vue源码学习--合并策略对象mergeOptions
Posted MachLau
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了vue源码学习--合并策略对象mergeOptions相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
源码vue在实例化对象、vue子类声明的时候会对父实例和子实例的参数使用设定好的合并策略合并父、子实例的参数。以及实例化前期、数据绑定时均有使用到合并策略合并参数。
定义合并策略的js文件路径是:\\vue-dev\\src\\core\\util\\options.js
在合并策略中对不同类型的参数使用了不同的合并策略。例如:strat.data合并data、defaultStrat合并[el、propsData和name]、mergrHook 合并生命周期的钩子函数、mergeAssets合并[component、directives、filter]等。
这些合并策略通过入口函数mergeOptions (parent, child, vm)中对合并参数对象中的不同属性进行合并策略选择。

1 export function mergeOptions ( 2 parent: Object, 3 child: Object, 4 vm?: Component 5 ): Object { 6 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\') { 7 checkComponents(child) 8 } 9 10 if (typeof child === \'function\') { 11 child = child.options 12 } 13 14 normalizeProps(child, vm)//格式化prop为基于对象的格式 15 normalizeInject(child, vm)//格式化Inject为基于对象的格式 16 normalizeDirectives(child)//格式化directives为对象的格式 17 const extendsFrom = child.extends 18 if (extendsFrom) { 19 parent = mergeOptions(parent, extendsFrom, vm) 20 } 21 if (child.mixins) { 22 for (let i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) { 23 parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.mixins[i], vm) 24 } 25 } 26 const options = {} 27 let key 28 for (key in parent) { 29 mergeField(key) 30 } 31 for (key in child) { 32 if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) { 33 mergeField(key) 34 } 35 } 36 function mergeField (key) { 37 const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat 38 options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key) 39 } 40 return options 41 }
从上面mergeField函数中可以看出,Strats绑定处理参数中的各种数据的方法,统一在入口方法mergeOptions中被调用。源码在定义strats的时的注释也做了相应的说明,如下:
1 /** 2 * Option overwriting strategies are functions that handle 3 * how to merge a parent option value and a child option 4 * value into the final value. 5 */ 6 const strats = config.optionMergeStrategies
- 合并生命周期的钩子函数和props参数的方法为mergeHook
1 export const LIFECYCLE_HOOKS = [ 2 \'beforeCreate\', 3 \'created\', 4 \'beforeMount\', 5 \'mounted\', 6 \'beforeUpdate\', 7 \'updated\', 8 \'beforeDestroy\', 9 \'destroyed\', 10 \'activated\', 11 \'deactivated\', 12 \'errorCaptured\' 13 ]
14 LIFECYCLE_HOOKS.forEach(hook => { 15 strats[hook] = mergeHook 16 })
mergeHook方法实现思路及源码如下:
