Servlet基本概念及其部署
Posted 沿海地带
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Servlet基本概念及其部署相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
什么servlet?
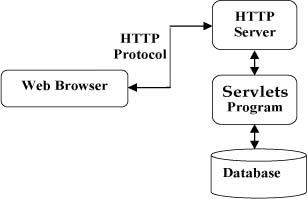
Servlet架构,在软件里面位置如下:
Tomcat:
很多人用过Tomcat,但是不甚其解,市场上有许多 Web 服务器支持 Servlet,Tomcat是其中应用得较多的一款,
Apache Tomcat 是一款 Java Servlet 和 JavaServer Pages 技术的开源软件实现,可以作为测试 Servlet 的独立服务器,而且可以集成到 Apache Web 服务器。
这里不做赘述,关于Tomcat具体可见:http://www.runoob.com/servlet/servlet-environment-setup.html
生命周期:


( 右图来自http://www.runoob.com/servlet/servlet-life-cycle.html,侵删)
方法说明:
init():
一开始创建,只创建一次,可以简单地创建或加载一些数据,这些数据将被用于 Servlet 的整个生命周期。
1 public void init() throws ServletException { 2 // 初始化代码... 3 }
service() :这一层不用管,只需要重写doGet和doPost方法
service() 方法检查 HTTP 请求类型(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等),并在适当的时候调用 doGet、doPost、doPut,doDelete 等方法。
下面是doGet方法和doPost方法的代码:
//全部根据传入的参数来执行响应操作,一般是get接受服务器请求,post对请求发出响应 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Servlet 代码 } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Servlet 代码 }
destroy() :
destroy() 方法和init()方法一样,被调用一次,在 Servlet 生命周期结束时被调用。destroy() 方法可以让您的 Servlet 关闭数据库连接、停止后台线程、把 Cookie 列表或点击计数器写入到磁盘,并执行其他类似的清理活动。在调用 destroy() 方法之后,servlet 对象被标记为垃圾回收。
Servlet 部署:
这里是很关键的位置,因为你每写完一个Servlet都需要在配置文件里面部署一下,记住过程当然简单,但是还是弄清楚为什么是这样还是很有必要!
下面以一个案例为例:

如图,写了一个CoreServlet实例。在里面实现了doGet()和Post()方法。现在要将其部署在web.xml当中,下面是没有写入的。(这个是动态web工程,可以在Eclipse里面直接生成)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"> <display-name>WeixinDFF</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>
现在要写入内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"> <display-name>WeixinDFF</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>coreServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.dff.weixin.servlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>coreServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/coreServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
ServletConfig获取配置参数的方法和ServletContext获取配置参数的方法完全一样,只是ServletConfig是取得当前Servlet的配置参数,而ServletContext是获取整个Web应用的配置参数。使用<init-param>子元素将初始化参数名和参数值传递给Servlet,访问Servlet配置参数通过ServletConfig对象来完成。
参数说明:
1.<servlet>必须含有<servlet-name>和<servlet-class>,或者<servlet-name>和<jsp-file>。
<servlet-name>用来定义servlet的名称,该名称在整个应用中必须是惟一的
<servlet-class>用来指定servlet的完全限定的名称。这里就是指包名。
<jsp-file>用来指定应用中JSP文件的完整路径。这个完整路径必须由/开始。
2.<servlet-mapping>要含有<servlet-name>和<url-pattern>
<url-pattern>:指定相对于Servlet的URL的路径。该路径相对于web应用程序上下文的根路径。<servlet-mapping>将URL模式映射到某个Servlet,即该Servlet处理的URL。
其余参数:
加载过程:
容器的Context对象对请求路径(URL)做出处理,去掉请求URL的上下文路径后,按路径映射规则和Servlet映射路径(<url- pattern>)做匹配,如果匹配成功,则调用这个Servlet处理请求。
扩展:DispatcherServlet在web.xml中的配置:
<!-- Spring view分发器 对所有的请求都由business对应的类来控制转发 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>business</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>publishContext</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet>
<load-on-startup>
如果load-on-startup元素存在,而且也指定了jsp-file元素,则JSP文件会被重新编译成Servlet,同时产生的Servlet也被载入内存。<load-on-startup>的内容可以为空,或者是一个整数。这个值表示由Web容器载入内存的顺序。
例如:如果有两个Servlet元素都含有<load-on-startup>子元素,则<load-on-startup>子元素值较小的Servlet将先被加载。如果<load-on-startup>子元素值为空或负值,则由Web容器决定什么时候加载Servlet。如果两个Servlet的<load-on-startup>子元素值相同,则由Web容器决定先加载哪一个Servlet。<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>表示启动容器时,初始化Servlet。
里面有很多部分用到了web.xml,关于他的步骤,这篇博客里面有写【http://blog.csdn.net/believejava/article/details/43229361】,我自己也有总结,感兴趣可以去我的博客里面看看。
以上是关于Servlet基本概念及其部署的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章