线程池的原理及实现
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线程池的原理及实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、线程池简介:
多线程技术主要解决处理器单元内多个线程执行的问题,它可以显著减少处理器单元的闲置时间,增加处理器单元的吞吐能力。
假设一个服务器完成一项任务所需时间为:T1 创建线程时间,T2 在线程中执行任务的时间,T3 销毁线程时间。
如果:T1 + T3 远大于 T2,则可以采用线程池,以提高服务器性能。
一个线程池包括以下四个基本组成部分:
1、线程池管理器(ThreadPool):用于创建并管理线程池,包括 创建线程池,销毁线程池,添加新任务;
2、工作线程(PoolWorker):线程池中线程,在没有任务时处于等待状态,可以循环的执行任务;
3、任务接口(Task):每个任务必须实现的接口,以供工作线程调度任务的执行,它主要规定了任务的入口,任务执行完后的收尾工作,任务的执行状态等;
4、任务队列(taskQueue):用于存放没有处理的任务。提供一种缓冲机制。
线程池技术正是关注如何缩短或调整T1,T3时间的技术,从而提高服务器程序性能的。它把T1,T3分别安排在服务器程序的启动和结束的时间段或者一些空闲的时间段,这样在服务器程序处理客户请求时,不会有T1,T3的开销了。线程池不仅调整T1,T3产生的时间段,而且它还显著减少了创建线程的数目,看一个例子:
假设一个服务器一天要处理50000个请求,并且每个请求需要一个单独的线程完成。在线程池中,线程数一般是固定的,所以产生线程总数不会超过线程池中线程的数目,而如果服务器不利用线程池来处理这些请求则线程总数为50000。一般线程池大小是远小于50000。所以利用线程池的服务器程序不会为了创建50000而在处理请求时浪费时间,从而提高效率。
线程池实现代码:
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /** 7 * 线程池类 8 * @author wangbo 9 * 10 */ 11 public class ThreadPool { 12 13 private static int worker_num = 5;//线程池中线程的个数,默认为5 14 15 private WorkThread[] workthreads;//工作线程 16 17 private static volatile int finished_task = 0;//未处理的任务 18 19 private List<Runnable> taskQueue = new LinkedList<Runnable>();//任务队列 20 21 private static ThreadPool threadPool; 22 23 /** 24 * 无参构造器,创建线程池 25 */ 26 private ThreadPool(){ 27 this(5); 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 含参构造器,创建线程池 32 * @param num 33 */ 34 private ThreadPool(int num){ 35 worker_num = num; 36 workthreads = new WorkThread[num]; 37 for (int i = 0; i < workthreads.length; i++) { 38 workthreads[i] = new WorkThread(); 39 workthreads[i].start();//开启线程 40 } 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * 获得一个默认线程个数的线程池 45 * @return 46 */ 47 public static ThreadPool getThreadPool(){ 48 return getThreadPool(ThreadPool.worker_num); 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * 获得一个指定线程个数的线程池 53 * @param num 54 * @return 55 */ 56 public static ThreadPool getThreadPool(int num) { 57 if (num <= 0) { 58 num = ThreadPool.worker_num; 59 } 60 if (threadPool == null) { 61 threadPool = new ThreadPool(num); 62 } 63 return threadPool; 64 } 65 66 /** 67 * 将任务单个添加到队列 68 * @param task 69 */ 70 public void execute(Runnable task){ 71 synchronized (taskQueue) { 72 taskQueue.add(task); 73 taskQueue.notify(); 74 } 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * 将任务批量添加到队列 79 * @param tasks 80 */ 81 public void execute(Runnable[] tasks){ 82 synchronized (taskQueue) { 83 for (Runnable runnable : tasks) { 84 taskQueue.add(runnable); 85 } 86 taskQueue.notify(); 87 } 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * 将任务批量添加到队列 92 * @param tasks 93 */ 94 public void execute(List<Runnable> tasks){ 95 synchronized (taskQueue) { 96 for (Runnable runnable : tasks) { 97 taskQueue.add(runnable); 98 } 99 taskQueue.notify(); 100 } 101 } 102 103 /** 104 * 销毁线程池 105 */ 106 public void destroy(){ 107 //还有任务没有执行完 108 while(!taskQueue.isEmpty()){ 109 try { 110 Thread.sleep(10); 111 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 112 e.printStackTrace(); 113 } 114 } 115 //停止工作线程,且置为null 116 for (int i = 0; i < workthreads.length; i++) { 117 workthreads[i].stopWorker(); 118 workthreads[i] = null; 119 } 120 threadPool = null; 121 taskQueue.clear();//清空队列 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * 获取工作线程的个数 126 * @return 127 */ 128 public int getWorkThreadNumber(){ 129 return worker_num; 130 } 131 132 /** 133 * 获取已完成任务数量 134 * @return 135 */ 136 public int getFinishedTaskNumber(){ 137 return finished_task; 138 } 139 140 /** 141 * 获取未完成任务数量 142 * @return 143 */ 144 public int getWaitTaskNumber(){ 145 return taskQueue.size(); 146 } 147 148 /** 149 * 获取线程池信息 150 */ 151 @Override 152 public String toString() { 153 return "工作线程数量:" + getWorkThreadNumber() 154 + ",已完成任务数量" + getFinishedTaskNumber() 155 + ",未完成任务数量" + getWaitTaskNumber(); 156 157 } 158 159 /** 160 * 内部类,工作线程 161 * @author wangbo 162 * 163 */ 164 private class WorkThread extends Thread{ 165 166 private boolean isRunning = true;//线程有效标志 167 168 @Override 169 public void run() { 170 Runnable runnable = null; 171 while (isRunning) { 172 synchronized (taskQueue) { 173 //队列为空 174 while (isRunning && taskQueue.isEmpty()) { 175 try { 176 taskQueue.wait(20); 177 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 178 e.printStackTrace(); 179 } 180 } 181 //队列不为空 182 if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) { 183 runnable = taskQueue.remove(0);//去除任务 184 } 185 } 186 if (runnable != null) { 187 runnable.run();//执行任务 188 } 189 finished_task++; 190 runnable = null; 191 } 192 193 } 194 195 /** 196 * 停止线程 197 */ 198 public void stopWorker() { 199 isRunning = false; 200 } 201 202 } 203 204 }
测试代码:
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 public class ThreadPoolTest { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // 创建3个线程的线程池 7 ThreadPool t = ThreadPool.getThreadPool(3); 8 t.execute(new Runnable[] { new Task(), new Task(), new Task() }); 9 t.execute(new Runnable[] { new Task(), new Task(), new Task() }); 10 System.out.println(t); 11 t.destroy();//所有线程都执行完成才destory 12 System.out.println(t); 13 } 14 15 // 任务类 16 static class Task implements Runnable { 17 18 private static volatile int i = 1; 19 20 @Override 21 public void run() {// 执行任务 22 System.out.println("任务 " + (i++) + " 完成"); 23 } 24 } 25 26 }
