VI nagios
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了VI nagios相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
VI nagios
一、相关概念:
cacti(监控工具;收集数据,根据数据绘图,如收集到CPU load:0.8 1.2等是具体的数据,做聚合后绘图;thold插件实现报警功能)
nagios:
监控工具;
监控对象(主机、服务|资源、联系人、时段、命令)
nagios对监控对象的监控有四种状态,只取状态值(OK、CRITICAL、WARNING、UNKNOWN),不论数值是多少,只取状态值,例如将监控对象CPU利用率定义好,在90%定义为CRITICAL,80%时为WARNING,其它数值则OK,监测不到时为UNKNOWN,不论监控对象是什么,只取监控的四种状态,简化使得管理员只关心监控对象是否正常,而不管当前的值是多少,更重要的是nagios在这样分析的结果之上提供了功能非常强大的报警系统,而cacti中是用thold插件实现报警能力,它与nagios比报警能力差太远了
cacti和nagios的着眼点不同,cacti收集数据绘图、展示走势;nagios分析监控结果,返回四种状态的某一种,并在状态危急时启动强大的报警机制给管理员发送通知,到现今nagios被广泛采用,已成为工业标准,强大到nagios本身是高度插件式的,nagios core不做任何监控工作,只是支持监控本身的工作运行,可将nagios core理解为nagios的工作平台,所有的监控功能都通过插件实现,nagios有一堆的plugins,可用官方提供,用户自己也可开发,plugin每次检测主机资源通过分析四种状态中的一种,nagios core取回nagios plugin返回的状态值来判断接下来处理的动作,高度插件化使得nagios整个工作机制和配置过程极具灵活性(越灵活复杂度越高)
nagios的整个工作过程是靠几种监控对象实现的:
主机--主机组(主机是一种对象,主机组也是一种对象)
服务|资源—服务组(服务和资源都统一称为服务)
联系人—联系人组(nagios的重大功能是一旦出问题报警,要能联系到谁,将通知发给谁,发给哪一组人)
时段timeperiod(定义对主机服务的监控时间段,联系人在什么时间段可接受通知,如server策略白天一定要正常,若不正常要能接到通知,晚上不正常则无所谓,就没必要接到通知)
命令command(非常重要的对象,nagios通过plugin监控主机或服务,简单来讲plugin就是一堆script,这个script本身对哪些对象进行监控,如对linux主机或win主机的监控方式不一样,对于httpd和nginx的监控方式也不一样,尽管都是web service,对于不同对象的监控通常使用特定的script来实现,script要应用到特定的对象上去,就算是同一个script对于不同的监控对象接受的参数、使用的方式都有可能不同(例如某一主机同时在线500个用户认为OK,1000个则WARNING,1500就是CRITICAL,而另一主机性能差在线100个OK,200个就WARNING了,500个就CRITICAL),command就是将插件揉合进定义好的命令模板中,这个模板可以应用到某个或某些监控对象上,以实现具体的监控)
这些监控对象彼此间有紧密的联系(非常复杂),如主机要有联系人(出现故障给谁通知),在哪个时段可发送给指定联系人,监控使用什么命令,对象之间有时需要互相引用,每一个监控对象,主机|服务|资源,都要定义出来,以主机为例给它起个名字,给出描述信息,使用什么命令监控,出现什么样的问题发送通知,是WARNING就告知还是CRITICAL才告知,还要说明发送通知给谁,在什么时候发送通知等
nagios支持模板进行配置(有时需要定义N个主机,若这N个主机都是linux-server,这些server除名字和描述信息不同之外,其它的要监控的内容都可以相同,对于多个监控对象,如果有很多属性相同时可使用template(对象模板)、联系人模板、主机|服务都可使用模板,在定义对象时直接套用模板,在模板中继承一些属性,再定义一些独有的属性即可
nagios要完成监控工作要定义对象,这些对象就是定义好的实体、并对它们加以区别
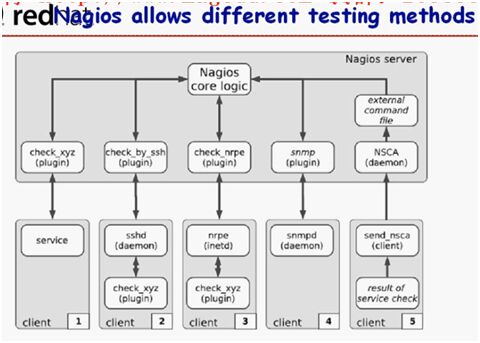
如下图,nagios对某一监控对象进行监控,要通过某一手段获取远端主机相关的属性状态信息,cacti基于SNMP工作,nagios也如此,nagios core不进行任何监控工作,通过各种插件来监控,插件分五类:check_by_ssh、check_nrpe、snmp、NSCA、check_xyz
ssh(在远端server(被监控端)上运行sshdaemon,被监控端要能接受监控端的ssh命令,插件将取得的结果予以分析,将分析的结果返回给nagios core,由core决定是否报警)
