map的默认排序和自定义排序
Posted 不知期
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了map的默认排序和自定义排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
STL的容器map为我们处理有序key-value形式数据提供了非常大的便利,由于内部红黑树结构的存储,查找的时间复杂度为O(log2N)。
一般而言,使用map的时候直接采取map<typename A, typename B>的形式即可,map的内部实现默认使用A类型变量的升序来排序map的值。
但是有时我们需要对map的值做特殊的排序(不经其他容器的辅助),这就需要在定义map变量时做些特殊的处理。
STL中map的定义是:
1 template<class _Kty, 2 class _Ty, 3 class _Pr = less<_Kty>, 4 class _Alloc = allocator<pair<const _Kty, _Ty>>> 5 class map 6 : public _Tree<_Tmap_traits<_Kty, _Ty, _Pr, _Alloc, false>> 7 {
这是一个模板类,我们的特殊处理主要改造的就是class _Pr = less<_Kty>,并且从这里我们也能看到,无论做哪种修改,排序都是针对key而言的,要实现value的自定义排序,
不是修改_Pr类型能完成的。
替换_Pr的也必须是一个类型,即至少我们要自己创建一个类型,用来做key的比较。自然,我们需要做的是重载函数调用操作符"()",一般的形式为
1 class T{ 2 public: 3 bool operator()(const T& lhs, const T& rhs)const 4 { 5 ... 6 } 7 };
代码需包含头文件<algorithm>、<functional>。
下面是常见的一些自定义排序:
a.对基本类型的key以降序排列
map默认提供的是less<_Kty>类型的排序方式,阅读STL源码
1 template<class _Ty = void> 2 struct less 3 { // functor for operator< 4 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty first_argument_type; 5 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty second_argument_type; 6 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef bool result_type; 7 8 constexpr bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const 9 { // apply operator< to operands 10 return (_Left < _Right); 11 } 12 };
修改上述代码的第10行,为修改后的类型起一个自定义名字很简单,不过STL已经为我们提供了整个类型定义:
1 template<class _Ty = void> 2 struct greater 3 { // functor for operator> 4 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty first_argument_type; 5 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty second_argument_type; 6 _CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef bool result_type; 7 8 constexpr bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const 9 { // apply operator> to operands 10 return (_Left > _Right); 11 } 12 };
我们直接使用就行:
1 std::map<int, int, std::greater<int>> mi; 2 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 3 { 4 mi[i] = i * 2; 5 } 6 7 std::for_each(mi.begin(), mi.end(), 8 [](const std::map<int, int, std::greater<int>>::value_type& vl) { 9 cout << "key:" << vl.first << " value:" << vl.second << \'\\n\'; 10 });
对应的输出为:
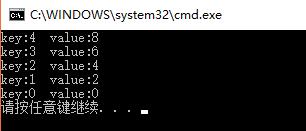
这里,我们实现了按key降序排列的目的。
b.为自定义类型的key做排序:
自定义类型的key定义map时(使用map默认排序),我们一般都要做一件事:为自定义类型重载“<”操作符,显然,这是为了map创建对象时可以使用less。
因此,我们替换less<_Kty>也同样是要做这样的事:自定义排序规则, 比如:
1 class MyKey { 2 public: 3 MyKey(int fidx = 0, int sidx = 0) 4 :m_firstIdx(fidx), m_secondIdx(sidx) {} 5 6 int m_firstIdx; 7 int m_secondIdx; 8 }; 9 10 class MyCompare{ 11 public: 12 bool operator()(const MyKey& lhs, const MyKey& rhs)const 13 { 14 if (lhs.m_firstIdx > rhs.m_firstIdx) 15 { 16 return true; 17 } 18 else if (lhs.m_firstIdx == rhs.m_firstIdx) 19 { 20 return lhs.m_secondIdx > rhs.m_secondIdx; 21 } 22 return false; 23 } 24 }; 25 26 class MyCompare2 { 27 public: 28 bool operator()(const MyKey& lhs, const MyKey& rhs)const 29 { 30 return lhs.m_firstIdx > rhs.m_firstIdx; 31 } 32 };
使用MyCompare:
1 std::map<MyKey, int, MyCompare> mi; 2 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 3 { 4 mi[MyKey(i * 2, i)] = i * 2; 5 } 6 7 std::for_each(mi.begin(), mi.end(), 8 [](const std::map<MyKey, int, MyCompare>::value_type& vl) { 9 cout << "key:" << vl.first.m_firstIdx << "-" << vl.first.m_secondIdx << " value:" << vl.second << \'\\n\'; 10 });
使用MyCompare2:
1 std::map<MyKey, int, MyCompare2> mi; 2 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 3 { 4 mi[MyKey(i * 2, i)] = i * 2; 5 } 6 7 std::for_each(mi.begin(), mi.end(), 8 [](const std::map<MyKey, int, MyCompare2>::value_type& vl) { 9 cout << "key:" << vl.first.m_firstIdx << "-" << vl.first.m_secondIdx << " value:" << vl.second << \'\\n\'; 10 });
以上两种有相同的输出:
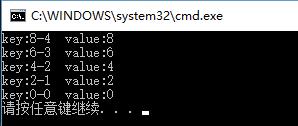
我们实现了自定义类型自定义排序的目的。
可以看到,使用map其实有很大的自由度,我们完全可以定制自己的map,为我们解决问题、精简代码带来很大的便利。
以上是关于map的默认排序和自定义排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章