结构型模式 享元模式
Posted 云水
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了结构型模式 享元模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
结构型模式 享元模式
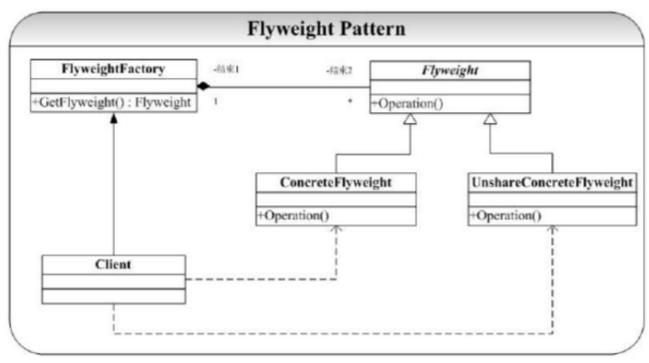
抽象享元角色:
所有具体享元类的父类,规定一些需要实现的公共接口。
具体享元角色:
抽象享元角色的具体实现类,并实现了抽象享元角色规定的方法。
享元工厂角色:
负责创建和管理享元角色。
使用场景:
是以共享的方式,高效的支持大量的细粒度的对象。
/** * 结构型模式 享元模式 * Flyweight模式也叫享元模式,是构造型模式之一,它通过与其他类似对象共享数据来减小内存占用。 * */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> class Person { public: Person(std::string name, int age, int sex) { m_name = name; m_age = age; m_sex = sex; } std::string getName() { return m_name; } int getAge() { return m_age; } int getSex() { return m_sex; } protected: //注意: 保护属性变量 std::string m_name; int m_age; int m_sex; }; class Teacher: public Person { public: Teacher(std::string id, std::string name, int age, int sex): Person(name, age, sex) { m_id = id; } std::string getID() { return m_id; } void printT() { std::cout << "id: " << m_id << "\\t" << "name: " << m_name << "\\t" << "age: " << m_age << "\\t" << "sex: " << m_sex << std::endl; } private: std::string m_id; }; class TeacherFactory { public: TeacherFactory() { m_tpool.clear(); } ~TeacherFactory() { while (!m_tpool.empty()) // 在工厂中创建老师结点,在工厂中销毁老师结点 { Teacher *temp = nullptr; std::map<std::string, Teacher *>::iterator it = m_tpool.begin(); temp = it->second; m_tpool.erase(it); delete temp; } } // 通过Teacher的pool,来存放老师结点,在TeacherFactory中创建老师、销毁老师 Teacher *getTeacher(std::string tid) { std::string name; int age; int sex; Teacher *temp = nullptr; std::map<std::string, Teacher *>::iterator it = m_tpool.find(tid); if (it == m_tpool.end()) { std::cout << "id为: " << tid << "的老师不存在, 系统为你创建该老师, 请输入以下信息" << std::endl; std::cout << "请输入老师的姓名: " << std::endl; std::cin >> name; std::cout << "请输入老师的年龄: " << std::endl; std::cin >> age; std::cout << "请输入老师的性别代号(1: 男 2: 女): " << std::endl; std::cin >> sex; temp = new Teacher(tid, name, age, sex); m_tpool.insert(std::pair<std::string, Teacher *>(tid, temp)); } else { temp = it->second; } return temp; } private: std::map<std::string, Teacher *> m_tpool; }; void mytest() { TeacherFactory *teacherFactory = new TeacherFactory(); Teacher *t1 = teacherFactory->getTeacher("001"); t1->printT(); Teacher *t2 = teacherFactory->getTeacher("002"); t1->printT(); Teacher *t3 = teacherFactory->getTeacher("001"); t1->printT(); delete teacherFactory; teacherFactory = nullptr; return; } int main() { mytest(); system("pause"); return 0; }
以上是关于结构型模式 享元模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章