一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-对象的调用-属性注入容器的对象
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-对象的调用-属性注入容器的对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实现功能
需求:在类的成员属性使用@Autowirde注解注入容器中的对象。
实现思路
要实现这个功能。我们首先要思考一个问题:类与类的关系是在调用的建立的,还是说在创建对象的时候就就将建立了?
---我实现的方案是,在在程序启动后,所有对象创建后直接就将对象的属性和属性之间的关系创建了。接下来我就用这个思路来实现,将根据@Autowirde建立对象与对象之间的关系。
为什么一定要对象全部创建后再实现对象与对象直接的关系呢?
这个是逻辑问题,如果对象没有创建完就建立对象与对象之间的关系,人家都还没有创建,你怎么引用呢?对吧。所有一定在所有对象创建完后建立对象与对象的关系。
实现步骤
1.Context接口增加一个方法。用于通过Map的和属性名对象或者对象的类型与属性的类型对象,给属性匹配对象。定义如代码的说明
1 /** 2 * 根据类的类型以及设置的对象名返回容器对象 3 * 如果传入的类型容器中有对应key的对象,而且返回类型是兼容的,直接返回对应的对象。 4 * 如果传入的类型容器中有没有对应key的对象,那么判断传入的类型是否和容器的对象的找到唯一配置的。 5 * 如果传入类型唯一匹配,返回对象。如果没有或者配配多个对象,都报一个RuntimeException异常 6 * @param classType 7 * @return 8 */ 9 Object getObject(Class<?> classType,String key);
2.在ContextImpl容器实现类实现这个方法
1 @Override 2 public Object getObject(Class<?> classType, String key) { 3 // 1.判断是否有对应key的对象 4 Object object = objects.get(key); 5 // 2.如果有,而且类型也兼容。直接返回该对象。 6 if (object != null && classType.isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) { 7 return object; 8 } else { 9 // 3.如果没有对应key的对象,那么就在容器里检索,是否有兼容类型的对象。 10 Collection<Object> values = objects.values(); 11 Iterator<Object> iterator = values.iterator(); 12 int count = 0; 13 Object currentObject = null; 14 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 15 Object nextObject = iterator.next(); 16 //判断classType是否是nextObject.getClass()的兼容类型。 17 boolean from = classType.isAssignableFrom(nextObject.getClass()) ; 18 if (from) { 19 //如果发现有对象,计数加1 20 count++; 21 //并将对象赋予当前对象 22 currentObject = nextObject; 23 } 24 } 25 // 如果兼容类型的对象只有一个,返回这个对象。如果大于一个,返回null 26 if (count == 1) { 27 return currentObject; 28 } else { 29 //如果发现一个类型容器中有多个异常,抛异常 30 throw new RuntimeException("容器中找不到对应的对象或者找到的对象不是唯一的!请确认是否一个接口继承了多个类"); 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 }
3.在AbstractApplicationContext容器操作类实现属性的注入方法 autowired()
1 /** 2 * 给对象的属性注入关联的对象 3 * @throws IllegalArgumentException 4 * @throws IllegalAccessException 5 */ 6 private void autowired() throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { 7 // 1.获得容器 8 Context context = contexts.get(); 9 // 2.获得容器中的所有对象。 10 Map<String, Object> objects = context.getObjects(); 11 // 3.获得容器中所有的对象值 12 Collection<Object> values = objects.values(); 13 // 4.获得对象的迭代器 14 Iterator<Object> iterator = values.iterator(); 15 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 16 Object object = iterator.next(); 17 // 5.获得对象的表结构 18 Class<? extends Object> classType = object.getClass(); 19 // 6.获得字段的结构 20 Field[] fields = classType.getDeclaredFields(); 21 for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { 22 // autowired获得注解 23 Autowired autowired = fields[i].getAnnotation(Autowired.class); 24 if (autowired != null) { 25 Class<?> fieldType = fields[i].getType(); 26 String fieldName = fields[i].getName(); 27 // 如果容器里面有对应的对象 28 Object fieldObject = context.getObject(fieldType, fieldName); 29 // 允许访问私有方法 30 if (fieldObject != null) { 31 // 属性是私有的也可以访问 32 fields[i].setAccessible(true); 33 // 将属性值赋予这个对象的属性 34 fields[i].set(object, fieldObject); 35 } 36 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 }
