分析用户的访问偏好
Posted 小江_xiaojiang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了分析用户的访问偏好相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文主要介绍了在Hadoop平台下统计分析Web用户的访问偏好,项目流程如下图所示:
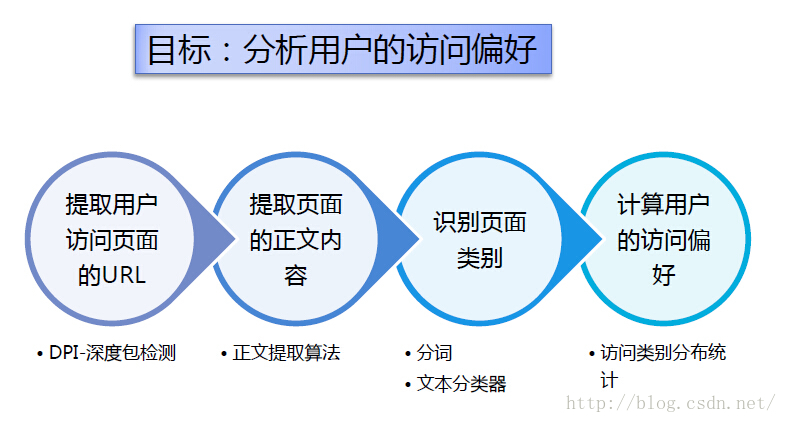
数据采集
项目流程中,提取用户访问页面的URL和URL对应的正文内容,由本人在公司参与一起开发的爬虫系统爬取相应门户网站(新浪)上的数据。爬虫核心代码见我的另一篇文章:httpclient使用详解(爬虫)
爬虫的框架使用的是java多线程开发,由于数据时效性不是很强,所以并没有采用分布式爬取,其实对于我个人来讲,这个框架的运营原理和分布式是一样的。框架主要思想如下:
1、爬虫主线程负责将用户访问页面的url抓取到redis中(增量爬取、分组爬取)
2、主线程管理一个线程池,线程池中有如下线程:
threadPool.addThread(new SaveRunningInfoThread(this)); //运行信息线程
threadPool.addThread(new CleanThread(this)); //清洗线程
for(int i=0; i<this.runParam.getSpiderThreads();i++){ //爬取url对应文章的信息 这里的线程数可以根据电脑硬件设置数量
threadPool.addThread(new SpiderThread(this));
}
注:如果是分布式爬虫,可以将多线程分配到多台电脑上,这样可以实现更快的爬虫
3、注意爬虫的时候使用代理,我这里使用的是免费代理,所以要在指定时间内更新代理池
文本预处理
文本预处理主要难题:1、中文分词 2、hadoop处理小文件输入
中文分词
对于中文分词,目前比较流行的开源分词有:Paoding、IK、mmseg4j等等。中文分词见我的另一篇文章:中文分词
Hadoop处理小文件输入
InputFormat
Hadoop中文本输入都是继承InputFormat,其工作原理如下:

InputFormat扮演的角色:
1、将输入数据切分成逻辑的分片(Split),一个分片将被分配给一个单独的Mapper
2、提供RecordReader的对象,该对象会从分片中读出<Key-Value>对供Mapper处理
InputFormat的Mapper的影响:
1、决定了Mapper的数量 见 Hadoop如何计算map数和reduce数
2、决定了Mapper的map函数接收的Key和Value
InputFormat源码解析:
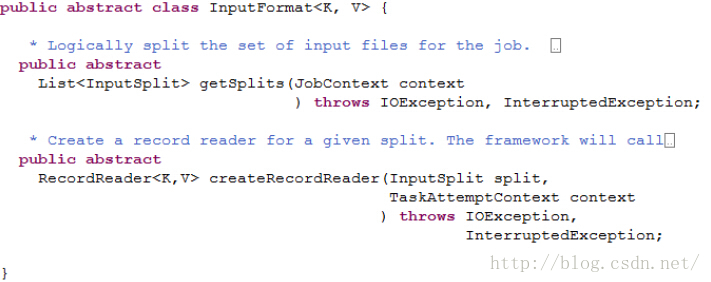
getSplits负责将输入数据进行划分,生成一组分片,
createRecordReader返回的对象,负责从分片中读取<Key-Value>对

