uboot学习之二----主Makefile学习之四----两种编译方法:原地编译和单独输出文件夹编译
Posted 岳睿_02
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了uboot学习之二----主Makefile学习之四----两种编译方法:原地编译和单独输出文件夹编译相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
第57-123行:
57 #
58 # U-boot build supports producing a object files to the separate external
59 # directory. Two use cases are supported:
60 #
61 # 1) Add O= to the make command line
62 # \'make O=/tmp/build all\'
63 #
64 # 2) Set environement variable BUILD_DIR to point to the desired location
65 # \'export BUILD_DIR=/tmp/build\'
66 # \'make\'
67 #
68 # The second approach can also be used with a MAKEALL script
69 # \'export BUILD_DIR=/tmp/build\'
70 # \'./MAKEALL\'
71 #
72 # Command line \'O=\' setting overrides BUILD_DIR environent variable.
73 #
74 # When none of the above methods is used the local build is performed and
75 # the object files are placed in the source directory.
76 #
77
78 ifdef O
79 ifeq ("$(origin O)", "command line")
80 BUILD_DIR := $(O)
81 endif
82 endif
83
84 ifneq ($(BUILD_DIR),)
85 saved-output := $(BUILD_DIR)
86
87 # Attempt to create a output directory.
88 $(shell [ -d ${BUILD_DIR} ] || mkdir -p ${BUILD_DIR})
89
90 # Verify if it was successful.
91 BUILD_DIR := $(shell cd $(BUILD_DIR) && /bin/pwd)
92 $(if $(BUILD_DIR),,$(error output directory "$(saved-output)" does not exist))
93 endif # ifneq ($(BUILD_DIR),)
94
95 OBJTREE := $(if $(BUILD_DIR),$(BUILD_DIR),$(CURDIR))
96 SRCTREE := $(CURDIR)
97 TOPDIR := $(SRCTREE)
98 LNDIR := $(OBJTREE)
99 export TOPDIR SRCTREE OBJTREE
100
101 MKCONFIG := $(SRCTREE)/mkconfig
102 export MKCONFIG
103