4. 在AbstractApplicationContext构造方法最后调用属性注入方法autowired,注意标红处
1 public AbstractApplicationContext(Class<?> classType) { 2 try { 3 // 判断配置类是否有Configuration注解 4 Configuration annotation = classType.getDeclaredAnnotation(Configuration.class); 5 if (annotation != null) { 6 // 获得组件扫描注解 7 ComponentScan componentScan = classType.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); 8 // 获得包名 9 this.basePackage = componentScan.basePackages(); 10 // 根据包名获得类全限制名 11 // Set<String> classNames = 12 // PackageUtils.getClassName(this.basePackage[0], true); 13 // 将扫描一个包,修改为多个包 14 Set<String> classNames = PackageUtils.getClassNames(this.basePackage, true); 15 // 通过类名创建对象 16 Iterator<String> iteratorClassName = classNames.iterator(); 17 while (iteratorClassName.hasNext()) { 18 19 String className = iteratorClassName.next(); 20 // System.out.println(className); 21 22 // 通过类全名创建对象 23 Class<?> objectClassType = Class.forName(className); 24 /* 25 * 判断如果类权限名对应的不是接口,并且包含有@Component|@Controller|@Service| 26 * 27 * @Repository 才可以创建对象 28 */ 29 if (this.isComponent(objectClassType)) { 30 Object instance = objectClassType.newInstance(); 31 // 修改为,默认对象支持首字符小写 32 String objectName = null; 33 // 获得组件注解的name属性值 34 String componentName = this.getComponentOfName(objectClassType); 35 36 if (componentName == null) { 37 // 如果组件注解的name属性没有值,使用默认命名对象 38 objectName = NamingUtils.firstCharToLower(instance.getClass().getSimpleName()); 39 } else { 40 // 如果组件注解的name属性有值,使用自定义命名对象 41 objectName = componentName; 42 } 43 this.getContext().addObject(objectName, instance); 44 } 45 46 } 47 } 48 //1.注入对象到属性中。 49 autowired(); 50 } catch (InstantiationException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 } 57 58 }
测试代码
测试类目录结构
1.修改UserController代码,增加注入UserService的代码
1 package ioc.core.test.controller; 2 3 import ioc.core.annotation.Autowired; 4 import ioc.core.annotation.stereotype.Controller; 5 import ioc.core.test.service.UserService; 6 7 @Controller 8 public class UserController { 9 10 /** 11 * 通过@Autowired可以注入UserService的对象。 12 */ 13 @Autowired 14 private UserService userServiceImpl; 15 16 public void login(){ 17 System.out.println("-登录Controller-"); 18 userServiceImpl.login(); 19 } 20 21 }
2.调用UserController 对象
1 package ioc.core.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 import ioc.core.impl.AnntationApplicationContext; 6 import ioc.core.test.config.Config; 7 import ioc.core.test.controller.UserController; 8 9 public class AnntationApplicationContextTest { 10 11 @Test 12 public void login(){ 13 try { 14 AnntationApplicationContext context=new AnntationApplicationContext(Config.class); 15 UserController userController = context.getBean("userController", UserController.class); 16 userController.login(); 17 System.out.println(context.getContext().getObjects()); 18 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 }
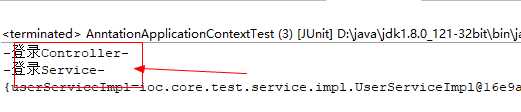
3.输出结果
同时输出了UserController的内容和UserService的内容
以上是关于一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-对象的调用-属性注入容器的对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-对象的调用-@Bean注解注入容器的对象
一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-基础功能-组件注解支持自定义的对象名
一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-基础功能-容器对象名默认首字母小写