nrpe(非常独特,专用于监控linux或unix主机的机制,要在远端server上专门安装一nrpe程序,nrpe在被监控端运行将有监控结果,将结果返回给监控端的nrpe,监控端的nrpe再将结果返回给nagios core,可将这种方式理解为是C/S架构,监控端的nrpe是client,而被监控端是server-side)
snmp(在监控端每隔一段时间运行一堆snmp命令,联系到被监控端的snmpd(161port),通过本地的插件分析将结果返回至nagios core,snmp专用于监控那些既不支持ssh又不支持nrpe的主机,如win主机支持snmp、nrpe,但nagios并不优先使用基于snmp来监控win,而是使用NSclient++(专门在win主机上的客户端工具,是win的WMI组件),这个工具运行起来可实现nagios与win通信并且可获取win上资源的运行状态,并最终返回给nagios core)
nsca(snmp协议中有一种机制是trap,被监控端可主动通知监控端,nsca就是这么一种被监控机制,让nagios实现被动监控功能)
监控linux|unix有nrpe/snmp/nsca;监控win在win上安装NSclient++;监控router/switch/printer用snmp
ssh|nrpe|NSclient|snmp|nsca有些实现专门监控主机有些实现专门监控服务,这些本身并不是监控,而具体监控是由插件来实现的,这些只是让插件获取性能数据的一种手段、一种基础,而有些服务在监控时可直接使用插件来实现而不用借助额外的任何手段
例如要监控一台linux主机:
要定义主机对象(实例化监控对象的过程,说明监控的是哪个主机ip地址);
要使用什么命令来监控(要定义命令对象,定义监控这个主机使用什么插件来监控,真正监控靠的是插件,插件能够监控的对象有很多,可用的插件也有很多,定义好命令把插件写里面,用这个命令对象监控这个主机对象,创建命令的过程就是实例化具体化插件的过程,创建对象的过程就是实例化被监控对象的过程;可使用多个命令来监控主机,如有的是监控主机资源、有的监控主机服务等,它们之间未必是一对一关系);
一旦这个主机出故障应通知给谁(定义联系人对象,联系人对象名字、邮件、手机号,说明白通知的接收者,可使用联系人组
监控工作什么时候进行(要定义时段,是7*24都监控还是只在工作日内监控,联系人可在哪些时段接受通知,若server出现的是微小故障不是特别严重不必要半夜接到通知,还可定义例行维护时段不做监控)
nagios还可定义主机间的依赖关系(如router下有swith,switch下有N个主机,nagios既监控router、switch也监控这些主机,若switch故障就要发警告信息,由于switch故障其下的主机当然不能监控到,可定义依赖如switch故障就不需要再检测监控主机了,否则会收到一堆信息
依赖有彼此间依赖(双向依赖)和上下依赖(父子间依赖);如两台host间相互依赖,那host1故障将不会收到host2的警告信息(不监控host2),host2故障也不收host1的警告信息(不监控host1);如既监控某主机,又监控主机上的一些服务,当这台主机挂掉时其上运行的服务就没必要监控了
nagios强大到能分析这些依赖关系,要事先定义好
以上nagios是种监控机制,通过插件进行监控,监控状态很简单只返回4种状态,OK、WARNING、CRITICAL、UNKNOWN
发通知要由一种状态转为另一种状态才向管理员发通知(如OK-->CRITICAL);有可能这样一种特殊情况,nagios监控某主机的一个服务,这个服务由于过于繁忙没及时响应(监控触发到被监控端,被监控端要消耗一些资源予以响应监控端),状态这时为UNKNOWN
状态有软状态和硬状态之分(当监控端发现状态发生改变,会重复多次检测,如OK-->UNKNOWN并不会立即发通知,再重复两次若仍为UNKNOWN就转为硬状态这时才通知,因为软状态的错误可能是临时性、偶然性的
还有一种非正常状态叫flapping(OK-->WARNING-->CRITICAL-->OK-->UNKNOWN-->OK),一旦主机处于此状态也要发通知
nagios提供了web接口(依赖php),像cacti那样展示出来(不但展示还发告警通知),要使用web接口则要装httpd,nagios的web server也要依赖于php,它也是一堆php script,在某些情况下要用到mysql(状态数据并不需要保存在mysql中,除非使用别的工具时),编译安装nagios时要装mysql,要监控mysql server时要调用mysql的头文件、库文件
nagios通常由一个主程序nagios(或叫nagioscore),一个插件程序(nagios-plugins)和四个可选的附件addon(NRPE、NSCA、NSclient++、NDOUtils)组成