InputSplit是一个抽象类,分片的类都继承自它;
方法getLength()用于获取分片的大小 ;
方法getLocations()用于获取存储分片的位置列表
Mapper中的run方法
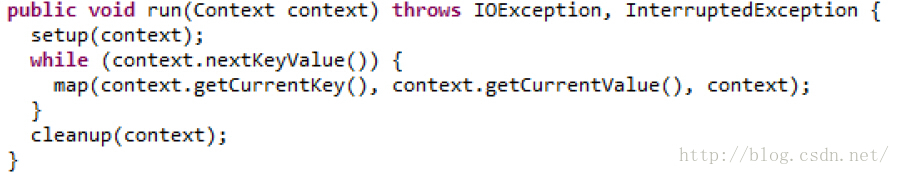
Mapper通过context来获取Key-Value对,而context的nextKeyValue、getCurrentKey、getCurrentKey方法,就是调用InputFormat返回的RecordReader对象
FileInputFormat
FileInputFormat是InputFormat的子类,所有使用文件为数据源的输入格式类都继承自它;它实现了getSplits方法,返回的分片类型是FileSplit,是InputSplit的一个子类,里面加入了描述文件路径,分片开始位置的信息;但是它没有实现createRecordReader方法;它也是一个抽象类
TextInputFormat
TextInputFormat是hadoop的默认输入格式,也是FileInputFormat的一个子类,继承了它的getSplit方法,并实现了自己的createRecordReader方法。
createRecordReader返回的是lineRecordReader的对象,每行生成一条<key-value>记录
key:每个数据的记录在数据分片中字节偏移量,类型是LongWritable
value:每行的内容,类型是Text
CombineFileInputFormat
CombineFileInputFormat是hadoop针对小文件设计的输入格式,它也是继承FileInputFormat;
重写了getSplit方法,返回的分片类型是CombineFileSplit,也是InputSplit的一个子类,其包含多个文件的路径;
CombineFileInputFormat也是一个抽象类,编写具体类需要实现createRecordReader方法:
建议返回值的类型是CombineFileRecordReader,它用于处理类型为CombineFileSplit的分片
CombineFileRecordReader的构造函数中,还需指定一个RecordReader,用于处理分片内的单个文件。
自定义输入格式MyInputFormat
自定义输入格式有如下要求:
1、确保文件不被分割,每个文件都只分配到一个分片
2、一个分片可包含多个文件
3、输出的每条<key-value>对应一个完整的文本文件
key:文件所属的类别名,类型为Text
value:文件的文本内容,类型是Text
MyInputFormat类代码如下:
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodec;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodecFactory;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileRecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.LineReader;
public class MyInputFormat extends CombineFileInputFormat<Text, Text> {
/**
* 确保文本不被分割
*/
@Override
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path file) {
return false;
}
/**
* 返回CombineFileRecordReader对象
*/
@Override
public RecordReader<Text, Text> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
CombineFileRecordReader<Text, Text> recordReader = new CombineFileRecordReader<Text, Text>(
(CombineFileSplit)split, context, MyRecordReader.class);
return recordReader;
}
}
MyRecordReader类的代码如下:
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
public class MyRecordReader extends RecordReader<Text, Text> {
private CombineFileSplit combineFileSplit; // 当前处理的分片
private int totalLength; // 分片包含的文件数量
private int currentIndex; // 当前处理的文件索引
private float currentProgress = 0; // 当前的进度
private Text currentKey = new Text(); // 当前的Key
private Text currentValue = new Text(); // 当前的Value
private Configuration conf; // 任务信息
private boolean processed; // 记录当前文件是否已经读取
/*
* combineFileSplit:待处理的Split
* context: 保存任务和系统信息
* index: 当前文件在Split中的索引
*/
public MyRecordReader(CombineFileSplit combineFileSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context, Integer index) throws IOException {
super();
this.currentIndex = index;
this.combineFileSplit = combineFileSplit;
conf = context.getConfiguration();
totalLength = combineFileSplit.getPaths().length;
processed = false;
}
@Override
public void initialize(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return currentKey;
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return currentValue;
}
@Override
public float getProgress() throws IOException { //计算处理进度
if (currentIndex >= 0 && currentIndex < totalLength) {
currentProgress = (float) currentIndex / totalLength;
return currentProgress;
}
return currentProgress;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
}
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (!processed) { // 如果文件未处理则读取文件并设置key-value
// 文件目录名为key
Path file = combineFileSplit.getPath(currentIndex);
currentKey.set(file.getParent().getName());
// 文件内容为 value
FSDataInputStream in = null;
byte[] contents = new byte[(int)combineFileSplit.getLength(currentIndex)];
try {
FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(conf);
in = fs.open(file);
in.readFully(contents);
currentValue.set(contents);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
in.close();
}
processed = true;
return true;
}
return false; //如果文件已经处理,必须返回false
}
}分词TokenizeMapper类代码:
package tokenize;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader;
import net.paoding.analysis.analyzer.PaodingAnalyzer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.TokenStream;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.tokenattributes.CharTermAttribute;
public class TokenizeMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
private Text outKey = new Text();
private Text outValue = new Text();
PaodingAnalyzer analyzer = new PaodingAnalyzer();
public void map(Text key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// set key
outKey.set(key);
// set value
String line = value.toString();
StringReader sr = new StringReader(line);
TokenStream ts = analyzer.tokenStream("", sr);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try{
while (ts.incrementToken()) {
CharTermAttribute ta = ts.getAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class);
sb.append(ta.toString());
sb.append(" ");
}
}catch(Exception e){
context.getCounter(Counter.FAILDOCS).increment(1);
}
outValue.set(sb.toString());
// output keyvalue pair
context.write(outKey, outValue);
}
}
package tokenize;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import tokenize.inputformat.MyInputFormat;
public class TokenizeDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// set configuration
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.setLong("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize", 4000000); //max size of Split
Job job = new Job(conf,"Tokenizer");
job.setJarByClass(TokenizeDriver.class);
// specify input format
job.setInputFormatClass(MyInputFormat.class);
// specify mapper
job.setMapperClass(tokenize.TokenizeMapper.class);
// specify output types
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// specify input and output DIRECTORIES
Path inPath = new Path(args[0]);
Path outPath = new Path(args[1]);
try { // input path
FileSystem fs = inPath.getFileSystem(conf);
FileStatus[] stats = fs.listStatus(inPath);
for(int i=0; i<stats.length; i++)
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, stats[i].getPath());
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
return;
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outPath); // output path
// delete output directory
try{
FileSystem hdfs = outPath.getFileSystem(conf);
if(hdfs.exists(outPath))
hdfs.delete(outPath);
hdfs.close();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return ;
}
// run the job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
预处理结果

