65)STL中string的知识
Posted 小油菜123
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了65)STL中string的知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

1)代码展示: string是一个类,只不过封装了 char* 而且还封装了 很多的字符串操作函数
2)string类的初始化:
string的构造函数
² 默认构造函数:
string(); //构造一个空的字符串string s1。
² 拷贝构造函数:
string(const string &str); //构造一个与str一样的string。如string s1(s2)。
² 带参数的构造函数
string(const char *s); //用字符串s初始化
string(int n,char c); //用n个字符c初始化
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 //字符串对象的初始化 6 void hanshu() 7 { 8 string s1="dhajds"; 9 string s2=string("dhskad"); 10 string s3=string(s1);//此时s3和s1是一样的,将s3内容复制一份给了s3 11 string s4=string(\'a\',4);//用4个a对s4进行初始化 12 }
4)字符串的遍历
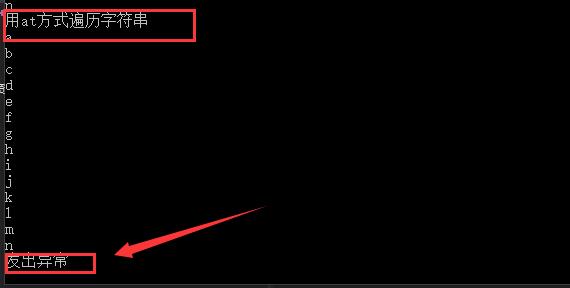
总共是三种,其中那个at()是可以抛出异常,我们可以捕捉的:
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 //字符串对象的初始化 6 void hanshu() 7 { 8 string s1="dhajds"; 9 string s2=string("dhskad"); 10 string s3=string(s1);//此时s3和s1是一样的,将s3内容复制一份给了s3 11 string s4=string(\'a\',4);//用4个a对s4进行初始化 12 } 13 //字符串的遍历 14 void bianli(string s) 15 { 16 //第一种,因为字符串重载了数组操作符 所以可以像遍历数组那样,进行遍历 17 18 //数组方式 19 cout<<"数组方式来进行遍历字符串"<<endl; 20 for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) 21 { 22 cout<<s[i]<<endl; 23 } 24 25 ///第二种是 通过迭代器 26 cout<<"迭代器方式来进行遍历字符串"<<endl; 27 for(string::iterator t=s.begin();t<s.end();t++) 28 { 29 cout<<*t<<endl; 30 } 31 32 //第三种,用at方式 33 cout<<"用at方式遍历字符串"<<endl; 34 try{ 35 for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) 36 { 37 cout<<s.at(i)<<endl;//抛出异常 38 } 39 } 40 catch(...){ 41 cout<<"发出异常"<<endl; 42 } 43 44 } 45 int main() 46 { 47 string s="abcdefghijklmn"; 48 bianli(s); 49 return 0; 50 }
然后 ,加入我的代码发生了问题,比如 我的 数组遍历方式有问题
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 //字符串对象的初始化 6 void hanshu() 7 { 8 string s1="dhajds"; 9 string s2=string("dhskad"); 10 string s3=string(s1);//此时s3和s1是一样的,将s3内容复制一份给了s3 11 string s4=string(\'a\',4);//用4个a对s4进行初始化 12 } 13 //字符串的遍历 14 void bianli(string s) 15 { 16 //第一种,因为字符串重载了数组操作符 所以可以像遍历数组那样,进行遍历 17 18 //数组方式 19 cout<<"数组方式来进行遍历字符串"<<endl; 20 for(int i=0;i<s.length()+3;i++)//我这里i多了3,越界了 21 { 22 cout<<s[i]<<endl; 23 } 24 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 string s="abcdefghijklmn"; 29 bianli(s); 30 return 0; 31 }
最后结果展示 直接代码崩掉
然后你再看我的at(),有异常抛出的代码处理问题的方式:
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 //字符串对象的初始化 6 void hanshu() 7 { 8 string s1="dhajds"; 9 string s2=string("dhskad"); 10 string s3=string(s1);//此时s3和s1是一样的,将s3内容复制一份给了s3 11 string s4=string(\'a\',4);//用4个a对s4进行初始化 12 } 13 //字符串的遍历 14 void bianli(string s) 15 { 16 //第三种,用at方式 17 cout<<"用at方式遍历字符串"<<endl; 18 try{ 19 for(int i=0;i<s.length()+3;i++) 20 { 21 cout<<s.at(i)<<endl;//抛出异常 22 } 23 } 24 catch(...){ 25 cout<<"发出异常"<<endl; 26 } 27 28 } 29 int main() 30 { 31 string s="abcdefghijklmn"; 32 bianli(s); 33 return 0; 34 }
结果展示:
5)字符串:字符指针和string类的转换
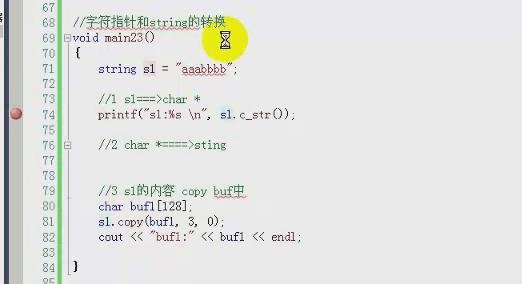
copy 不会在 拷贝的字符后面加 \'\\0\' 所以 要自己加上,而且 最好 char buf【128】={0},这样初始化
6)字符串的赋值
1 string &operator=(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前的字符串 2 string &assign(const char *s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串 3 string &assign(const char *s, int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串 4 string &assign(const string &s); //把字符串s赋给当前字符串 5 string &assign(int n,char c); //用n个字符c赋给当前字符串 6 string &assign(const string &s,int start, int n); //把字符串s中从start开始的n个字符赋给当前字符串