注:NDOUtils用来将nagios的配置信息和各事件产生的数据存入数据库,以实现这些数据的快速检索和处理,可理解为是broker掮客,它能阻断nagios core自身的工作,在nagios core上附加一层新功能,将nagios core本来应该保存在文件中的信息,夺过来保存到数据库中(改变了原先应该走的方向)
安装nagios server-side要装nagios、nagios-plugins、httpd
NRPE(要实现基于NRPE监控linux则要装NRPE,客户端也要装NRPE,NRPE的运行依赖nagios-plugins,在client装NRPE前先安装nagios-plugins)
若要使用snmp监控别的主机,nagios-plugins已提供了snmp功能
若要监控windows,在win上装NSclient++
若要用NSCA,客户端要装上send-nsca,服务器端只要开启NSCA的功能(nagios自带的功能)
nagios监控win的手段有两种(snmp和NSClinet++)
注:NSClient++功能非常强大,可监测win的各种资源,如cpu/memory/disk spare/process/services,此工具还提供nrpe的能力和nsca的能力)
nagios与NSClient++通信(通信机制有N种,默认的且最简单常用的一种是nagios使用插件check_nt(如要监控win主机CPU状况使用check_nt命令并传递一些参数给NSClient++,NSClient++收到后在本地执行检测命令再返回给check_nt),这种方式虽易用但监测能力是最弱的;还可用nrpe功能,使用check_nrpe,建议使用此种check_nrpe监测能力更强大;通过nsca可实现被动检测,nagios监控端需要nsca daemon接受对方发来的检测结果)
注:check_nt的监控能力较弱,最好用check_nrpe
NRPE(nagios remote pluginexecutor)
二、操作:
[[email protected] ~]# uname -a(redhat6.5)
Linux localhost.localdomain2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Sun Nov 10 22:19:54 EST 2013 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64GNU/Linux
准备LAMP环境
同步系统时间
准备软件包:
nagios-3.3.1.tar.gz
nagios-plugins-1.4.14.tar.gz
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install httpd php php-mysql mysql mysql-devel mysql-server
[[email protected] ~]# groupadd nagcmd(nagios的运行需要特殊的用户和组,这个组至关重要,很多nagios的管理功能一些cgi脚本的执行都要有这个组的权限才能执行)
[[email protected] ~]# useradd -G nagcmd nagios
[[email protected] ~]# passwd nagios
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf(二进制格式包安装的httpd,用户名和组为apache,源码方式安装为daemon)
User apache
Group apache
[[email protected] ~]# usermod -a -G nagcmd apache
[[email protected] ~]# tar xf nagios-3.3.1.tar.gz
[[email protected] ~]# cd nagios
[[email protected] nagios]# ./configure --help| less
[[email protected] nagios]# ./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd --enable-event-broker --sysconfdir=/etc/nagios(--enable-event-broker,enables integration of event broker routines为ndo-utils作准备,无这个选项要使用nagios得重新编译)
……
Review the options above for accuracy. If they look okay,
type ‘make all‘ to compile the main program and CGIs.
