使用sklean进行多分类下的二分类
Posted similarface
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用sklean进行多分类下的二分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
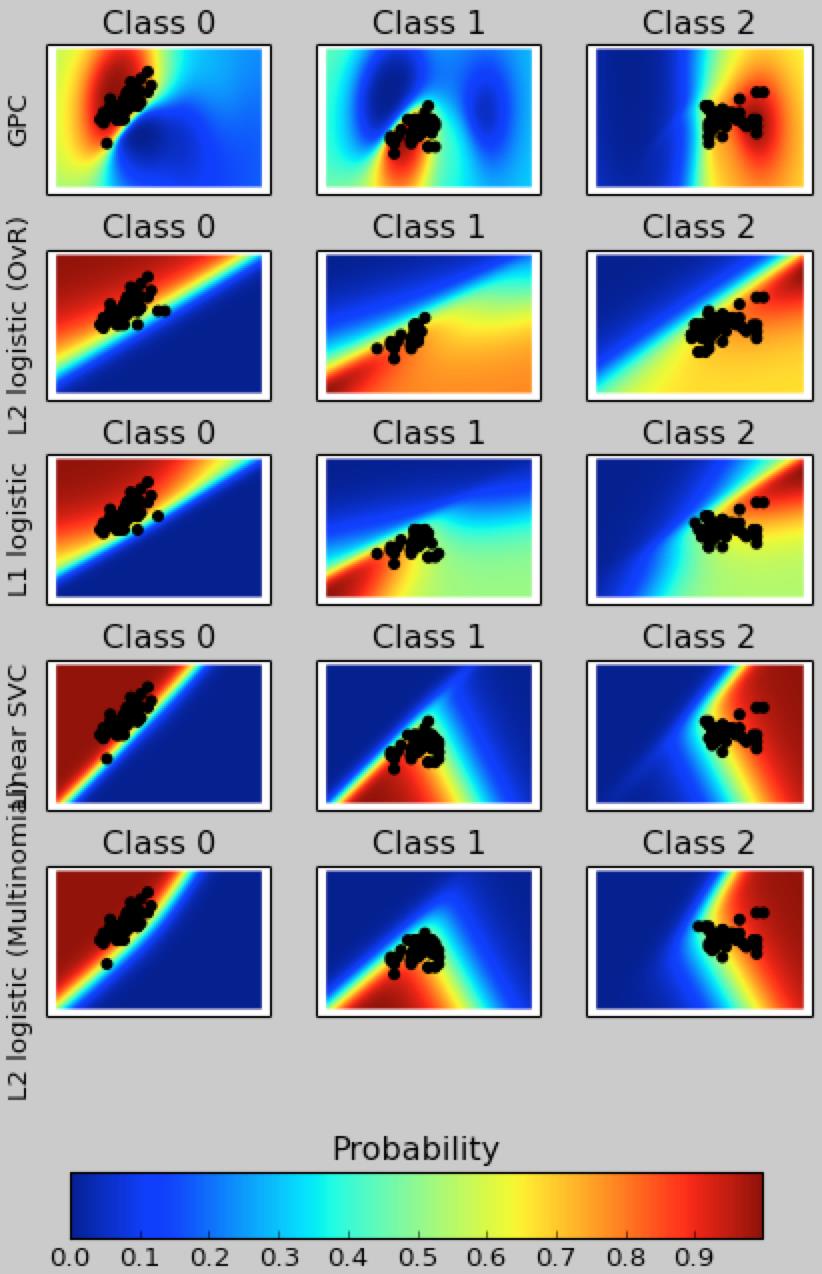
#coding:utf-8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF from sklearn import datasets iris = datasets.load_iris() #花萼长度 花萼宽度 X = iris.data[:, 0:2] # we only take the first two features for visualization #所属种类 y = iris.target print X.shape print y #两个因数 n_features = X.shape[1] C = 1.0 kernel = 1.0 * RBF([1.0, 1.0]) # for GPC # Create different classifiers. The logistic regression cannot do # multiclass out of the box. classifiers = {\'L1 logistic\': LogisticRegression(C=C, penalty=\'l1\'), \'L2 logistic (OvR)\': LogisticRegression(C=C, penalty=\'l2\'), \'Linear SVC\': SVC(kernel=\'linear\', C=C, probability=True,random_state=0), \'L2 logistic (Multinomial)\': LogisticRegression(C=C, solver=\'lbfgs\', multi_class=\'multinomial\'), \'GPC\': GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel) } n_classifiers = len(classifiers) plt.figure(figsize=(3 * 2, n_classifiers * 2)) plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=.2, top=.95) #3-9 的100个平均分布的值 xx = np.linspace(3, 9, 100) #1-5 的100个平均分布的值 yy = np.linspace(1, 5, 100).T # xx, yy = np.meshgrid(xx, yy) #纵列连接数据 构造虚拟:花萼长度 花萼宽度 Xfull = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()] for index, (name, classifier) in enumerate(classifiers.items()): classifier.fit(X, y) y_pred = classifier.predict(X) classif_rate = np.mean(y_pred.ravel() == y.ravel()) * 100 print("classif_rate for %s : %f " % (name, classif_rate)) # 查看预测概率 probas = classifier.predict_proba(Xfull) #3个种类 n_classes = np.unique(y_pred).size for k in range(n_classes): plt.subplot(n_classifiers, n_classes, index * n_classes + k + 1) plt.title("Class %d" % k) if k == 0: plt.ylabel(name) #构造颜色 imshow_handle = plt.imshow(probas[:, k].reshape((100, 100)),extent=(3, 9, 1, 5), origin=\'lower\') plt.xticks(()) plt.yticks(()) idx = (y_pred == k) if idx.any(): plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], marker=\'o\', c=\'k\') ax = plt.axes([0.15, 0.04, 0.7, 0.05]) plt.title("Probability") plt.colorbar(imshow_handle, cax=ax, orientation=\'horizontal\') plt.show()
以上是关于使用sklean进行多分类下的二分类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章