104 ifneq ($(OBJTREE),$(SRCTREE))
105 REMOTE_BUILD := 1
106 export REMOTE_BUILD
107 endif
108
109 # $(obj) and (src) are defined in config.mk but here in main Makefile
110 # we also need them before config.mk is included which is the case for
111 # some targets like unconfig, clean, clobber, distclean, etc.
112 fneq ($(OBJTREE),$(SRCTREE))
113 obj := $(OBJTREE)/
114 src := $(SRCTREE)/
115 else
116 obj :=
117 src :=
118 endif
119 export obj src
120
121 # Make sure CDPATH settings don\'t interfere
122 unexport CDPATH
123
编译复杂项目:makefile提供两种编译管理方法,默认情况是原地编译。
原地编译的缺点:
第一:污染源文件目录。第二:一套源代码只能按照一种配置和编译方法进行处理,无法同时维护超过两个或两个以上的配置编译方法。
输出文件夹编译:
为了解决以上缺陷,采用单独输出文件夹的方式编译,Linux kernel支持这样的方法,具体实现思路是:将所有编译生成的.o文件或者
其他文件全部输出到指定好的目录。uboot也学习了这样的方法。
具体做法:
见57行---76行的注释:
①在命令行编译时制定make O=输出目录(注意配置时也要加O=输出目录)
make O=/tmp/build all
比如我们在root@ubuntu:/usr/local/arm/qt_x210v3/uboot这里面创建一个output文件夹来作为输出目录:
三步: make O=output/ distclean
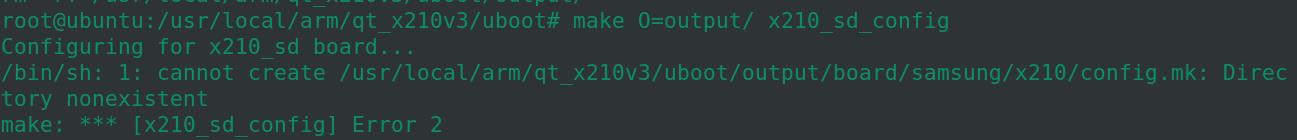
make O=output/ x210_sd_config
这一步出错:
解决方法:进入output文件夹后手工创建这个文件:
root@ubuntu:/usr/local/arm/qt_x210v3/uboot/output# mkdir board/samsung/x210 -p
然后重新配置。
make O=output/ all
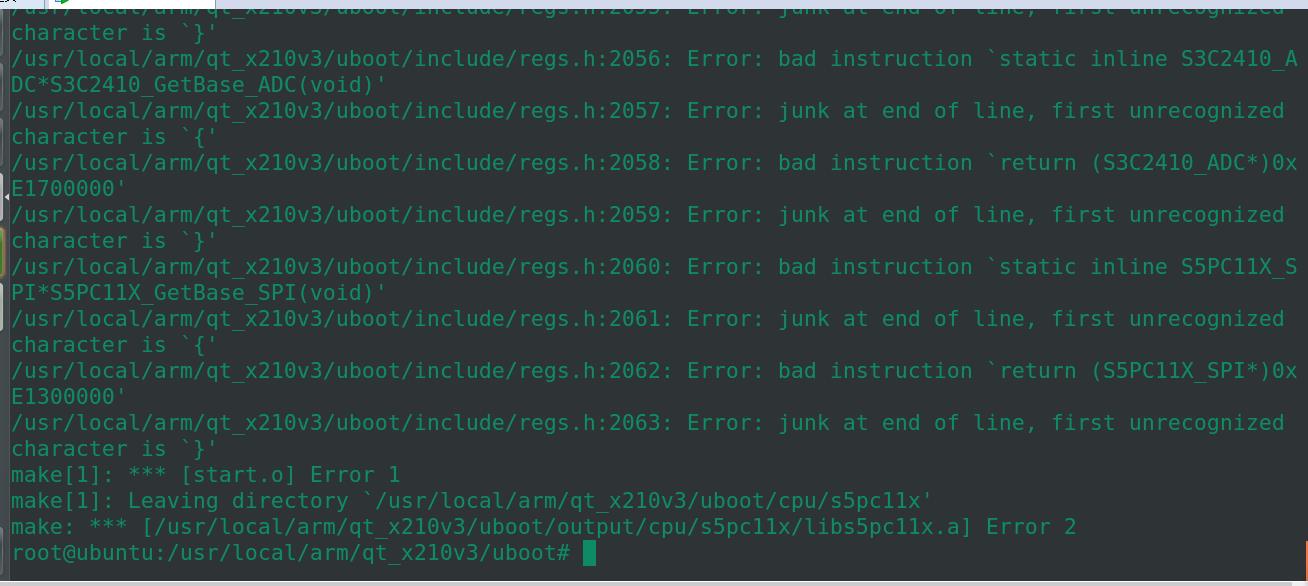 最后发现还是有问题。应该是整个uboot移植时还是不行的。我们以后使用三星版本的uboot进行移植再来研究。
最后发现还是有问题。应该是整个uboot移植时还是不行的。我们以后使用三星版本的uboot进行移植再来研究。
②设置环境变量BUILD_DIR指出期望的输出目录。
\'export BUILD_DIR=/tmp/build\'
\'make\'
第二种方法也可以通过MAKEALL脚本实现。
\'export BUILD_DIR=/tmp/build\' \'./MAKEALL\'
make o=输出目录会覆盖BUILD_DIR
很多bsp开发都使用这样的方式,所以有利于后面学习。
两种编译方法的makefile代码实现在78---123行
以上是关于uboot学习之二----主Makefile学习之四----两种编译方法:原地编译和单独输出文件夹编译的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章