PCL系列——如何逐渐地配准一对点云
Posted xuezhisdc
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PCL系列——如何逐渐地配准一对点云相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
博客新址: http://blog.xuezhisd.top
邮箱:xuezhisd@126.com
PCL系列
- PCL系列——读入PCD格式文件操作
- PCL系列——将点云数据写入PCD格式文件
- PCL系列——拼接两个点云
- PCL系列——从深度图像(RangeImage)中提取NARF关键点
- PCL系列——如何可视化深度图像
- PCL系列——如何使用迭代最近点法(ICP)配准
- PCL系列——如何逐渐地配准一对点云
- PCL系列——三维重构之泊松重构
- PCL系列——三维重构之贪婪三角投影算法
- PCL系列——三维重构之移动立方体算法
说明
通过本教程,我们将会学会:
- 如何配准多个点云图。
- 配准的方法是:点云图两两配准,计算它们的变换矩阵,然后计算总的变换矩阵。
- 两个点云配准使用的是非线性ICP算法,它是ICP的算法的变体,使用Levenberg-Marquardt最优化。
操作
- 在VS2010 中新建一个文件
pairwise_incremental_registration.cpp,然后将下面的代码复制到文件中。 - 参照之前的文章,配置项目的属性。设置包含目录和库目录和附加依赖项。
#include <boost/make_shared.hpp> //共享指针
//点/点云
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_representation.h>
//pcd文件输入/输出
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
//滤波
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter.h>
//特征
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
//配准
#include <pcl/registration/icp.h> //ICP方法
#include <pcl/registration/icp_nl.h>
#include <pcl/registration/transforms.h>
//可视化
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
//命名空间
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
//定义类型的别名
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNormalT> PointCloudWithNormals;
//全局变量
//可视化对象
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer *p;
//左视区和右视区,可视化窗口分成左右两部分
int vp_1, vp_2;
//定义结构体,用于处理点云
struct PCD
{
PointCloud::Ptr cloud; //点云指针
std::string f_name; //文件名
//构造函数
PCD() : cloud (new PointCloud) {}; //初始化
};
// 定义新的点表达方式< x, y, z, curvature > 坐标+曲率
class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation <PointNormalT> //继承关系
{
using pcl::PointRepresentation<PointNormalT>::nr_dimensions_;
public:
MyPointRepresentation ()
{
//指定维数
nr_dimensions_ = 4;
}
//重载函数copyToFloatArray,以定义自己的特征向量
virtual void copyToFloatArray (const PointNormalT &p, float * out) const
{
//< x, y, z, curvature > 坐标xyz和曲率
out[0] = p.x;
out[1] = p.y;
out[2] = p.z;
out[3] = p.curvature;
}
};
//在窗口的左视区,简单的显示源点云和目标点云
void showCloudsLeft(const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_source)
{
p->removePointCloud ("vp1_target"); //根据给定的ID,从屏幕中去除一个点云。参数是ID
p->removePointCloud ("vp1_source"); //
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> tgt_h (cloud_target, 0, 255, 0); //目标点云绿色
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> src_h (cloud_source, 255, 0, 0); //源点云红色
p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1); //加载点云
p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_h, "vp1_source", vp_1);
PCL_INFO ("Press q to begin the registration.\\n"); //在命令行中显示提示信息
p-> spin();
}
//在窗口的右视区,简单的显示源点云和目标点云
void showCloudsRight(const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_source)
{
p->removePointCloud ("source"); //根据给定的ID,从屏幕中去除一个点云。参数是ID
p->removePointCloud ("target");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> tgt_color_handler (cloud_target, "curvature"); //目标点云彩色句柄
if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable ())
PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> src_color_handler (cloud_source, "curvature"); //源点云彩色句柄
if (!src_color_handler.isCapable ())
PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!");
p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_color_handler, "target", vp_2); //加载点云
p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_color_handler, "source", vp_2);
p->spinOnce();
}
// 读取一系列的PCD文件(希望配准的点云文件)
// 参数argc 参数的数量(来自main())
// 参数argv 参数的列表(来自main())
// 参数models 点云数据集的结果向量
void loadData (int argc, char **argv, std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > &models)
{
std::string extension (".pcd"); //声明并初始化string类型变量extension,表示文件后缀名
// 通过遍历文件名,读取pcd文件