[[email protected] nagios]# make all
[[email protected] nagios]# make install(安装nagios)
[[email protected] nagios]# make install-init(安装nagios的相关脚本,例如可使用servicestart|stop等)
[[email protected] nagios]# make install-commandmode(命令权限)
[[email protected] nagios]# make install-config(安装生成配置文件)
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -gnagios -d /etc/nagios
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -gnagios -d /etc/nagios/objects
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/nagios.cfg /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/cgi.cfg /etc/nagios/cgi.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 660 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/resource.cfg /etc/nagios/resource.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/templates.cfg /etc/nagios/objects/templates.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/commands.cfg/etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/contacts.cfg /etc/nagios/objects/contacts.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/timeperiods.cfg/etc/nagios/objects/timeperiods.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/localhost.cfg /etc/nagios/objects/localhost.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/windows.cfg/etc/nagios/objects/windows.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/printer.cfg /etc/nagios/objects/printer.cfg
/usr/bin/install -c -b -m 664 -o nagios -gnagios sample-config/template-object/switch.cfg /etc/nagios/objects/switch.cfg
*** Config files installed ***
Remember, these are *SAMPLE* configfiles. You‘ll need to read
the documentation for more information onhow to actually define
services, hosts, etc. to fit yourparticular needs.
[[email protected] nagios]# make install-webconf(会自动在/etc/httpd/conf.d/下生成nagios.conf配置文件,用于web接口,用于识别nagios程序配置,网页在/usr/local/nagios/share/下,这个配置文件可理解为路径别名,之后可通过http://192.168.23.137/nagios访问)
/usr/bin/install -c -m 644sample-config/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf
*** Nagios/Apache conf file installed ***
[[email protected] nagios]# htpasswd -c /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin(nagios的登录认证机制是用httpd的方式实现的)
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user nagiosadmin
[[email protected] nagios]# service httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
Starting httpd: [ OK ]
[[email protected] nagios]# chkconfig --add nagios
[[email protected] nagios]# chkconfig --list nagios
nagios 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[[email protected] nagios]# service nagios start
Starting nagios: done.
[[email protected] nagios]# cd ..
[[email protected] ~]# tar xf nagios-plugins-1.4.14.tar.gz
[[email protected] ~]# cd nagios-plugins-1.4.14
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-1.4.14]#./configure --help | less
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-1.4.14]#./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios--sysconfdir=/etc/nagios
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-1.4.14]#make && make install
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-1.4.14]#service nagios restart(要关掉selinux否则会阻止cgi脚本的运行,#setenforce 0)
Running configuration check...done.
Stopping nagios: done.
Starting nagios: done.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-1.4.14]# cd
[[email protected] ~]# ls /etc/nagios
cgi.cfg htpasswd.users nagios.cfg objects resource.cfg
[[email protected] ~]# ls /etc/nagios/objects(objects/下的这些对象可放在任意位置,只要在主配置文件nagios.cfg中将其包含进来即可)