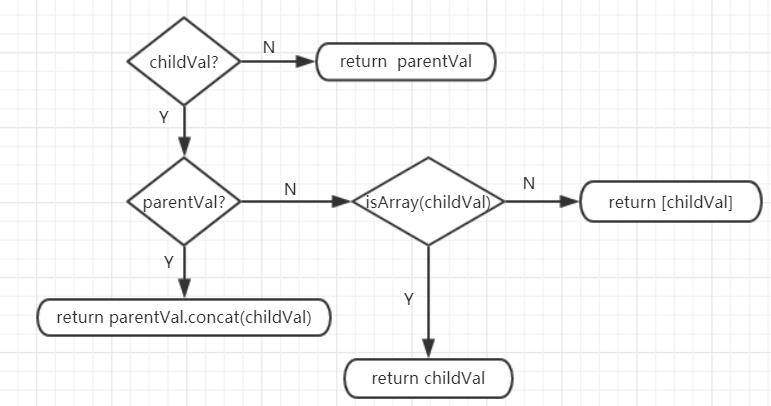
用人话总结这个合并规则就是:只有父时返回父,只有子时返回数组类型的子。父、子都存在时,将子添加在父的后面返回组合而成的数组。这也是父子均有钩子函数的时候,先执行父的后执行子的的原因。源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Hooks and props are merged as arrays. 3 */ 4 function mergeHook ( 5 parentVal: ?Array<Function>, 6 childVal: ?Function | ?Array<Function> 7 ): ?Array<Function> { 8 return childVal 9 ? parentVal 10 ? parentVal.concat(childVal) 11 : Array.isArray(childVal) 12 ? childVal 13 : [childVal] 14 : parentVal 15 }
2.strats.data合并data数据,代码逻辑如下:
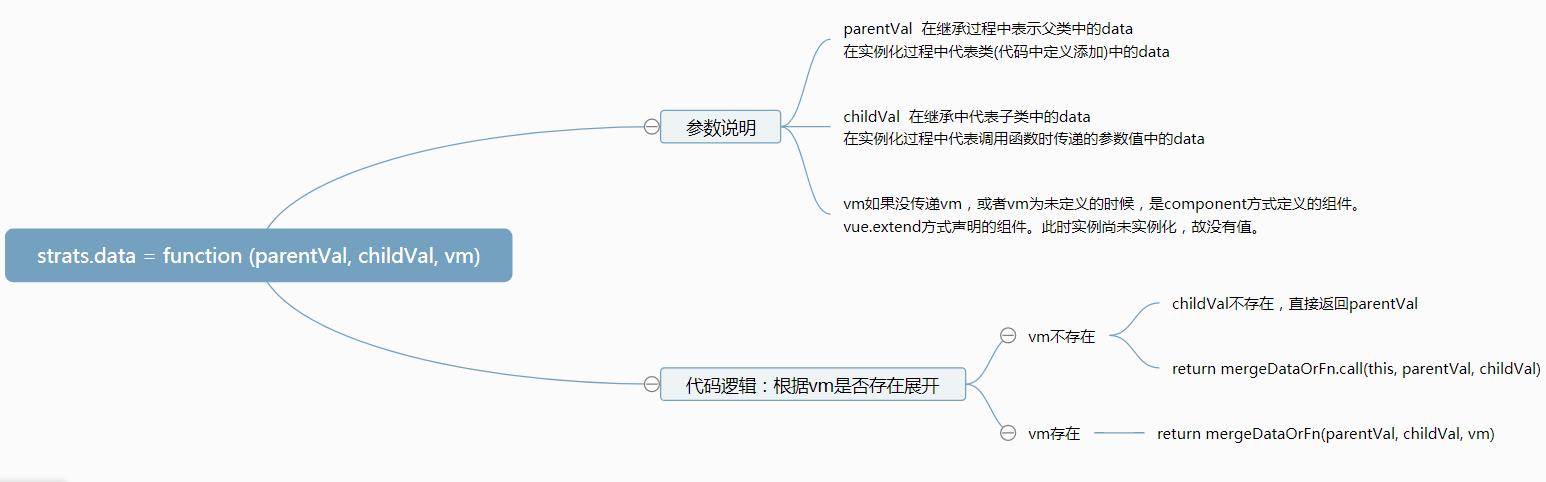
源码如下:
1 strats.data = function ( 2 parentVal: any, 3 childVal: any, 4 vm?: Component 5 ): ?Function { 6 if (!vm) { 7 if (childVal && typeof childVal !== \'function\') { 8 process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\' && warn( 9 \'The "data" option should be a function \' + 10 \'that returns a per-instance value in component \' + 11 \'definitions.\', 12 vm 13 ) 14 15 return parentVal 16 } 17 return mergeDataOrFn.call(this, parentVal, childVal) 18 } 19 20 return mergeDataOrFn(parentVal, childVal, vm) 21 }
由源码最后可知无论是vm存在与否最后都调用了mergeDataOrFn函数。这个函数根据vm是否存在,对parentVal和childVal做出不同的处理。但是无论vm存在不存在最终都会调用mergeData函数,将parentVal和childVal合并成最终值。所以介绍mergeDataOrFn函数之前先介绍mergeData这个函数。源码如下:
1 function mergeData (to: Object, from: ?Object): Object { 2 if (!from) return to 3 let key, toVal, fromVal 4 const keys = Object.keys(from) 5 for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) { 6 key = keys[i] 7 toVal = to[key] 8 fromVal = from[key] 9 if (!hasOwn(to, key)) { 10 set(to, key, fromVal) 11 } else if (isPlainObject(toVal) && isPlainObject(fromVal)) { 12 mergeData(toVal, fromVal) 13 } 14 } 15 return to 16 }
用人话总结这个合并规则就是:
1.如果from【childVal】中的某个属性to【parentVal】中也有,保留to中的,什么也不做
2.如果to中没有,将这个属性添加到to中
3.如果to和from中的某个属性值都是对象,则递归调用,进行深度合并。
无论vm存在不存在mergeDataOrFn最终都会调用mergeData函数,将parentVal和childVal合并成最终值。那么接下来看mergeDataOrFn中对parentVal和childVal做了什么处理。
逻辑图如下:
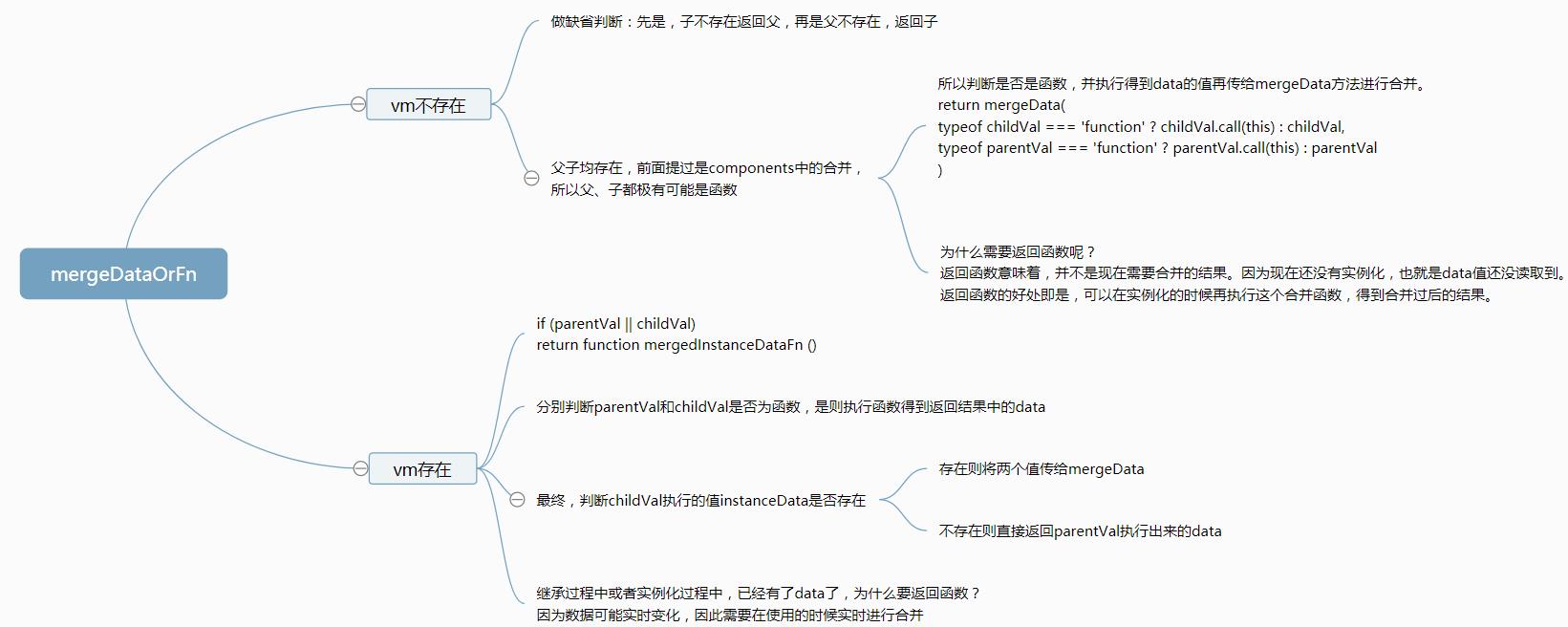
源码如下:
