设计模式(十四)——组合模式
Posted 知止
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式(十四)——组合模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.描述
将对象组合成树形结构一以表示“部分——整体”的层次结构。组合模式使用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
2.模式的使用
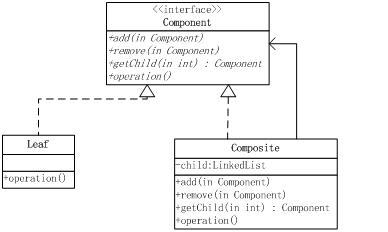
·抽象组件(Component):是一个接口或抽象类,该接口定义了个体对象和组合对象需要实现的关于操作器子节点的方法,比如添加add()、删除remove()、等方法。
·Composite节点(Composite Node):实现Component接口类的实例,节点不但实现Component接口,也可以包含其他Composite节点或Leaf节点的引用
·Leaf节点(Leaf Node):实现Component接口的类的实例,Leaf节点实现Component节点,不可以包含其他Composite节点或Leaf节点的引用。
3.使用情景
·当想表示对象的部分——整体层次结构。
·希望用户用一致的处理方式处理个体对象和组合对象。
4.优点
·组合模式包含个体对象和组合对象,并形成树形结构,使用户可以方便的处理个体对象和组合对象。
·组合对象和个体对象吧实现了统一接口,用户一般无需区分个体对象和组合对象。
·当增加新的Conposite节点或时,用户的重要代码不需要修改。
5.UML图
6案例
某军队的编制中,连长下面两个排长,排长下面三个班长,班长下面10个士兵。使用组合模式将这些对象构造成属性结构(一些姓名、工资属性不是重点)。
1 package 组合模式; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.LinkedList; 5 6 public class test1 { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 11 } 12 13 public static double computeSalary(MilitaryPerson person){//计算该单位下所有成员工资总和 14 //使用的递归 15 double sum = 0; 16 if(person.isLeaf()) 17 sum += person.getSalary(); 18 19 if(!person.isLeaf()){ 20 sum += person.getSalary(); 21 Iterator<MilitaryPerson> iterator = person.getAllChildren(); 22 while(iterator.hasNext()){ 23 MilitaryPerson p = iterator.next(); 24 sum = sum + computeSalary(p); 25 } 26 } 27 return sum; 28 } 29 } 30 31 /* 32 * 抽象组件 33 */ 34 interface MilitaryPerson{ 35 public void add(MilitaryPerson person);//添加成员 36 public void remove(MilitaryPerson person);//删除成员 37 public MilitaryPerson getChild(int index);//按下表获取成员 38 public Iterator<MilitaryPerson> getAllChildren();//获取该单位下面所有成员的遍历迭代器 39 public boolean isLeaf();//判断是否为Leaf节点 40 public double getSalary(); 41 public void setSalary(double salary); 42 } 43 44 /* 45 * composite节点——班长、排长、连长 46 */ 47 class MilitaryOfficer implements MilitaryPerson{ 48 LinkedList<MilitaryPerson> list; 49 String name; 50 double salary; 51 MilitaryOfficer(String name, double salary){ 52 this.name = name; 53 this.salary = salary; 54 list = new LinkedList<MilitaryPerson>(); 55 } 56 public void add(MilitaryPerson person) { 57 list.add(person); 58 } 59 60 public void remove(MilitaryPerson person) { 61 list.remove(person); 62 } 63 64 public MilitaryPerson getChild(int index) { 65 return list.get(index); 66 } 67 68 public Iterator<MilitaryPerson> getAllChildren() { 69 return list.iterator(); 70 } 71 72 public boolean isLeaf() { 73 return false; 74 } 75 76 public double getSalary() { 77 return salary; 78 } 79 80 public void setSalary(double salary) { 81 this.salary = salary; 82 } 83 84 } 85 86 /* 87 * Leaf节点——士兵 88 */ 89 class MilitarySoldier implements MilitaryPerson{ 90 double salary; 91 String name; 92 MilitarySoldier(double salary, String name){ 93 this.salary = salary; 94 this.name = name; 95 } 96 public void add(MilitaryPerson person) {} 97 98 public void remove(MilitaryPerson person) {} 99 100 public MilitaryPerson getChild(int index) {return null;} 101 102 public Iterator<MilitaryPerson> getAllChildren() {return null;} 103 104 public boolean isLeaf() {return true;} 105 106 public double getSalary() { 107 return salary; 108 } 109 110 public void setSalary(double salary) { 111 this.salary = salary; 112 } 113 114 }
大概结构就是这样,如果演示的话需要创建一堆士兵和长官的对象,太麻烦。
以上是关于设计模式(十四)——组合模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章