commands.cfg contacts.cfg localhost.cfg printer.cfg switch.cfg templates.cfg timeperiods.cfg windows.cfg
访问http://192.168.23.137/nagios
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg(cfg_dir定义的目录下的所有文件都会加载进来)
log_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.log
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/contacts.cfg
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/timeperiods.cfg
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/templates.cfg
cfg_file=/etc/nagios/objects/localhost.cfg
#cfg_dir=/etc/nagios/servers
resource_file=/etc/nagios/resource.cfg
status_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/status.dat
status_update_interval=10
check_external_commands=1
command_check_interval=-1
command_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagiosNaNd
lock_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.lock
temp_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.tmp
temp_path=/tmp
log_rotation_method=d
……
注:command_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagiosNaNd,定义command的执行权限和执行身份,不是定义command本身
[[email protected] ~]# vim/etc/nagios/resource.cfg(对nagios而言$USER1$是宏(变量),由变量定义的配置文件,nagios支持32个宏,从$USER1$到$USER32$,默认$USER1$已使用,这些宏可理解为是nagios的环境变量,除31个可自定义的宏外,nagios还支持原生态的宏,不必事先定义的,如$HOSTADDRESS$会根据上下文的不同用来表示不同的主机;resource.cfg此文件一般不允许通过前端的web接口访问,正是通过此配置文件剥离了用户接口与cgi的内容,cgi若要访问用户的配置信息可调用这个文件,但在web接口访问不到,加强其安全性)
$USER1$=/usr/local/nagios/libexec
[[email protected] ~]# ls /usr/local/nagios/libexec(其下是一堆的插件,要引用某一个插件时,使用$USER1$/PLUGINS_NAME即可)
[[email protected] ~]# vim /usr/local/nagios/var/status.dat(nagios监测的某一服务或主机在某一时刻都有状态,保留所有状态的数据文件)
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/nagios/objects
[[email protected] objects]# vim commands.cfg
define command{
command_name notify-host-by-email(必须要全局唯一,两个command_name一定不能重名,至关重要)
command_line /usr/bin/printf"%b" "***** Nagios *****\n\nNotification Type:$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$\nHost: $HOSTNAME$\nState: $HOSTSTATE$\nAddress: $HOSTADDRESS$\nInfo:$HOSTOUTPUT$\n\nDate/Time: $LONGDATETIME$\n" | /bin/mail -s "**$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$ Host Alert: $HOSTNAME$ is $HOSTSTATE$ **"$CONTACTEMAIL$
}
……
define command{
command_name check-host-alive
command_line $USER1$/check_ping-H $HOSTADDRESS$ -w 3000.0,80% -c 5000.0,100% -p 5(-w,warning,警告预值,有80%的丢包率且延迟为3000ms就警告;-c,critical的预值;-p,package,共检测几个数据包)
}
define command{
command_name check_local_disk
command_line $USER1$/check_disk-w $ARG1$ -c $ARG2$ -p $ARG3$($ARG#$在不同的主机上可传递不同的参数)
}
[[email protected] objects]# vim contacts.cfg
define contact{
contact_name nagiosadmin ; Shortname of user(contact_name定义的要全局唯一)
use generic-contact ; Inheritdefault values from generic-contact template (defined above)(use从哪个模板继承的一些属性)
alias Nagios Admin ; Fullname of user(描述性的名字,方便查看)
email [email protected] ;<<***** CHANGE THIS TO YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS ******
}
[[email protected] objects]# vim timeperiods.cfg
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name 24x7(timeperiod_name全局唯一)
alias 24 Hours A Day, 7Days A Week
sunday 00:00-24:00
monday 00:00-24:00
tuesday 00:00-24:00
wednesday 00:00-24:00
thursday 00:00-24:00
friday 00:00-24:00
saturday 00:00-24:00
}
[[email protected] objects]# vim localhost.cfg
define host{
use linux-server ; Name of host template to use
; This host definition will inherit all variables that are defined(use使用哪个模板)
