集合(Map可变参数Collections)
Posted 作巴
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了集合(Map可变参数Collections)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
集合
第1章 Map接口
1.1 Map接口概述
我们通过查看Map接口描述,发现Map接口下的集合与Collection接口下的集合,它们存储数据的形式不同,如下图。
l Collection中的集合,元素是孤立存在的(理解为单身),向集合中存储元素采用一个个元素的方式存储。
l Map中的集合,元素是成对存在的(理解为夫妻)。每个元素由键与值两部分组成,通过键可以找对所对应的值。
l Collection中的集合称为单列集合,Map中的集合称为双列集合。
l 需要注意的是,Map中的集合不能包含重复的键,值可以重复;每个键只能对应一个值。
l Map中常用的集合为HashMap集合、LinkedHashMap集合。

1.2 Map接口中常用集合概述
通过查看Map接口描述,看到Map有多个子类,这里我们主要讲解常用的HashMap集合、LinkedHashMap集合。
l HashMap<K,V>:存储数据采用的哈希表结构,元素的存取顺序不能保证一致。由于要保证键的唯一、不重复,需要重写键的hashCode()方法、equals()方法。
l LinkedHashMap<K,V>:HashMap下有个子类LinkedHashMap,存储数据采用的哈希表结构+链表结构。通过链表结构可以保证元素的存取顺序一致;通过哈希表结构可以保证的键的唯一、不重复,需要重写键的hashCode()方法、equals()方法。
l 注意:Map接口中的集合都有两个泛型变量<K,V>,在使用时,要为两个泛型变量赋予数据类型。两个泛型变量<K,V>的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同。
1.3 Map接口中的常用方法

l put方法:将指定的键与值对应起来,并添加到集合中
l 方法返回值为键所对应的值
使用put方法时,若指定的键(key)在集合中没有,则没有这个键对应的值,返回null,并把指定的键值添加到集合中;
使用put方法时,若指定的键(key)在集合中存在,则返回值为集合中键对应的值(该值为替换前的值),并把指定键所对应的值,替换成指定的新值。
l get方法:获取指定键(key)所对应的值(value)
l remove方法:根据指定的键(key)删除元素,返回被删除元素的值(value)。
Map接口的方法演示
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//给map中添加元素
map.put("星期一", "Monday");
map.put("星期日", "Sunday");
System.out.println(map); // {星期日=Sunday, 星期一=Monday}
//当给Map中添加元素,会返回key对应的原来的value值,若key没有对应的值,返回null
System.out.println(map.put("星期一", "Mon")); // Monday
System.out.println(map); // {星期日=Sunday, 星期一=Mon}
//根据指定的key获取对应的value
String en = map.get("星期日");
System.out.println(en); // Sunday
//根据key删除元素,会返回key对应的value值
String value = map.remove("星期日");
System.out.println(value); // Sunday
System.out.println(map); // {星期一=Mon}
}
}
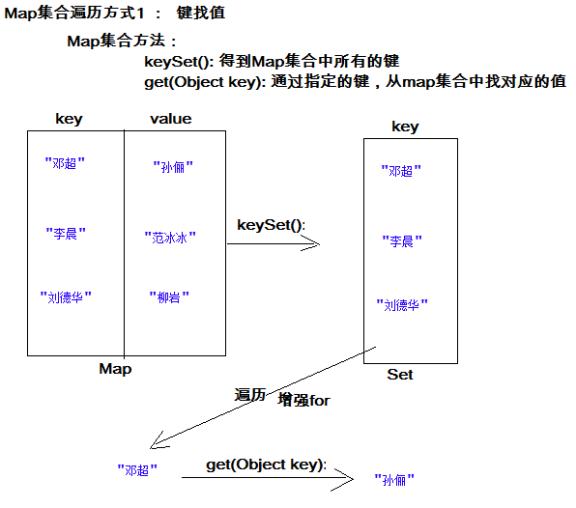
1.4 Map集合遍历键找值方式
键找值方式:即通过元素中的键,获取键所对应的值
操作步骤与图解:
1.获取Map集合中所有的键,由于键是唯一的,所以返回一个Set集合存储所有的键