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) //遍历所有的文件名(略过程序名)
{
std::string fname = std::string (argv[i]);
if (fname.size () <= extension.size ()) //文件名的长度是否符合要求
continue;
std::transform (fname.begin (), fname.end (), fname.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); //将某操作(小写字母化)应用于指定范围的每个元素
//检查文件是否是pcd文件
if (fname.compare (fname.size () - extension.size (), extension.size (), extension) == 0)
{
// 读取点云,并保存到models
PCD m;
m.f_name = argv[i];
pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[i], *m.cloud); //读取点云数据
//去除点云中的NaN点(xyz都是NaN)
std::vector<int> indices; //保存去除的点的索引
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*m.cloud,*m.cloud, indices); //去除点云中的NaN点
models.push_back (m);
}
}
}
//简单地配准一对点云数据,并返回结果
//参数cloud_src 源点云
//参数cloud_tgt 目标点云
//参数output 输出点云
//参数final_transform 成对变换矩阵
//参数downsample 是否下采样
void pairAlign (const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt, PointCloud::Ptr output, Eigen::Matrix4f &final_transform, bool downsample = false)
{
//
//为了一致性和速度,下采样
// \\note enable this for large datasets
PointCloud::Ptr src (new PointCloud); //创建点云指针
PointCloud::Ptr tgt (new PointCloud);
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> grid; //VoxelGrid 把一个给定的点云,聚集在一个局部的3D网格上,并下采样和滤波点云数据
if (downsample) //下采样
{
grid.setLeafSize (0.05, 0.05, 0.05); //设置体元网格的叶子大小
//下采样 源点云
grid.setInputCloud (cloud_src); //设置输入点云
grid.filter (*src); //下采样和滤波,并存储在src中
//下采样 目标点云
grid.setInputCloud (cloud_tgt);
grid.filter (*tgt);
}
else //不下采样
{
src = cloud_src; //直接复制
tgt = cloud_tgt;
}
//计算曲面的法向量和曲率
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src (new PointCloudWithNormals); //创建源点云指针(注意点的类型包含坐标和法向量)
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt (new PointCloudWithNormals); //创建目标点云指针(注意点的类型包含坐标和法向量)
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, PointNormalT> norm_est; //该对象用于计算法向量
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ()); //创建kd树,用于计算法向量的搜索方法
norm_est.setSearchMethod (tree); //设置搜索方法
norm_est.setKSearch (30); //设置最近邻的数量
norm_est.setInputCloud (src); //设置输入云
norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_src); //计算法向量,并存储在points_with_normals_src
pcl::copyPointCloud (*src, *points_with_normals_src); //复制点云(坐标)到points_with_normals_src(包含坐标和法向量)
norm_est.setInputCloud (tgt); //这3行计算目标点云的法向量,同上
norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::copyPointCloud (*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);
//创建一个 自定义点表达方式的 实例
MyPointRepresentation point_representation;
//加权曲率维度,以和坐标xyz保持平衡
float alpha[4] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
point_representation.setRescaleValues (alpha); //设置缩放值(向量化点时使用)
//创建非线性ICP对象 并设置参数
pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear<PointNormalT, PointNormalT> reg; //创建非线性ICP对象(ICP变体,使用Levenberg-Marquardt最优化)
reg.setTransformationEpsilon (1e-6); //设置容许的最大误差(迭代最优化)
//***** 注意:根据自己数据库的大小调节该参数
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (0.1); //设置对应点之间的最大距离(0.1m),在配准过程中,忽略大于该阈值的点
reg.setPointRepresentation (boost::make_shared<const MyPointRepresentation> (point_representation)); //设置点表达
//设置源点云和目标点云
//reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src); //版本不符合,使用下面的语句
reg.setInputCloud (points_with_normals_src); //设置输入点云(待变换的点云)
reg.setInputTarget (points_with_normals_tgt); //设置目标点云
reg.setMaximumIterations (2); //设置内部优化的迭代次数
// Run the same optimization in a loop and visualize the results
Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), prev, targetToSource;
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src; //用于存储结果(坐标+法向量)
for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i) //迭代
{
PCL_INFO ("Iteration Nr. %d.\\n", i); //命令行显示迭代的次数
//保存点云,用于可视化
points_with_normals_src = reg_result; //
//估计
//reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src);
