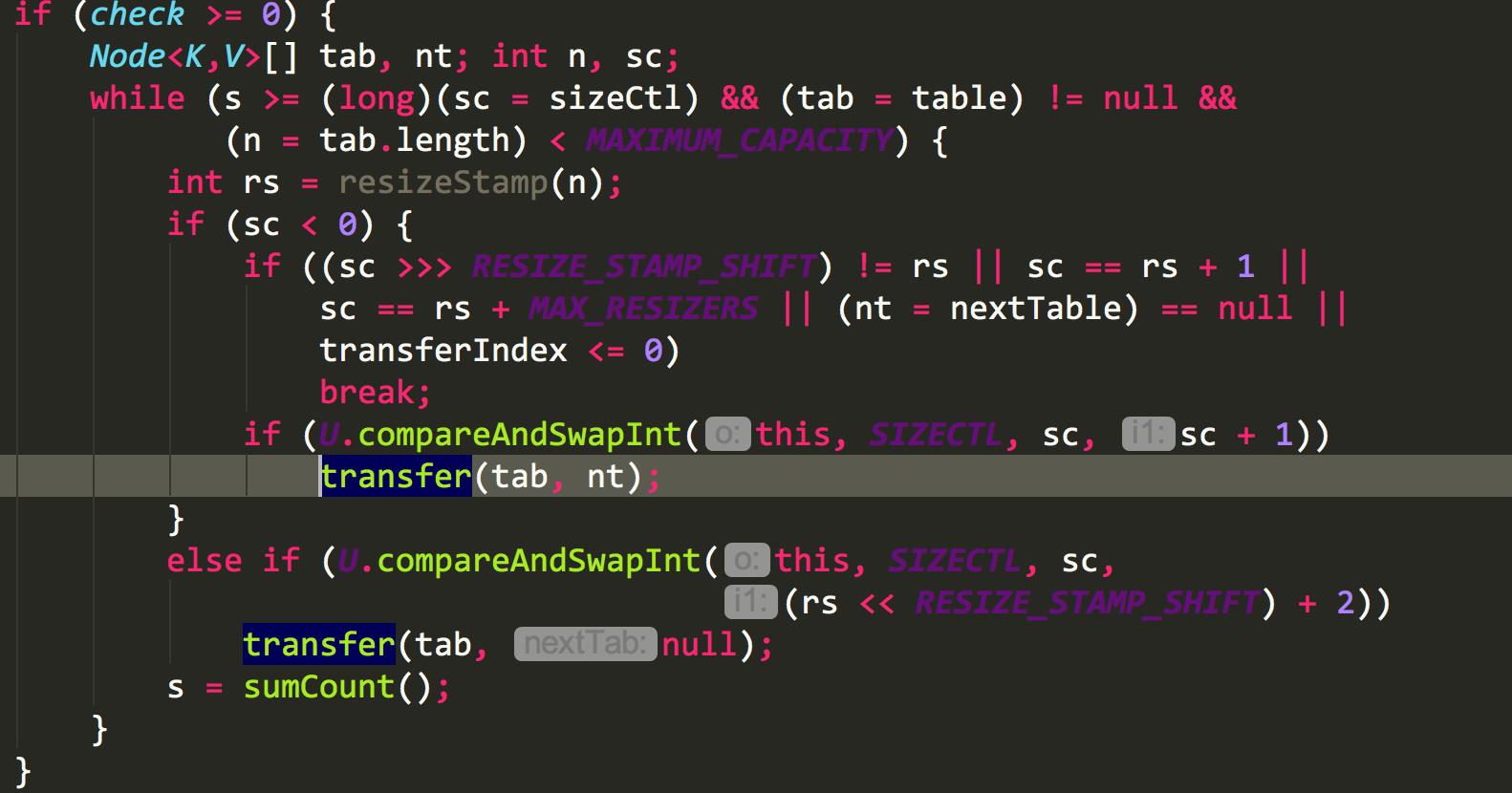
2.扩容的执行:
1 /** 2 * 一个过渡的table表 只有在扩容的时候才会使用 3 */ 4 private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable; 5 6 /** 7 * Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See 8 * above for explanation. 9 */ 10 private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { 11 int n = tab.length, stride; 12 if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE) 13 stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range 14 if (nextTab == null) { // initiating 15 try { 16 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 17 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];//构造一个nextTable对象 它的容量是原来的两倍 18 nextTab = nt; 19 } catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME 20 sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 21 return; 22 } 23 nextTable = nextTab; 24 transferIndex = n; 25 } 26 int nextn = nextTab.length; 27 ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);//构造一个连节点指针 用于标志位 28 boolean advance = true;//并发扩容的关键属性 如果等于true 说明这个节点已经处理过 29 boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab 30 for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) { 31 Node<K,V> f; int fh; 32 //这个while循环体的作用就是在控制i-- 通过i--可以依次遍历原hash表中的节点 33 while (advance) { 34 int nextIndex, nextBound; 35 if (--i >= bound || finishing) 36 advance = false; 37 else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) { 38 i = -1; 39 advance = false; 40 } 41 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt 42 (this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex, 43 nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ? 44 nextIndex - stride : 0))) { 45 bound = nextBound; 46 i = nextIndex - 1; 47 advance = false; 48 } 49 } 50 if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) { 51 int sc; 52 if (finishing) { 53 //如果所有的节点都已经完成复制工作 就把nextTable赋值给table 清空临时对象nextTable 54 nextTable = null; 55 table = nextTab; 56 sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);//扩容阈值设置为原来容量的1.5倍 依然相当于现在容量的0.75倍 57 return; 58 } 59 //利用CAS方法更新这个扩容阈值,在这里面sizectl值减一,说明新加入一个线程参与到扩容操作 60 if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) { 61 if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) 62 return; 63 finishing = advance = true; 64 i = n; // recheck before commit 65 } 66 } 67 //如果遍历到的节点为空 则放入ForwardingNode指针 68 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null) 69 advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd); 70 //如果遍历到ForwardingNode节点 说明这个点已经被处理过了 直接跳过 这里是控制并发扩容的核心 71 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) 72 advance = true; // already processed 73 else { 74 //节点上锁 75 synchronized (f) { 76 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { 77 Node<K,V> ln, hn; 78 //如果fh>=0 证明这是一个Node节点 79 if (fh >= 0) { 80 int runBit = fh & n; 81 //以下的部分在完成的工作是构造两个链表 一个是原链表 另一个是原链表的反序排列 82 Node<K,V> lastRun = f; 83 for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) { 84 int b = p.hash & n; 85 if (b != runBit) { 86 runBit = b; 87 lastRun = p; 88 } 89 } 90 if (runBit == 0) { 91 ln = lastRun; 92 hn = null; 93 } 94 else { 95 hn = lastRun; 96 ln = null; 97 } 98 for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { 99 int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val; 100 if ((ph & n) == 0) 101 ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln); 102 else 103 hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn); 104 } 105 //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表 106 setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); 107 //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表 108 setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); 109 //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点 110 setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); 111 //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i--操作 112 advance = true; 113 } 114 //对TreeBin对象进行处理 与上面的过程类似 115 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { 116 TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f; 