2.遍历键的Set集合,得到每一个键
3.根据键,获取键所对应的值
代码演示:
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//给map中添加元素
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");
map.put("李晨", "范冰冰");
map.put("刘德华", "柳岩");
//获取Map中的所有key
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
//遍历存放所有key的Set集合
Iterator<String> it =keySet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//得到每一个key
String key = it.next();
//通过key获取对应的value
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
1.5 Entry键值对对象
在Map类设计时,提供了一个嵌套接口:Entry。Entry将键值对的对应关系封装成了对象。即键值对对象,这样我们在遍历Map集合时,就可以从每一个键值对(Entry)对象中获取对应的键与对应的值。

l Entry是Map接口中提供的一个静态内部嵌套接口。

l getKey()方法:获取Entry对象中的键
l getValue()方法:获取Entry对象中的值

l entrySet()方法:用于返回Map集合中所有的键值对(Entry)对象,以Set集合形式返回。
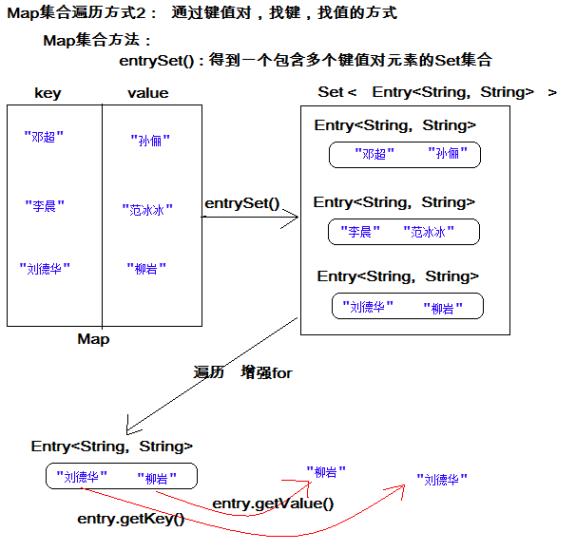
1.6 Map集合遍历键值对方式
键值对方式:即通过集合中每个键值对(Entry)对象,获取键值对(Entry)对象中的键与值。
操作步骤与图解:
1.获取Map集合中,所有的键值对(Entry)对象,以Set集合形式返回。