; in (or inherited by) the linux-server host template definition.
host_name localhost(host_name全局唯一)
alias localhost
address 127.0.0.1
}
define service{
use local-service ; Name ofservice template to use
host_name localhost(先定义好主机,再定义服务,服务必须是某个主机的服务,服务要全局唯一)
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%(!100.0,20%,表示传递的第一个参数,!500.0,60%表示传递的第二个参数;要先在commands.cfg中定义好check_ping)
}
1、
通过check_nt方式监控windows主机
windows-side(被监控端):
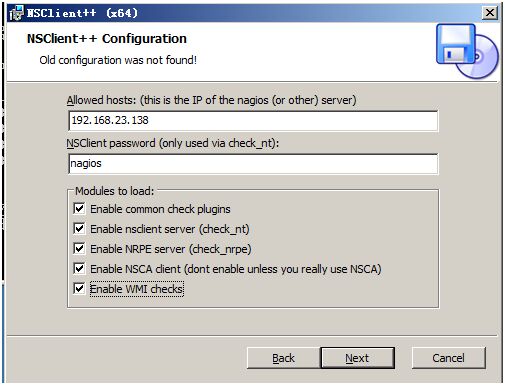
在win主机上安装NSClinet++(http://nsclient.org/)
注意Allowed hosts为监控端naigos的地址
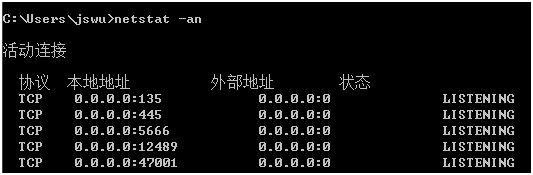
在win上使用netstat -an查看12489port是否开启,默认是1248已改为12489,这是check_nt插件与NSClient++通信的端口;5666是nrpe使用的端口
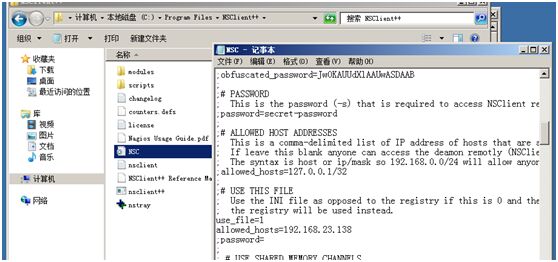
修改win上MSC配置文件将password注释掉,方便监控端配置,否则监控端每个监控语句都要多配置一个参数用来传递密码(生产环境中要设置)
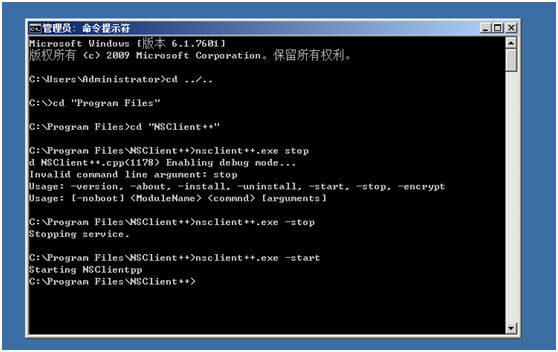
在win命令行下重启服务(>nsclinet++.exe -stop,>nsclient++.exe-start)
nagios-side(监控端):
[[email protected] objects]# ifconfig | grep "inet addr:"
inet addr:192.168.23.138 Bcast:192.168.23.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
[[email protected] objects]# cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec/
[[email protected] libexec]# ll check_nt
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 nagios nagios 95456 Apr 1 15:59 check_nt
[[email protected] libexec]# ./check_nt -h
Usage:check_nt -H host -v variable [-p port] [-w warning] [-c critical] [-l params] [-d SHOWALL] [-u] [-t timeout]
注:-H,--hostname=HOST
-v,--variable=STRING(variable有CLIENTVERSION,CPULOAD,UPTIME,USEDDISKSPACE,MEMUSE,SERVICESTATE,PROCSTATE,COUNTER,INSTANCES)
[[email protected] libexec]# ./check_nt -H 192.168.23.140 -v UPTIME -p 12489 -s nagios
System Uptime - 0 day(s) 0 hour(s) 40minute(s)
[[email protected] libexec]# ./check_nt -H 192.168.23.140 -p 12489 -v CPULOAD -w 80 -c 90 -l 5,80,90 -s nagios(显示的结果分性能信息和一般信息,用竖线|隔开,注意若自己开发插件时,性能信息和一般信息必须要使用竖线隔开)
CPU Load 0% (5 min average) | ‘5 min avg Load‘=0%;80;90;0;100
[[email protected] libexec]# ./check_nt -H 192.168.23.140 -p 12489 -v USEDDISKSPACE -w 80 -c 90 -l C -s nagios
C:\ - total: 40.00 Gb - used: 8.96 Gb (22%)- free 31.04 Gb (78%) | ‘C:\ Used Space‘=8.96Gb;32.00;36.00;0.00;40.00
[[email protected] libexec]# cd /etc/nagios/objects
[[email protected] objects]# vim commands.cfg
define command{
command_name check_nt
command_line $USER1$/check_nt-H $HOSTADDRESS$ -p 12489 -v $ARG1$ $ARG2$
}
[[email protected] objects]# vim windows.cfg
define host{
use windows-server ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name winserver ; The name we‘re giving to this host
alias My WindowsServer ; A longer name associatedwith the host
address 192.168.23.140 ; IP address of the host
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description NSClient++Version
check_command check_nt!CLIENTVERSION
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description Uptime
check_command check_nt!UPTIME
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nt!CPULOAD!-l 5,80,90
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description MemoryUsage
check_command check_nt!MEMUSE!-w 80 -c 90
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description C:\ DriveSpace
check_command check_nt!USEDDISKSPACE!-l c -w 80 -c 90
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description W3SVC
check_command check_nt!SERVICESTATE!-d SHOWALL -l W3SVC
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name winserver
service_description
以上是关于VI nagios的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章