第四次课后作业及Sring类型的应用
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第四次课后作业及Sring类型的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
作业1.加密字符串
一.程序设计思想
(1).首先设计一个类,用于装载所需要的函数。
(2).分别设置两个函数,用于加密和解密。
(3).在主函数中判断用户输入的字符是否合法,然后调用加密解密函数,解决问题。
二.程序流程图
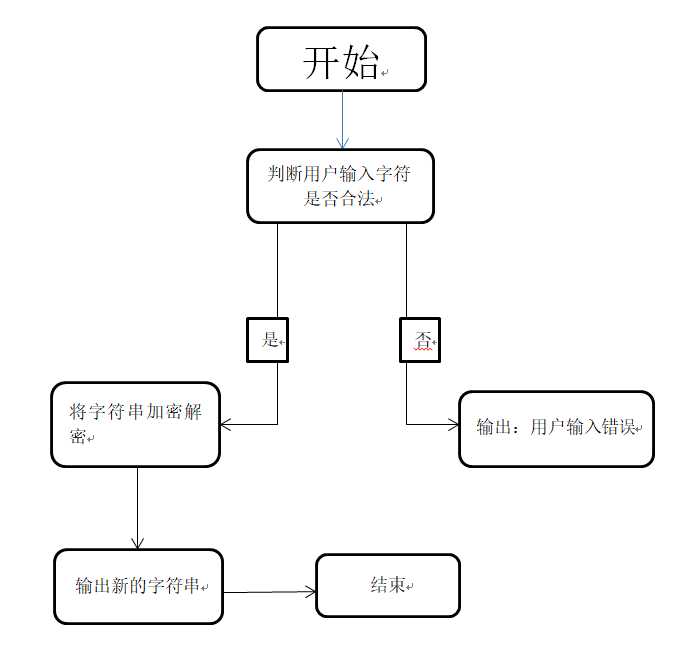
三.源代码
package 加密字符串; import java.util.Scanner; class Rome { String string; public Rome(String string) { this.string=string; } public void encryption() { char letter[]=new char[string.length()]; letter=string.toCharArray(); int i=0; for(i=0;i<string.length();i++) { if((letter[i]>=65&&letter[i]<=87)||(letter[i]>=97&&letter[i]<=119)) { letter[i]+=3; } else { letter[i]-=23; } } for(i=0;i<string.length();i++) { System.out.print(letter[i]); } } public void decryption() { char letter[]=new char[string.length()]; letter=string.toCharArray(); int i=0; for(i=0;i<string.length();i++) { if((letter[i]>=68&&letter[i]<=90)||(letter[i]>=100&&letter[i]<=122)) { letter[i]-=3; } else { letter[i]+=23; } } for(i=0;i<string.length();i++) { System.out.print(letter[i]); } System.out.print("\\n"); } } public class Jiami { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("请输入字符串:"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String letter="***"; int choose=0; if(input.hasNextLine()) { letter=input.nextLine(); } else { System.out.println("输入错误!"); System.exit(0); } Rome R=new Rome(letter); System.out.println("请选择您要进行的操作:1.加密 2.解密"); System.out.println("请选择:"); if(input.hasNextInt()) { choose=input.nextInt(); } else { System.out.println("输入错误!"); System.exit(0); } if(choose==1) { R.encryption(); } else if(choose==2) { R.decryption(); } else { System.out.println("输入错误!"); System.exit(0); } } }
四.程序运行结果截图


作业二:动手动脑以及String类型应用
1.String.equals()
① 当比较两个对象时,用”==”返回false,用equals函数返回true
eg:
String s1=new String(“Hello!”);
String s2=new String(“Hello!”);
System.out.println(s1==s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
原因:两个String类型的变量s1和s2都通过new关键字分别创建了一个新的String对象,这个new关键字为创建的每个对象分配一块新的、独立的内存。因此当通过"=="来比较它们所引用的是否是同一个对象时,将返回false。而通过equals()方法来比较时,则返回true。
② 比较同一对象时,“==”与equals函数的结果相同
eg:
String s1=new String(“java”);
String s2=s1;
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
原因:虽然变量s1通过new关键字来创建了一个String对象,但是s2是由s1赋值而来,即把s1的引用赋值给了s2,所以s2所引用的对象其实就是s1所引用的对象。当通过"=="来比较时,返回true。
③ 当String作为基本数据类型来使用时,“==”和equals函数结果相同
eg:
String s1=”Hello!”;
String s2=”Hello!”;
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
原因:String对象是作为一个基本类型来使用的,虚拟机不会为这两个String对象分配新的内存堆,而是到String缓冲池中来寻找。此时,s1和s2所引用的是同一个对象。
2.String.length()
语法:public int length()
功能:此方法返回由该对象表示的字符序列的长度。
eg:
String str=”dwfsdfwfsadf”;
System.out.println("length of string =”+str.length());
运行结果为:
length of string = 15
3.String. charAt()
语法:public charAt(int index)
功能:用于返回index处的字符。
eg:
String s = "www.runoob.com";
char result = s.charAt(8);
System.out.println(result);
运行结果为:
o
4.String.getChars()
语法:public void getChars(int start,int end,char c[],int offset)
功能:将当前字符串从start到end-1位置上的字符复制到字符数组c中,并从c的offset处开始存放
eg:
String str = "abcdefghikl";
Char[] ch = new char[8];
str.getChars(2,5,ch,0);
System.out.println(ch);
运行结果为:
cde
5.String.replace()
语法:public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
功能:通过用 newChar 字符替换字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 字符,并返回替换后的新字符串。
eg:
String Str = new String("hello");
System.out.print("返回值 :" );
System.out.println(Str.replace(‘o‘, ‘T‘));
运行结果为:
返回值:hellT
6.String.toUpperCase()
语法:public String toUpperCase()
功能:转换为大写的字符串。
eg:
System.out.println(new String(“hello”).toUpperCase());
运行结果为:
HELLO
7.String.toLowerCase()
语法:public String toLowerCase()
功能:将字符串全部转换成小写
eg:
System.out.println(new String(“HELLO”).toLowerCase());
运行结果为:
hello
8.String. trim()
语法:public String trim()
功能:返回一个字符串副本,并忽略(去除)开头和结尾的空白
eg:
String x=“ abc def ”;
System.out.println(x.trim());
运行结果为:
abc def
9.String. toCharArray()
语法:public char[] toCharArray()
功能:将字符串转换成一个新的字符数组
eg:
String s1=new String("Hello World!");
char[] c=s1.toCharArray();
System.out.println("数组c的长度为:"+c.length);
System.out.println("c[4]:"+c[4]);
运行结果为:
数组c的长度为:12
c[4]:o
以上是关于第四次课后作业及Sring类型的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章