2、java类库中提供的线程池简介:
java.util.concurrent包提供了现成的线程池的实现。

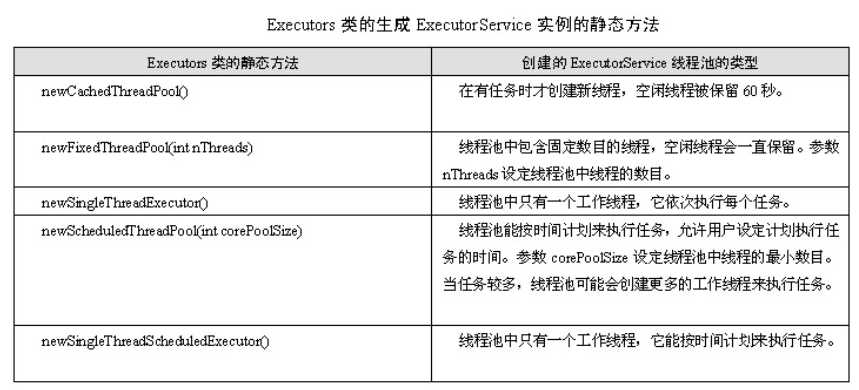
示例代码:
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 /** 6 * newCachedThreadPool() 7 * 线程池为无限大,当执行第二个任务时第一个任务已经完成,会复用执行第一个任务的线程,而不用每次新建线程。 8 * 有任务才会创建线程,空闲线程会被保留60s 9 * @author wangbo 10 * 11 */ 12 public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest1 { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 17 final int index = i; 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(1000); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() { 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 System.out.println(index); 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 28 } 29 }); 30 } 31 } 32 33 }
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 /** 6 * newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) 7 * 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。 8 * 线程池中包含固定数目的线程,空闲线程会一直保留,参数nThreads表示设定线程池中线程的数目 9 * @author wangbo 10 * 11 */ 12 public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest2 { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 17 final int index = i; 18 fixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() { 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 try { 22 System.out.println(index); 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 24 Thread.sleep(2000); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 } 29 }); 30 } 31 } 32 33 }
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 4 import java.util.Date; 5 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; 7 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 8 /** 9 * newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) 10 * 线程池能按时间计划来执行任务,允许用户设定计划执行任务的时间。 11 * 参数corePoolSize设定线程池中线程最小数目,当任务较多时,线程池可能会创建更多的工作线程来执行任务。 12 * @author wangbo 13 * 14 */ 15 public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest3 { 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 19 method1(); 20 method2(); 21 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 延迟3s执行 26 */ 27 private static void method1(){ 28 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 29 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); 30 scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() { 31 public void run() { 32 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 33 System.out.println("延迟2s执行"); 34 } 35 }, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * 延迟2s执行后每3s执行一次 40 */ 41 private static void method2() { 42 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 43 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); 44 scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { 45 public void run() { 46 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 47 System.out.println("延迟2s执行后每3s执行一次"); 48 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 49 } 50 }, 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 51 } 52 53 }
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 /** 6 * newSingleThreadExecutor(int nThreads) 7 * 线程池中只有一个线程,它依次执行每个任务。 8 * 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。 9 * @author wangbo 10 * 11 */ 12 public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest4 { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 17 final int index = i; 18 singleThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() { 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 try { 22 System.out.println(index); 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 24 Thread.sleep(2000); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 } 29 }); 30 } 31 } 32 33 }
1 package com.wb.thread; 2 3 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 4 import java.util.Date; 5 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; 7 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 8 /** 9 * newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() 10 * 线程池中只有一个线程,它能按照时间计划执行每个任务。 11 * @author wangbo 12 * 13 */ 14 public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest5 { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 18 method1(); 19 method2(); 20 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 延迟3s执行 25 */ 26 private static void method1(){ 27 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 28 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); 29 scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() { 30 public void run() { 31 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 32 System.out.println("延迟2s执行"); 33 } 34 }, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 延迟2s执行后每3s执行一次 39 */ 40 private static void method2() { 41 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 42 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); 43 scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { 44 public void run() { 45 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); 46 System.out.println("延迟2s执行后每3s执行一次"); 47 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 48 } 49 }, 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 50 } 51 52 }
以上是关于线程池的原理及实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章