2.遍历包含键值对(Entry)对象的Set集合,得到每一个键值对(Entry)对象
3.通过键值对(Entry)对象,获取Entry对象中的键与值。
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//给map中添加元素
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");
map.put("李晨", "范冰冰");
map.put("刘德华", "柳岩");
//获取Map中的所有key与value的对应关系
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//遍历Set集合
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,String>> it =entrySet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//得到每一对对应关系
Map.Entry<String,String> entry = it.next();
//通过每一对对应关系获取对应的key
String key = entry.getKey();
//通过每一对对应关系获取对应的value
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
注意:Map集合不能直接使用迭代器或者foreach进行遍历。但是转成Set之后就可以使用了。
1.7 HashMap存储自定义类型键值
练习:每位学生(姓名,年龄)都有自己的家庭住址。那么,既然有对应关系,则将学生对象和家庭住址存储到map集合中。学生作为键, 家庭住址作为值。
注意,学生姓名相同并且年龄相同视为同一名学生。
l 学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
//编写构造方法,文档中已省略
//编写get,set方法,文档中已省略
//编写toString方法,文档中已省略
}
l 测试类
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1,创建hashmap集合对象。
Map<Student,String> map = new HashMap<Student,String>();
//2,添加元素。
map.put(new Student("lisi",28), "上海");
map.put(new Student("wangwu",22), "北京");
map.put(new Student("zhaoliu",24), "成都");
map.put(new Student("zhouqi",25), "广州");
map.put(new Student("wangwu",22), "南京");
//3,取出元素。键找值方式
Set<Student> keySet = map.keySet();
for(Student key : keySet){
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key.toString()+"....."+value);
}
//取出元素。键值对方式
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : entrySet) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key.toString()+"....."+value);
}
}
}
l 当给HashMap中存放自定义对象时,如果自定义对象作为key存在,这时要保证对象唯一,必须复写对象的hashCode和equals方法(如果忘记,请回顾HashSet存放自定义对象)。
l 如果要保证map中存放的key和取出的顺序一致,可以使用LinkedHashMap集合来存放。
1.8 静态导入
在导包的过程中我们可以直接导入静态部分,这样某个类的静态成员就可以直接使用了。在源码中经常会出现静态导入。
静态导入格式:
import static XXX.YYY; 导入后YYY可直接使用。
例如:Map.Entry的访问,简化后为Entry
import static java.util.Map.Entry;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1,创建hashmap集合对象。
Map<Student,String> map = new HashMap<Student,String>();
//取出元素。键值对方式
//Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Set<Entry<Student, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : entrySet) {
for (Entry<Student, String> entry : entrySet) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key.toString()+"....."+value);
}
}
}
1.9 可变参数
在JDK1.5之后,如果我们定义一个方法需要接受多个参数,并且多个参数类型一致,我们可以对其简化成如下格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型... 形参名){ }
其实这个书写完全等价与
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型[] 形参名){ }
只是后面这种定义,在调用时必须传递数组,而前者可以直接传递数据即可。
jdk1.5以后。出现了简化操作。... 用在参数上,称之为可变参数。
同样是代表数组,但是在调用这个带有可变参数的方法时,不用创建数组(这就是简单之处),直接将数组中的元素作为实际参数进行传递,其实编译成的class文件,将这些元素先封装到一个数组中,在进行传递。这些动作都在编译.class文件时,自动完成了。
代码演示:
public class ParamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {21,89,32};
int sum = add(arr);
System.out.println(sum);
sum = add(21,89,32);//可变参数调用形式
System.out.println(sum);
}
//JDK1.5之后写法
public static int add(int...arr){
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
//原始写法
/*
public static int add(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
*/
}
l 上述add方法在同一个类中,只能存在一个。因为会发生调用的不确定性
注意:如果在方法书写时,这个方法拥有多参数,参数中包含可变参数,可变参数一定要写在参数列表的末尾位置。
1.10 Collections集合工具类
Collections是集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作。部分方法如下:
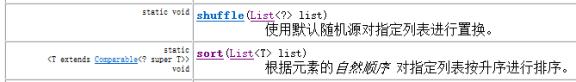
l public static <T> void sort(List<T> list) // 集合元素排序
//排序前元素list集合元素 [33,11,77,55]
Collections.sort( list );
//排序后元素list集合元素 [11,33,55,77]
l public static void shuffle(List<?> list) // 集合元素存储位置打乱
//list集合元素 [11,33,55,77]
Collections.shuffle( list );
//使用shuffle方法后,集合中的元素为[77,33,11,55],每次执行该方法,集合中存储的元素位置都会随机打乱
1.11 集合嵌套
集合嵌套并不是一个新的知识点,仅仅是集合内容又是集合,如Collection集合嵌套、Collection集合与Map集合相互嵌套、Map集合嵌套。
l ArrayList嵌套 ArrayList
ArrayList< ArrayList<String> >
Collection< ArrayList<Integer> >
l Map嵌套 ArrayList
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Person>>
ArrayList< HashMap<String, String>>
l Map集合嵌套
HashMap<String, HashMap<String,String>>
HashMap<String, HashMap<Person,String>>
1.12 集合继承体系的面向对象思想
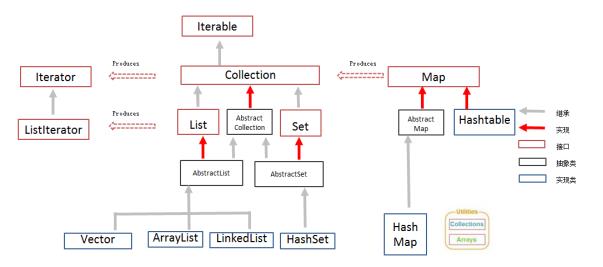
l 接口:用来明确所有集合中该具有的功能,相当于在定义集合功能标准;
l 抽象类:把多个集合中功能实现方式相同的方法,抽取到抽象类实现,具体集合不再遍写,继承使用即可;
l 具体类:继承抽象类,实现接口,重写所有抽象方法,达到具备指定功能的集合。每个具体集合类,根据自身的数据存储结构方式,对接口中的功能方法,进行不同方式的实现。
第2章 模拟斗地主洗牌发牌
2.1 案例介绍
按照斗地主的规则,完成洗牌发牌的动作。

具体规则:
1. 组装54张扑克牌
2. 将54张牌顺序打乱
3. 三个玩家参与游戏,三人交替摸牌,每人17张牌,最后三张留作底牌。
4. 查看三人各自手中的牌(按照牌的大小排序)、底牌
l 手中扑克牌从大到小的摆放顺序:大王,小王,2,A,K,Q,J,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3
2.2 案例需求分析
l 准备牌:
完成数字与纸牌的映射关系:
使用双列Map(HashMap)集合,完成一个数字与字符串纸牌的对应关系(相当于一个字典)。
l 洗牌:
通过数字完成洗牌发牌
l 发牌:
将每个人以及底牌设计为ArrayList<String>,将最后3张牌直接存放于底牌,剩余牌通过对3取模依次发牌。
存放的过程中要求数字大小与斗地主规则的大小对应。
将代表不同纸牌的数字分配给不同的玩家与底牌。
l 看牌:
通过Map集合找到对应字符展示。
通过查询纸牌与数字的对应关系,由数字转成纸牌字符串再进行展示。