1 export function mergeDataOrFn ( 2 parentVal: any, 3 childVal: any, 4 vm?: Component 5 ): ?Function { 6 if (!vm) { 7 // in a Vue.extend merge, both should be functions 8 if (!childVal) { 9 return parentVal 10 } 11 if (!parentVal) { 12 return childVal 13 } 14 // when parentVal & childVal are both present, 15 // we need to return a function that returns the 16 // merged result of both functions... no need to 17 // check if parentVal is a function here because 18 // it has to be a function to pass previous merges. 19 return function mergedDataFn () { 20 return mergeData( 21 typeof childVal === \'function\' ? childVal.call(this) : childVal, 22 typeof parentVal === \'function\' ? parentVal.call(this) : parentVal 23 ) 24 } 25 } else if (parentVal || childVal) { 26 return function mergedInstanceDataFn () { 27 // instance merge 28 const instanceData = typeof childVal === \'function\' 29 ? childVal.call(vm) 30 : childVal 31 const defaultData = typeof parentVal === \'function\' 32 ? parentVal.call(vm) 33 : parentVal 34 if (instanceData) { 35 return mergeData(instanceData, defaultData) 36 } else { 37 return defaultData 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }
3.strats.provide = mergeDataOrFn。provide使用mergeDataOrFn进行合并
4.strats.watch源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Watchers. 3 * 4 * Watchers hashes should not overwrite one 5 * another, so we merge them as arrays. 6 */ 7 strats.watch = function ( 8 parentVal: ?Object, 9 childVal: ?Object, 10 vm?: Component, 11 key: string 12 ): ?Object { 13 // work around Firefox\'s Object.prototype.watch... 14 if (parentVal === nativeWatch) parentVal = undefined 15 if (childVal === nativeWatch) childVal = undefined 16 /* istanbul ignore if */ 17 if (!childVal) return Object.create(parentVal || null) 18 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\') { 19 assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm) 20 } 21 if (!parentVal) return childVal 22 const ret = {} 23 extend(ret, parentVal) 24 for (const key in childVal) { 25 let parent = ret[key] 26 const child = childVal[key] 27 if (parent && !Array.isArray(parent)) { 28 parent = [parent] 29 } 30 ret[key] = parent 31 ? parent.concat(child) 32 : Array.isArray(child) ? child : [child] 33 } 34 return ret 35 }
注释里说了:watchers不应该重写,应该保存在一个数组里。这就是watch数据合并的策略核心。
1.定义ret并让ret获得parentVal的所有属性。
2.遍历 childVal的所有属性,如果ret(即parentVal)中也有的话,就把ret的属性值弄成一个数组,把childVal的同名属性值放在ret同名值得后面。如果不存在就把childVal弄成一个数组。
3.最后都将数组的值赋值给ret,拓展ret的属性和属性值。
这个策略其实就是,子组件、父组件都存在的时候,把watch相同值得方法放在一个数组里,父前子后。
5.strats.component、strats.directive、strats.filter源码如下:
1 export const ASSET_TYPES = [ 2 \'component\', 3 \'directive\', 4 \'filter\' 5 ] 6 /** 7 * Assets 8 * 9 * When a vm is present (instance creation), we need to do 10 * a three-way merge between constructor options, instance 11 * options and parent options. 12 */ 13 function mergeAssets ( 14 parentVal: ?Object, 15 childVal: ?Object, 16 vm?: Component, 17 key: string 18 ): Object { 19 const res = Object.create(parentVal || null) 20 if (childVal) { 21 process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\' && assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm) 22 return extend(res, childVal) 23 } else { 24 return res 25 } 26 } 27 28 ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) { 29 strats[type + \'s\'] = mergeAssets 30 })
这个合并策略的核心就是:将childVal的全部属性通过原型委托在parentVal上。parentVal成为了childVal的原型对象。
所以需要查找某个component、directive、filter,首先会在childVal中查找,如果没有就在其原型对象上查找。
即子组件有就用子组件的,子组件没有向上在父组件中寻找。
6.strats.props 、strats.methods 、strats.inject 、strats.computed源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Other object hashes. 3 */ 4 strats.props = 5 strats.methods = 6 strats.inject = 7 strats.computed = function ( 8 parentVal: ?Object, 9 childVal: ?Object, 10 vm?: Component, 11 key: string 12 ): ?Object { 13 if (childVal && process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\') { 14 assertObjectType(key, childVal, vm) 15 } 16 if (!parentVal) return childVal 17 const ret = Object.create(null) 18 extend(ret, parentVal) 19 if (childVal) extend(ret, childVal) 20 return ret 21 }
这种合并策略的特点就是子会覆盖父。
1.先将parentVal的所有属性扩展给res
2.再将childVal的所有属性扩展给res。此时,若是parentVal和childVal拥有同名属性的话,子的属性就会覆盖父的。也就是同名方法只会执行子的。
7.其他的属性使用的就是默认合并策略:defaultStrat。源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Default strategy. 3 */ 4 const defaultStrat = function (parentVal: any, childVal: any): any { 5 return childVal === undefined 6 ? parentVal 7 : childVal 8 }
默认策略就是:子组件的选项不存在,才会使用父组件的选项,如果子组件的选项存在,使用子组件自身的。
因为是不会对parentVal和childVal进行分解的。所以默认策略一般用于合并比较简单,不包含函数的属性,例如el。
1 const defaultStrat = function (parentVal: any, childVal: any): any { 2 return childVal === undefined 3 ? parentVal 4 : childVal 5 }
注:本文章中学习的源码版本为vue 2.5.2. 文章中涉及的观点和理解均是个人的理解,如有偏颇或是错误还请大神指出,不吝赐教,万分感谢~
以上是关于vue源码学习--合并策略对象mergeOptions的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
ES源码分析强制合并分段(_forcemerge API)源码分析