三 概要模式 2) MR倒排索引性能分析搜索干扰词。
Posted rocky_24
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了三 概要模式 2) MR倒排索引性能分析搜索干扰词。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
有两种不同的反向索引形式:
后者的形式提供了更多的兼容性(比如短语搜索),但是需要更多的时间和空间来创建。
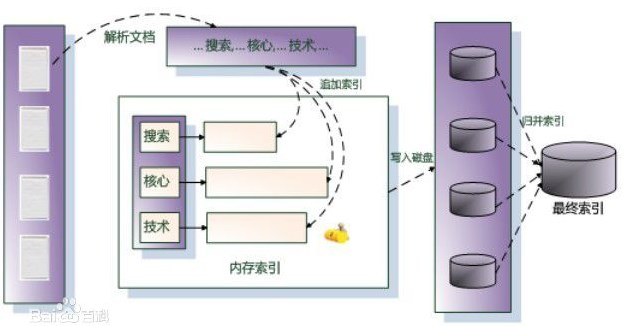
以英文为例,下面是要被索引的文本:
"it is what it is"
"what is it"
"it is a banana"
我们就能得到下面的反向文件索引:
"a": {2}
"banana": {2}
"is": {0, 1, 2}
"it": {0, 1, 2}
"what": {0, 1}
检索的条件"what", "is" 和 "it" 将对应这个集合: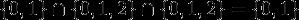 。
。
对相同的文字,我们得到后面这些完全反向索引,有文档数量和当前查询的单词结果组成的的成对数据。 同样,文档数量和当前查询的单词结果都从零开始。所以,"banana": {(2, 3)} 就是说 "banana"在第三个文档里 ( ),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
"a": {(2, 2)}
"banana": {(2, 3)}
"is": {(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 1)}
"it": {(0, 0), (0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 0)}
"what": {(0, 2), (1, 0)}
如果我们执行短语搜索"what is it" 我们得到这个短语的全部单词各自的结果所在文档为文档0和文档1。但是这个短语检索的连续的条件仅仅在文档1得到。
2.分析和设计
(1)Map过程
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容,Map过程首先必须分析输入的<key, value>对,得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档URI和词频,如图所示:
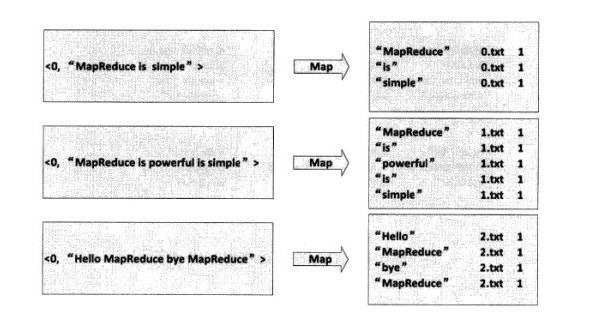
存在两个问题,第一:<key, value>对只能有两个值,在不使用Hadoop自定义数据类型的情况下,需要根据情况将其中的两个值合并成一个值,作为value或key值;
第二,通过一个Reduce过程无法同时完成词频统计和生成文档列表,所以必须增加一个Combine过程完成词频统计
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); //存储单词和URI的组合 private Text valueInfo = new Text();//存储词频 private FileSplit split; //存储Split对象 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获得<key,value>对所属的FileSplit对象 split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { //key值由单词和URI组成,如"MapReduce:1.txt" keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); // 词频初始为1 valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } }} |
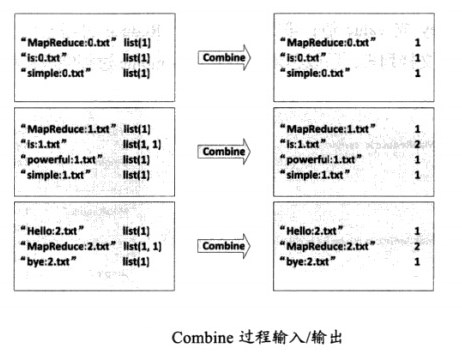
(2)Combine过程
将key值相同的value值累加,得到一个单词在文档中的词频,如图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //统计词频 int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); //重新设置value值由URI和词频组成 info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); //重新设置key值为单词 key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); }} |
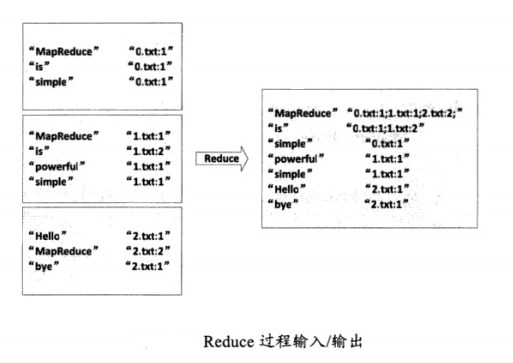
(3)Reduce过程
讲过上述两个过程后,Reduce过程只需将相同key值的value值组合成倒排索引文件所需的格式即可,剩下的事情就可以直接交给MapReduce框架进行处理了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //生成文档列表 String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); }} |
完整代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 | import java.io.IOException;import java.util.StringTokenizer;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;public class InvertedIndex { public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); private Text valueInfo = new Text(); private FileSplit split; public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } } } public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); } } public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub Configuration conf = new Configuration(); String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); if(otherArgs.length != 2) { System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>"); System.exit(2); } Job job = new Job(conf, "InvertedIndex"); job.setJarByClass(InvertedIndex.class); job.setMapperClass(InvertedIndexMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setCombinerClass(InvertedIndexCombiner.class); job.setReducerClass(InvertedIndexReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); }} |

以上是关于三 概要模式 2) MR倒排索引性能分析搜索干扰词。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章