继承与多肽:课后作业
Posted 呦呵呵丶
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了继承与多肽:课后作业相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }

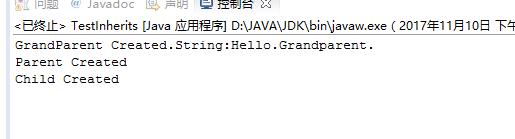
第一个是没有用super,第二个用到了super,super()括号中有参数,所以就调用了有参数的基类构造方法。当把super的语句放到后面的时候,程序报错,构造函数调用必须是构造函数中的第一个语句。
父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,这句调用代码必须是第一句,不然会报错。通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2、 为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
构造函数是一种特殊的方法 。主要在创建对象时初始化对象, 即为对象成员变量赋初值,总与new运算符一起使用在创建对象的语句中 。一个类可以有多个构造函数 ,可根据其参数个数的不同或参数类型的不同来区分它们 即构造函数的重载。构造函数的功能主要用于在类的对象创建时定义初始化的状态。
构造一个对象,先调用其构造方法,来初始化其成员函数和成员变量。
子类拥有父的成员变量和方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化。
不能反过来调用,因为父类不知道子类有什么变量,而且子类也得不到初始化的父类变量,导致程序运行出错!
package homework6;
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
运行截图
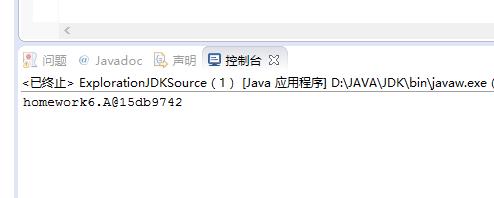
原因:使用javap –c命令反汇编这个程序,发现main方法实际上调用的是:public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。
valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() +"@" +
Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:public native int hashCode();
4、注意最后一句,为什么一个字串和一个对象“相加”,得到以下结果
package homework6;
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}
运行截图
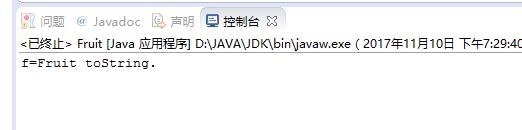
原因:在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
5、自行编写代码测试以下特性:在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
class Parent
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("111");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public void show()
{
super.show();
System.out.println("222");
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Child c = new Child();
c.show();
}
运行截图

结果分析:super方法在子类覆盖方法类使用,只有这样才能调用父类中被覆盖的方法,并且super语句放在子类覆盖方法第几句都行
6、现在有三个类: class Mammal{} class Dog extends Mammal {} class Cat extends Mammal{}
针对每个类定义三个变量并进行初始化 Mammal m=null ; Dog d=new Dog(); Cat c=new Cat();
下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么?
m=d; d=m; d=(Dog)m; d=c; c=(Cat)m;
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
//c=(Cat)m;
}
}
d=m;d=c;
不正确 子类对象可以直接赋给基类变量。
基类对象要赋给子类对象变量,必须执行类型转换,
其语法是:子类对象变量=(子类名)基类对象名;
c=(Cat)m
不正确 转换混乱。如果类型转换失败Java会抛出以下这种异常:ClassCastException
7、
package ketangceshi6;
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
运行截图
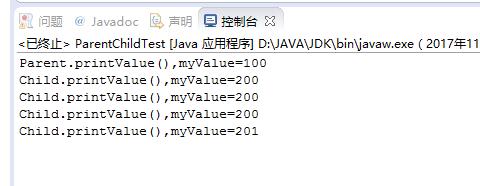
原因分析:通过强制类型转换子类的字符将父类的字符覆盖了
计算机是不会出错的,之所以得到这样的运行结果也是有原因的,那么从这些运行结果中,你能总结出Java的哪些语法特性?
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的。
8、这种编程方式有什么不合理的地方吗?
package homework6;
public class Zoo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Feeder f = new Feeder("小李");
// 饲养员小李喂养一只狮子
f.feedLion(new Lion());
// 饲养员小李喂养十只猴子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
f.feedMonkey(new Monkey());
}
// 饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
f.feedPigeon(new Pigeon());
}
}
}
class Feeder
{
public String name;
public Feeder(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void feedLion(Lion l)
{
l.eat();
}
public void feedPigeon(Pigeon p)
{
p.eat();
}
public void feedMonkey(Monkey m)
{
m.eat();
}
}
class Lion
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!");
}
}
class Monkey
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。");
}
}
class Pigeon
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。");
}
}
算法过于复杂。
运行截图
以上是关于继承与多肽:课后作业的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章