朴素贝叶斯模型
贝叶斯模型见:分类——朴素贝叶斯
我的另一篇播客中介绍了使用朴素贝叶斯对newsgroup文本进行分类测试,这个处理的是英文文本,不过原理是一样的:见文本分类——NaiveBayes
划分数据集
使用pig命令将数据划分为训练集和测试集
读入预处理后的文件
processed = load 'digital/processed' as (category:chararray, doc:chararray);
随机抽取20%的样本作为测试集
test = sample processed 0.2;
将剩下的样本作为训练集
jnt = join processed by (category, doc) left outer, test by (category, doc);
filt_test = filter jnt by test::category is null;
train = foreach filt_test generate processed::category as category, processed::doc as doc;
输出训练集和测试集
store test into 'digital/test'
store train into 'digital/train'
使用mahout训练朴素贝叶斯模型
mahout trainclassifier -i digital/train -o digital/model-bayes -type bayes -ng 1 -source hdfs
mahout trainclassifier -i digital/train -o digital/model-cbayes -type cbayes -ng 1 -source hdfs
使用mahout测试朴素贝叶斯模型
mahout testclassifier -d digital/test -m digital/model-bayes -type bayes -source hdfs -method mapreducemahout testclassifier -d digital/test -m digital/model-cbayes -type cbayes -source hdfs -method mapreduce
混淆矩阵