7)字符串的拼接:
1 string &operator+=(const string &s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾 2 string &operator+=(const char *s);//把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾 3 string &append(const char *s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾 4 string &append(const char *s,int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾 5 string &append(const string &s); //同operator+=() 6 string &append(const string &s,int pos, int n);//把字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾 7 string &append(int n, char c); //在当前字符串结尾添加n个字符c
8)与字符串比较
1 int compare(const string &s) const; //与字符串s比较 2 int compare(const char *s) const; //与字符串s比较 3 compare函数在>时返回 1,<时返回 -1,==时返回 0。比较区分大小写,比较时参考字典顺序,排越前面的越小。大写的A比小写的a小。
9)字符串的子串
string substr(int pos=0, int n=npos) const; //返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的子字符串
1 string s="abcdefghijklmn"; 2 cout<<s.substr(0,4)<<endl;
10)字符串的查找和替换
1 查找 2 int find(char c,int pos=0) const; //从pos开始查找字符c在当前字符串的位置 3 int find(const char *s, int pos=0) const; //从pos开始查找字符串s在当前字符串的位置 4 int find(const string &s, int pos=0) const; //从pos开始查找字符串s在当前字符串中的位置 5 find函数如果查找不到,就返回-1 6 int rfind(char c, int pos=npos) const; //从pos开始从后向前查找字符c在当前字符串中的位置 7 int rfind(const char *s, int pos=npos) const; 8 int rfind(const string &s, int pos=npos) const; 9 //rfind是反向查找的意思,如果查找不到, 返回-1 10 11 替换 12 string &replace(int pos, int n, const char *s);//删除从pos开始的n个字符,然后在pos处插入串s 13 string &replace(int pos, int n, const string &s); //删除从pos开始的n个字符,然后在pos处插入串s 14 void swap(string &s2); //交换当前字符串与s2的值 15 16 //4 字符串的查找和替换 17 void main25() 18 { 19 string s1 = "wbm hello wbm 111 wbm 222 wbm 333"; 20 size_t index = s1.find("wbm", 0); 21 cout << "index: " << index; 22 23 24 //求itcast出现的次数 25 size_t offindex = s1.find("wbm", 0); 26 while (offindex != string::npos) 27 { 28 cout << "在下标index: " << offindex << "找到wbm\\n"; 29 offindex = offindex + 1; 30 offindex = s1.find("wbm", offindex); 31 } 32 33 //替换 34 string s2 = "wbm hello wbm 111 wbm 222 wbm 333"; 35 s2.replace(0, 3, "wbm"); 36 cout << s2 << endl; 37 38 //求itcast出现的次数 39 offindex = s2.find("wbm", 0); 40 while (offindex != string::npos) 41 { 42 cout << "在下标index: " << offindex << "找到wbm\\n"; 43 s2.replace(offindex, 3, "WBM"); 44 offindex = offindex + 1; 45 offindex = s1.find("wbm", offindex); 46 } 47 cout << "替换以后的s2:" << s2 << endl; 48 }
11)字符串的区间删除和插入
1 string &insert(int pos, const char *s); 2 string &insert(int pos, const string &s); 3 //前两个函数在pos位置插入字符串s 4 string &insert(int pos, int n, char c); //在pos位置 插入n个字符c 5 6 string &erase(int pos=0, int n=npos); //删除pos开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串
12)字符串的算法相关
1 void main27() 2 { 3 string s2 = "AAAbbb"; 4 transform(s2.begin(), s2.end(), s2.begin(), toupper); 5 cout << s2 << endl; 6 7 string s3 = "AAAbbb"; 8 transform(s3.begin(), s3.end(), s3.begin(), tolower); 9 cout << s3 << endl; 10 }
以上是关于65)STL中string的知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
2022-08-05:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:65, string;B:A, string;C:65, int;D:报错。