2.3 实现代码步骤
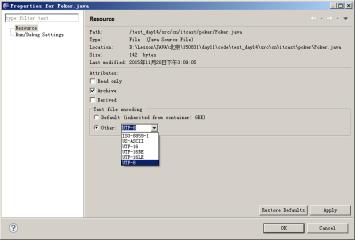
首先,要修改java文件编码,由GBK修改为UTF-8,因为默认的字符编码GBK没有我们要的梅花、方片、黑桃、红桃(♠♥♦♣)等特殊字符。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
/*
* 斗地主洗牌发牌排序
*/
public class Poker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//准备花色
ArrayList<String> color = new ArrayList<String>();
color.add("♠");
color.add("♥");
color.add("♦");
color.add("♣");
//准备数字
ArrayList<String> number = new ArrayList<String>();
Collections.addAll(number,"3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K","A","2");
//定义一个map集合:用来将数字与每一张牌进行对应
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
int index = 0;
for (String thisNumber : number) {
for (String thisColor : color) {
map.put(index++, thisColor+thisNumber);
}
}
//加入大小王
map.put(index++, "小☺");
map.put(index++, "大☻");
//一副54张的牌 ArrayList里边为0-53的数的新牌
ArrayList<Integer> cards = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i <= 53; i++) {
cards.add(i);
}
//洗牌
Collections.shuffle(cards);
//创建三个玩家和底牌
ArrayList<Integer> iPlayer = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> iPlayer2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> iPlayer3 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> itCards = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//遍历这副洗好的牌,遍历过程中,将牌发到三个玩家和底牌中
for (int i = 0; i < cards.size(); i++) {
if(i>=51) {
iCards.add(cards.get(i));
} else {
if(i%3==0) {
iPlayer.add(cards.get(i));
}else if(i%3==1) {
iPlayer2.add(cards.get(i));
}else {
iPlayer3.add(cards.get(i));
}
}
}
//对每个人手中的牌排序
Collections.sort(iPlayer);
Collections.sort(iPlayer2);
Collections.sort(iPlayer3);
//对应数字形式的每个人手中的牌,定义字符串形式的牌
ArrayList<String> sPlayer = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> sPlayer2 = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> sPlayer3 = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> sCards = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Integer key : iPlayer) {
sPlayer.add(map.get(key));
}
for (Integer key : iPlayer2) {
sPlayer2.add(map.get(key));
}
for (Integer key : iPlayer3) {
sPlayer3.add(map.get(key));
}
for (Integer key : iCards) {
sCards.add(map.get(key));
}
//看牌
System.out.println(sPlayer);
System.out.println(sPlayer2);
System.out.println(sPlayer3);
System.out.println(sCards);
}
}
第3章 总结
3.1 知识点总结
l Map集合:
map集合中的元素都是成对出现,成对存储的
map集合中的元素都是以一对键和值的形式组成存在的,称为键值对,理解为夫妻对
map集合中的键不能重复存储,值可以重复
map集合中的每一个键 对应着一个值
l 方法:
V put(K key, V value) 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中
V remove(Object key) 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的值
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)
V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值
Set<K> keySet() 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中
l Map集合遍历的两种方式
l 方式1:根据键找值的方式
//a, 获取到Map集合中所有的键,返回对应的Set集合
//b, 遍历键的集合,获取到每一个键
//c, 通过键,找到对应的值
//获取到Map集合中所有的键,返回对应的Set集合
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
//遍历键的集合,获取到每一个键
for (String key : keys) {
//通过键,找到对应的值
Student s = map.get(key);
System.out.println( key + "..." + s.getName() + "..." + s.getAge() );
}
l 方式2:根据键值对对象找键和值的方式
//a, 获取Map集合中所有的键值对元素,返回对应的Set集合
//b, 遍历键值对元素集合,获取到每一个键值对元素对象
//c, 通过键值对元素对象,获取对应的键,和对应的值
//获取Map集合中所有的键值对元素,返回对应的Set集合
Set< Map.Entry<String, Student>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//遍历键值对元素集合,获取到每一个键值对元素对象
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> entry : entrySet) {
//通过键值对元素对象,获取对应的键,和对应的值
//找键
String key = entry.getKey();
//找值
Student s = entry.getValue();
//打印
System.out.println( key+"..."+s.getName()+"..."+s.getAge() );
}
l HashMap:
l 特点:
是Map集合的子集合
底层采用哈希表结构
HashMap集合中的key不能重复,通过重写hashCode() 与 equals()方法来保证键的唯一。
不能保证元素存与取的顺序完全一致
l LinkedHashMap:
l 特点:
是HashMap集合的子集合
底层采用哈希表+链表结构
LinkedHashMap集合中的key不能重复,通过重写hashCode() 与 equals()方法来保证键的唯一。
l Collections中的方法:
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list) 排序
public static void shuffle(List<?> list) 集合中的元素存储位置随机打乱
以上是关于集合(Map可变参数Collections)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章