117 TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null; 118 TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null; 119 int lc = 0, hc = 0; 120 //构造正序和反序两个链表 121 for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) { 122 int h = e.hash; 123 TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V> 124 (h, e.key, e.val, null, null); 125 if ((h & n) == 0) { 126 if ((p.prev = loTail) == null) 127 lo = p; 128 else 129 loTail.next = p; 130 loTail = p; 131 ++lc; 132 } 133 else { 134 if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null) 135 hi = p; 136 else 137 hiTail.next = p; 138 hiTail = p; 139 ++hc; 140 } 141 } 142 //如果扩容后已经不再需要tree的结构 反向转换为链表结构 143 ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) : 144 (hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t; 145 hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) : 146 (lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t; 147 //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表 148 setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); 149 //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表 150 setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); 151 //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点 152 setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); 153 //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i--操作 154 advance = true; 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 } 160 }
插入:
1 final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { 2 //key和value都不能为空 3 if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 4 //计算hash值,让hash值分布更均匀 5 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); 6 int binCount = 0; 7 //什么时候插入成功,什么时候跳出 8 for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { 9 Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; 10 //如果table为空的话,进行初始化操作 11 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 12 tab = initTable(); 13 //根据hash值计算出在table里面的位置,返回table[i]这个节点信息,赋值给f 14 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { 15 //如果这个位置没有值 ,直接放进去,不需要加锁 16 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, 17 new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) 18 break; // no lock when adding to empty bin 19 } 20 //如果当前的这个节点正在扩容,那就帮助扩容线程进行扩容 21 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) 22 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); 23 else { 24 V oldVal = null; 25 //对节点加锁 26 synchronized (f) { 27 //再次判断,多线程下有可能会出问题 28 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { 29 //fh〉0 说明这个节点是一个链表的节点 不是树的节点 30 if (fh >= 0) { 31 binCount = 1; 32 //在这里遍历链表所有的结点 33 for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { 34 K ek; 35 //如果hash值和key值相同 则修改对应结点的value值 36 if (e.hash == hash && 37 ((ek = e.key) == key || 38 (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { 39 oldVal = e.val; 40 if (!onlyIfAbsent) 41 e.val = value; 42 break; 43 } 44 Node<K,V> pred = e; 45 //如果遍历到了最后一个结点,那么就证明新的节点需要插入 就把它插入在链表尾部 46 if ((e = e.next) == null) { 47 pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, 48 value, null); 49 break; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 //如果这个节点是树节点,就按照树的方式插入值 54 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { 55 Node<K,V> p; 56 binCount = 2; 57 if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, 58 value)) != null) { 59 oldVal = p.val; 60 if (!onlyIfAbsent) 61 p.val = value; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 if (binCount != 0) { 67 //如果链表长度已经达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构 68 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) 69 treeifyBin(tab, i); 70 if (oldVal != null) 71 return oldVal; 72 break; 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 //将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量+1 77 addCount(1L, binCount); 78 return null; 79 }
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f6730d5784ad
http://www.importnew.com/22007.html
以上是关于ConcurrentHashMap 解读的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章