评价指标
1、查全率和查准率(准确率和召回率)
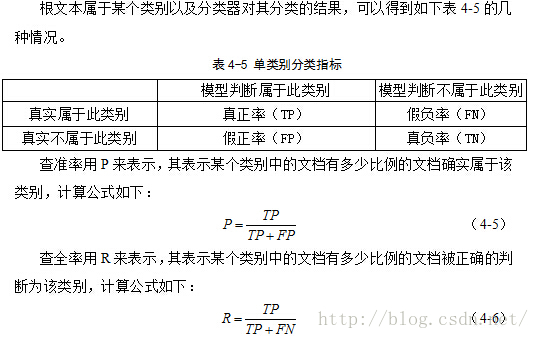
2、宏平均和微平均

3、F1度量

用户访问偏好分析
经过以上步骤之后,现在收集了一批用户浏览电商的文档信息,要求计算各个用户最偏好的产品类别。
数据存储描述:每个文件夹代表一个用户,里面存储的是用户浏览过的文本文件。
数据预处理
预处理的方法和前面讲述的过程一样
用户访问内容分类
在mapreduce的map端对文档进行分类,而后reduce统计各个文档的总和
map端流程图:
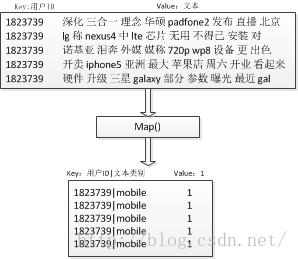
map端代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.ClassifierResult;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.Algorithm;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.BayesAlgorithm;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.BayesParameters;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.CBayesAlgorithm;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.ClassifierContext;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.Datastore;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.InMemoryBayesDatastore;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.InvalidDatastoreException;
import org.apache.mahout.common.nlp.NGrams;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import classifier.Counter;
public class ClassifierMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private Text outKey = new Text();
private static final IntWritable ONE = new IntWritable(1);
private int gramSize = 1;
private ClassifierContext classifier;
private String defaultCategory;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ClassifierMapper.class);
/**
* Parallel Classification
*
* @param key
* The label
* @param value
* the features (all unique) associated w/ this label
* @param context
*/
public void map(Text key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String docLabel = "";
String userID = key.toString();
List<String> ngrams = new NGrams(value.toString(), gramSize).generateNGramsWithoutLabel();
try {
ClassifierResult result;
result = classifier.classifyDocument(ngrams.toArray(new String[ngrams.size()])
, defaultCategory);
docLabel = result.getLabel();
} catch (InvalidDatastoreException e) {
log.error(e.toString(), e);
context.getCounter(Counter.FAILDOCS).increment(1);
}
// key is userID and docLabel
outKey.set(userID+"|"+docLabel);
context.write(outKey, ONE);
}
/**
* read the model
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void setup(Context context) throws IOException {
//读取配置信息
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
BayesParameters params = new BayesParameters(conf.get("bayes.parameters", ""));
//指定分类算法
Algorithm algorithm;
//保存模型数据
Datastore datastore;
algorithm = new BayesAlgorithm();
datastore = new InMemoryBayesDatastore(params);
classifier = new ClassifierContext(algorithm, datastore);
try {
classifier.initialize();
} catch (InvalidDatastoreException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
defaultCategory = params.get("defaultCat");
gramSize = params.getGramSize();
}
}
reduce端流程图:
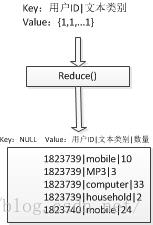
reduce端代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
public class ClassifierReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, NullWritable, Text> {
private Text outValue = new Text();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// get the number of labels that user read
int num = 0;
for(IntWritable value: values){
num += value.get();
}
outValue.set(key.toString()+"|"+num);
// output
context.write(NullWritable.get(), outValue);
}
}函数入口:
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.mahout.classifier.bayes.BayesParameters;
public class ClassifierDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// set bayes parameter
BayesParameters params = new BayesParameters();
params.setBasePath(args[2]);
params.set("classifierType", args[3]);
params.set("alpha_i", "1.0");
params.set("defaultCat", "unknown");
params.setGramSize(1);
// set configuration
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("bayes.parameters", params.toString());
// create job
Job job = new Job(conf,"Classifier");
job.setJarByClass(ClassifierDriver.class);
// specify input format
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class);
// specify mapper & reducer
job.setMapperClass(classifier.ClassifierMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(ClassifierReducer.class);
// specify output types of mapper and reducer
job.setOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// specify input and output DIRECTORIES
Path inPath = new Path(args[0]);
Path outPath = new Path(args[1]);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outPath); // output path
// delete output directory
try{
FileSystem hdfs = outPath.getFileSystem(conf);
if(hdfs.exists(outPath))
hdfs.delete(outPath);
hdfs.close();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return ;
}
// run the job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
统计每个用户阅读最多的类别

结果
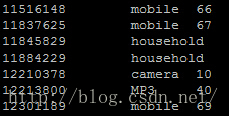
结束语
本文中很多地方都有参考网络各种资源,整个流程让我学习到了很多东西,由于整个文本的数据量不是很大(10000个文本),还不能真正的体现出hadoop的价值。不过这些都是做离线数据分析,现如今实时数据分析、实时推荐等都成为趋势,以后应该学习的目标是storm和spark。
以上是关于分析用户的访问偏好的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章