Codeforces Round #346 (Div. 2)
Posted Running_Time
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Codeforces Round #346 (Div. 2)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前三题水
A
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int main() {
int n, a, b; std::cin >> n >> a >> b;
int bb = b;
if (b < 0) bb = -b;
while (bb--) {
if (b < 0) {
a--;
} else {
a++;
}
if (a == 0) {
a = n;
} else if (a == n + 1) {
a = 1;
}
}
std::cout << a << ‘\n‘;
return 0;
}
B
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int M = 1e4 + 5;
struct Info {
std::string name;
int score;
bool operator < (const Info &rhs) const {
return score > rhs.score;
}
};
std::vector<Info> vec[M];
bool same_three(int a, int b, int c) {
return b == c;
}
bool same(int id) {
return same_three (vec[id][0].score, vec[id][1].score, vec[id][2].score);
}
int main() {
int n, m; std::cin >> n >> m;
std::string str; int num, score;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
std::cin >> str >> num >> score;
vec[num].push_back ((Info) {str, score});
}
for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) {
if (vec[i].size () < 2) {
puts ("?");
continue;
} else {
std::sort (vec[i].begin (), vec[i].end ());
if (vec[i].size () > 2 && same (i)) {
puts ("?");
} else {
std::cout << vec[i][0].name << " " << vec[i][1].name << ‘\n‘;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
C
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
std::map<int, bool> vis;
int main() {
int n, m; scanf ("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int a, i=0; i<n; ++i) {
scanf ("%d", &a);
vis[a] = true;
}
std::vector<int> vec;
int now = 1;
while (m - now >= 0) {
if (vis[now]) {
now++;
} else {
m -= now;
vec.push_back (now);
now++;
}
}
printf ("%d\n", vec.size ());
for (int i=0; i<vec.size (); ++i) {
printf ("%d%c", vec[i], i == vec.size () - 1 ? ‘\n‘ : ‘ ‘);
}
return 0;
}
几何(叉积) D - Bicycle Race
题意:一个人从最下面的位置逆时针沿着湖转一圈,当转角指向湖的方向认为是危险的,问有多少个危险的转角.
分析:分类讨论也就四种情况,但是注意出发点不一定是最左边的(最下面的);也可以用叉积来判断,大于0表示是顺时针满足危险的定义.
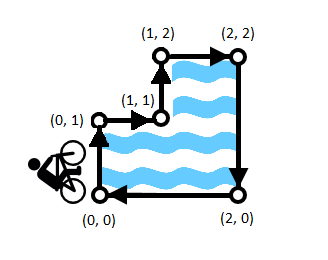
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
Point point[N];
int main() {
int n; scanf ("%d", &n);
for (int i=0; i<=n; ++i) {
scanf ("%d%d", &point[i].x, &point[i].y);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i=0; i<n-2; ++i) {
if (point[i].x == point[i+1].x) {
if (point[i+1].y > point[i].y) {
if (point[i+2].x < point[i+1].x) {
ans++;
}
} else {
if (point[i+2].x > point[i+1].x) {
ans++;
}
}
} else {
if (point[i].x < point[i+1].x) {
if (point[i+1].y < point[i+2].y) {
ans++;
}
} else {
if (point[i+1].y > point[i+2].y) {
ans++;
}
}
}
}
printf ("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
struct Point {
int x, y;
Point operator - (const Point &rhs) const {
return (Point) {x - rhs.x, y - rhs.y};
}
};
Point point[N];
typedef Point Vector;
int cross(Vector A, Vector B) {
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;
}
int main() {
int n; scanf ("%d", &n);
for (int i=0; i<=n; ++i) {
scanf ("%d%d", &point[i].x, &point[i].y);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i=1; i<n; ++i) {
if (cross (point[i-1] - point[i], point[i+1] - point[i]) < 0) {
ans++;
}
}
printf ("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
题意:n个点,m条边,每条边是单向的,问如何安排每条边的方向使得入度为0的点最少,最少是几个.
分析:进行DFS,如果访问到已访问过的点表示该连通块有环,也就是可以满足每个点的入度大于等于1.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
std::vector<int> G[N];
bool vis[N];
int n, m, add;
void DFS(int u, int fa) {
if (vis[u]) {
add = 0;
return ;
}
vis[u] = true;
for (int i=0; i<G[u].size (); ++i) {
int v = G[u][i];
if (v == fa) {
continue;
}
DFS (v, u);
}
}
int main() {
scanf ("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) {
int u, v; scanf ("%d%d", &u, &v);
G[u].push_back (v);
G[v].push_back (u);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) {
if (vis[i]) {
continue;
}
add = 1;
DFS (i, 0);
ans += add;
}
printf ("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
题意:n*m的矩阵有不同高度的干草,现要割成高度相同的连通块,且其中至少一个干草的高度没有变化,以及连通块的高度和等于k,求可行的方案.
分析:统计出每个可以高度不变化且被k整除,且连通块数量不小于k/a[i][j],那么BFS一次能的得到方案.按照高度从大到小排序,对于当前的干草累加上周围高度不小于它的连通块数量,DP思想或者说是求前缀,用并查集维护.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
ll a[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int n, m;
ll k, num, aim;
int rt[N*N], rk[N*N];
int Find(int x) {
return rt[x] == -1 ? x : rt[x] = Find (rt[x]);
}
void Union(int x, int y) {
x = Find (x);
y = Find (y);
if (x == y) {
return ;
}
rt[x] = y;
rk[y] += rk[x];
}
struct Info {
ll val;
int x, y;
bool operator < (const Info &rhs) const {
return val > rhs.val;
}
};
std::vector<Info> vec;
bool judge(int x, int y) {
if (x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m) {
return false;;
}
return true;
}
void BFS(int x, int y) {
std::queue<std::pair<int, int> > que;
que.push (std::make_pair (x, y));
vis[x][y] = true; num--;
while (!que.empty ()) {
int nx = que.front ().first, ny = que.front ().second;
que.pop ();
for (int i=0; i<4; ++i) {
int tx = nx + dx[i];
int ty = ny + dy[i];
if (num == 0) {
continue;
}
if (!judge (tx, ty)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[tx][ty]) {
continue;
}
if (a[tx][ty] < aim) {
continue;
}
vis[tx][ty] = true; num--;
que.push (std::make_pair (tx, ty));
}
}
}
void print() {
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) {
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) {
if (vis[i][j]) {
printf ("%I64d ", aim);
} else {
printf ("0 ");
}
}
puts ("");
}
}
int main() {
scanf ("%d%d%I64d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) {
for (int j=1; j<=m; ++j) {
scanf ("%I64d", &a[i][j]);
vec.push_back ((Info) {a[i][j], i, j});
}
}
std::sort (vec.begin (), vec.end ());
memset (rt, -1, sizeof (rt));
std::fill (rk, rk+N*N, 1);
for (int i=0; i<vec.size (); ++i) {
Info &r = vec[i];
if (r.val == 0) {
break;
}
for (int j=0; j<4; ++j) {
int tx = r.x + dx[j];
int ty = r.y + dy[j];
if (!judge (tx, ty)) {
continue;
}
if (a[tx][ty] >= r.val) {
Union ((tx-1)*m+ty, (r.x-1)*m+r.y);
}
}
int fa = Find ((r.x-1)*m+r.y);
if (k % r.val != 0 || k / r.val > rk[fa]) {
continue;
}
puts ("YES");
num = k / r.val; aim = r.val;
BFS (r.x, r.y);
print ();
return 0;
}
puts ("NO");
return 0;
}
以上是关于Codeforces Round #346 (Div. 2)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章