reg.setInputCloud (points_with_normals_src); //重新设置输入点云(待变换的点云),因为经过上一次迭代,已经发生变换了
reg.align (*reg_result); //对齐(配准)两个点云
Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation () * Ti; //累积(每次迭代的)变换矩阵
//如果这次变换和上次变换的误差比阈值小,通过减小最大的对应点距离的方法来进一步细化
if (fabs ((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation () - prev).sum ()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon ())
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance () - 0.001); //减小对应点之间的最大距离(上面设置过)
prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation (); //上一次变换的误差
//显示当前配准状态,在窗口的右视区,简单的显示源点云和目标点云
showCloudsRight(points_with_normals_tgt, points_with_normals_src);
}
targetToSource = Ti.inverse(); //计算从目标点云到源点云的变换矩阵
pcl::transformPointCloud (*cloud_tgt, *output, targetToSource); //将目标点云 变换回到 源点云帧
p->removePointCloud ("source"); //根据给定的ID,从屏幕中去除一个点云。参数是ID
p->removePointCloud ("target");
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tgt_h (output, 0, 255, 0); //设置点云显示颜色,下同
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_src_h (cloud_src, 255, 0, 0);
p->addPointCloud (output, cloud_tgt_h, "target", vp_2); //添加点云数据,下同
p->addPointCloud (cloud_src, cloud_src_h, "source", vp_2);
PCL_INFO ("Press q to continue the registration.\\n");
p->spin ();
p->removePointCloud ("source");
p->removePointCloud ("target");
//add the source to the transformed target
*output += *cloud_src; // 拼接点云图(的点)点数数目是两个点云的点数和
final_transform = targetToSource; //最终的变换。目标点云到源点云的变换矩阵
}
//**************** 入口函数 ************************
//主函数
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
//读取数据
std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > data; //模型
loadData (argc, argv, data); //读取pcd文件数据,定义见上面
//检查用户数据
if (data.empty ())
{
PCL_ERROR ("Syntax is: %s <source.pcd> <target.pcd> [*]", argv[0]); //语法
PCL_ERROR ("[*] - multiple files can be added. The registration results of (i, i+1) will be registered against (i+2), etc"); //可以使用多个文件
return (-1);
}
PCL_INFO ("Loaded %d datasets.", (int)data.size ()); //显示读取了多少个点云文件
//创建一个 PCLVisualizer 对象
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (argc, argv, "Pairwise Incremental Registration example"); //p是全局变量
p->createViewPort (0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1); //创建左视区
p->createViewPort (0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2); //创建右视区
//创建点云指针和变换矩阵
PointCloud::Ptr result (new PointCloud), source, target; //创建3个点云指针,分别用于结果,源点云和目标点云
//全局变换矩阵,单位矩阵,成对变换
//逗号表达式,先创建一个单位矩阵,然后将成对变换 赋给 全局变换
Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), pairTransform;
//遍历所有的点云文件
for (size_t i = 1; i < data.size (); ++i)
{
source = data[i-1].cloud; //源点云
target = data[i].cloud; //目标点云
showCloudsLeft(source, target); //在左视区,简单的显示源点云和目标点云
PointCloud::Ptr temp (new PointCloud); //创建临时点云指针
//显示正在配准的点云文件名和各自的点数
PCL_INFO ("Aligning %s (%d points) with %s (%d points).\\n", data[i-1].f_name.c_str (), source->points.size (), data[i].f_name.c_str (), target->points.size ());
//********************************************************
//配准2个点云,函数定义见上面
pairAlign (source, target, temp, pairTransform, true);
//将当前的一对点云数据,变换到全局变换中。
pcl::transformPointCloud (*temp, *result, GlobalTransform);
//更新全局变换
GlobalTransform = GlobalTransform * pairTransform;
//********************************************************
// 保存成对的配准结果,变换到第一个点云帧
std::stringstream ss; //这两句是生成文件名
ss << i << ".pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFile (ss.str (), *result, true); //保存成对的配准结果
}
}
- 重新生成项目。
- 到改项目的Debug目录下,按住Shift,同时点击鼠标右键,在当前窗口打开CMD窗口。
- 在命令行中输入
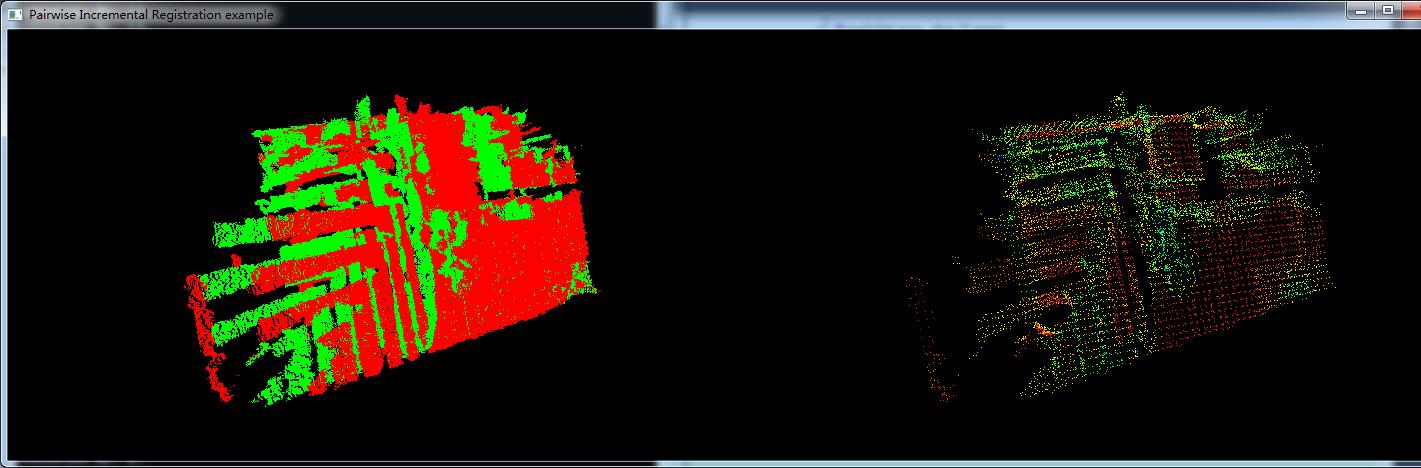
pairwise_incremental_registration.exe capture0001.pcd capture0002.pcd capture0003.pcd capture0004.pcd capture0005.pcd,执行程序。得到如下图所示的结果。
参考
以上是关于PCL系列——如何逐渐地配准一对点云的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章