简易四则运算
Posted 长夜雨
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了简易四则运算相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、实验目的
1.熟悉体系结构的风格的概念
2.理解和应用管道过滤器型的风格。
3、理解解释器的原理
4、理解编译器模型
二、实验环境
硬件:
软件:Python或任何一种自己喜欢的语言
三、实验内容
1、实现“四则运算”的简易翻译器。
结果要求:
1)实现加减乘除四则运算,允许同时又多个操作数,如:2+3*5-6 结果是11
2)被操作数为整数,整数可以有多位
3)处理空格
4)输入错误显示错误提示,并返回命令状态“CALC”

图1 实验结果示例
加强练习:
1、有能力的同学,可以尝试实现赋值语句,例如x=2+3*5-6,返回x=11。(注意:要实现解释器的功能,而不是只是显示)
2、尝试实现自增和自减符号,例如x++
3、采用管道-过滤器(Pipes and Filters)风格实现解释器
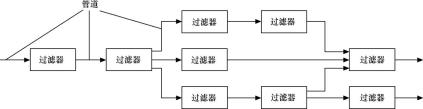
图2 管道-过滤器风格
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define Stack_Size 50
typedef struct
{
char elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SepStack;
typedef struct
{
int elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SepStackOperand;
typedef struct //运算符栈的定义
{
char elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SeqStack;
typedef struct //运算数栈的定义
{
int elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SeqStackOperand;
void CalFace(); //鼠标按键响应
void MainFace(); //界面
char ops[7]={\'+\', \'-\', \'*\', \'/\', \'(\', \')\', \'#\'};
int cmp[7][7]=
{
{2,2,1,1,1,2,2},
{2,2,1,1,1,2,2},
{2,2,2,2,1,2,2},
{2,2,2,2,1,2,2},
{1,1,1,1,1,3,0},
{2,2,2,2,0,2,2},
{1,1,1,1,1,0,3}
};
void InitStack(SeqStack*S) //初始化运算符栈
{
S->top=-1;
}
void InitStacknOperand(SeqStackOperand*S) //初始化运算数栈
{
S->top=-1;
}
int IsEmpty(SeqStack*S) //判断栈S为空栈时返回值为真,反之为假
{
return (S->top==-1?TRUE:FALSE);
}
int IsEmptynOperand(SeqStackOperand*S) //判断栈S为空栈时返回值为真,反之为假
{
return (S->top==-1?TRUE:FALSE);
}
int IsFull(SeqStack*S) //判断栈S为满栈时返回值为真,反之为假
{
return (S->top==Stack_Size-1?TRUE:FALSE);
}
int IsFullOperand(SeqStackOperand*S) //判断栈S为满栈时返回值为真,反之为假
{
return (S->top==Stack_Size-1?TRUE:FALSE);
}
int Push(SeqStack*S, char x) //运算符栈入栈函数
{
if(S->top==Stack_Size-1)
{
printf("Stack is full!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
S->top++;
S->elem[S->top]=x;
return TRUE;
}
}
int PushOperand(SeqStackOperand*S, int x) //运算数栈入栈函数
{
if(S->top==Stack_Size-1)
{
printf("Stack is full!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
S->top++;
S->elem[S->top]=x;
return TRUE;
}
}
int Pop(SeqStack*S, char *x) //运算符栈出栈函数
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("运算符栈空!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
*x=S->elem[S->top];
S->top--;
return TRUE;
}
}
int PopOperand(SeqStackOperand*S, int *x) //运算数栈出栈函数
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("运算数栈空!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
*x=S->elem[S->top];
S->top--;
return TRUE;
}
}
char GetTop(SeqStack*S) //运算符栈取栈顶元素函数
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("运算符栈空!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return (S->elem[S->top]);
}
}
int GetTopOperand(SeqStackOperand*S) //运算数栈取栈顶元素函数
{
if(S->top==-1)
{
printf("运算符栈空!\\n");
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return (S->elem[S->top]);
}
}
int Isoperator(char ch) //判断输入字符是否为运算符函数,是返回TRUE,不是返回FALSE
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
if(ch==ops[i])
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
char Compare(char ch1, char ch2) //比
较运算符优先级函数
{
int i, m, n;
char pri;
int priority;
for(i=0; i<7; i++) //找到相比较的两个运算符在比较矩阵里的相对位置
{
if(ch1==ops[i])
m=i;
if(ch2==ops[i])
n=i;
}
priority=cmp[m][n];
switch(priority)
{
case 1:
pri=\'<\';
break;
case 2:
pri=\'>\';
break;
case 3:
pri=\'=\';
break;
case 0:
pri=\'$\';
printf("表达式错误!\\n");
break;
}
return pri;
}
int Execute(int a, char op, int b) //运算函数
{
int result;
switch(op)
{
case \'+\':
result=a+b;
break;
case \'-\':
result=a-b;
break;
case \'*\':
result=a*b;
break;
case \'/\':
result=a/b;
break;
}
return result;
}
int ExpEvaluation(char *str) //读入一个简单算术表达式并计算其值,operator和operand分别为运算符栈和运算数栈,ops为运算符集合
{
int a, b, v, temp;
char ch, op;
int i=0;
SeqStack operatordata;
SeqStackOperand operand;
InitStack (&operatordata);
InitStacknOperand (&operand);
Push (&operatordata, \'#\');
ch=*str++;
while(ch!=\'#\' || GetTop(&operatordata)!=\'#\')
{
if(!Isoperator(ch))
{
temp=ch-\'0\'; //将字符转换为十进制数
ch=*str++;
i++;
while(!Isoperator(ch))
{
temp=temp*10+ch-\'0\'; //将逐个读入运算符的各位转化为十进制数
ch=*str++;
i++;
}
PushOperand(&operand, temp);
}
else
{
switch(Compare(GetTop(&operatordata), ch))
{
case \'<\':
Push(&operatordata, ch);
ch=*str++;
i++;
break;
case \'=\':
Pop(&operatordata, &op);
ch=*str++;
i++;
break;
case \'>\':
Pop(&operatordata, &op);
PopOperand(&operand, &b);
PopOperand(&operand, &a);
v=Execute(a, op, b);
PushOperand(&operand, v);
break;
}
}
}
v=GetTopOperand(&operand);
return v;
}
void MainFace()
{
int i, j, ch, n;
initgraph(500, 300);
bar(15, 15, 480, 70);
setcolor(WHITE);
rectangle(10, 10, 490, 290);
setcolor(WHITE);
for(j=0; j<2; j++)
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
if(i<3)
circle(55+65*i, 110+65*j, 20);
else
rectangle(55+65*i-20, 110+65*j-20, 55+65*i+20, 110+65*j+20);
}
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
if(i<4)
circle(55+65*i, 110+65*j, 20);
else
rectangle(55+65*i-20, 110+65*j-20, 55+65*i+20, 110+65*j+20);
}
outtextxy(50, 105, "7");
outtextxy(115, 105, "8");
outtextxy(180, 105, "9");
outtextxy(240, 105, "C");
outtextxy(310, 105, "+");
outtextxy(375, 105, "(");
outtextxy(440, 105, ")");
outtextxy(50, 170, "4");
outtextxy(115, 170, "5");
outtextxy(180, 170, "6");
outtextxy(240, 170, ".");
outtextxy(310, 170, "-");
outtextxy(370, 170, "sqrt");
outtextxy(440, 170, "<-");
outtextxy(50, 235, "3");
outtextxy(115, 235, "2");
outtextxy(180, 235, "1");
outtextxy(240, 235, "0");
outtextxy(310, 235, "*");
outtextxy(370, 235, "/");
outtextxy(440, 235, "=
");
}
void CalFace()
{
int i, j, ch, n;
char string[50]="", str1[50]="", str2[10]="";
MOUSEMSG m; //定义一个鼠标动作
MainFace();
m=GetMouseMsg(); //记录鼠标操作
i=0;
while(true)
{
m=GetMouseMsg(); //记录鼠标操作
if(m.uMsg==WM_LBUTTONDOWN)
{
setcolor(WHITE);
if(m.x>35 && m.x<=75 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, "7");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>100 && m.x<=140 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, "8");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>165 && m.x<=205 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, "9");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>225 && m.x<=265 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
setcolor(WHITE);
bar(15, 15, 480, 70);
strcpy(string, "");
}
if(m.x>290 && m.x<=330 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, "+");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>355 && m.x<=395 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, "(");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>420 && m.x<=460 && m.y>90 && m.y<130)
{
strcat(string, ")");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>35 && m.x<=75 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
strcat(string, "4");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>100 && m.x<=140 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
strcat(string, "5");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>165 && m.x<=205 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
strcat(string, "6");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>225 && m.x<=265 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
strcat(string, ".");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>290 && m.x<=330 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
strcat(string, "-");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>355 && m.x<=395 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
n=strlen(string);
switch(n) //不超过位
{
case 5:
i=string[0]*10000+string[1]*1000+string[2]*100+string[3]*10+string[4];
break;
case 4:
i=string[0]*1000+string[1]*100+string[2]*10+string[3];
break;
case 3:
i=string[0]*100+string[1]*10+string[2];
break;
case 2:
i=string[0]*10+string[1];
break;
case 1:
i=string[0];
break;
}
itoa(sqrt(i), string, 10);
setcolor(BLACK);
bar(15, 15, 480, 70);
setcolor(WHITE);
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>420 && m.x<=460 && m.y>155 && m.y<195)
{
n=strlen(string);
printf("n=%d.", n);
string[n-1]=\'\\0\';
bar(15, 15, 480, 70);
setcolor(WHITE);
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>35 && m.x<=75 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "3");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>100 && m.x<=140 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "2");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>165 && m.x<=205 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "1");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>225 && m.x<=265
&& m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "0");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>290 && m.x<=330 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "*");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>355 && m.x<=395 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcat(string, "/");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
if(m.x>420 && m.x<=460 && m.y>215 && m.y<255)
{
strcpy(str1, string);
strcat(string, "=");
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
strcat(str1, "#");
itoa(ExpEvaluation(str1), str2, 10);
strcat(string, str2);
outtextxy(25, 40, string);
}
}
}
getch(); //按任意键继续
closegraph(); //关闭图形界面
}
int main(void)
{
CalFace();
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define Stack_Size 50
typedef struct
{
char elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SepStack;
typedef struct
{
int elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SepStackOperand;
typedef struct //运算符栈的定义
{
char elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SeqStack;
typedef struct //运算数栈的定义
{
int elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SeqStackOperand;
void CalFace(); //鼠标按键响应
void MainFace(); //界面
char ops[7]={\'+\', \'-\', \'*\', \'/\', \'(\', \')\', \'#\'};
int cmp[7][7]=
{
{2,2,1,1,1,2,2},
{2,2,1,1,1,2,2},
{2
以上是关于简易四则运算的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章