Linear Regression Using Gradient Descent 代码实现
Posted 照夜白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linear Regression Using Gradient Descent 代码实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考吴恩达<机器学习>, 进行 Octave, Python(Numpy), C++(Eigen) 的原理实现, 同时用 scikit-learn, TensorFlow, dlib 进行生产环境实现.
1. 原理
cost function
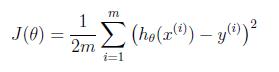
gradient descent

2. 原理实现
octave
cost function
function J = costFunction(X, Y, theta) m = size(X, 1); predictions = X * theta; sqrErrors = (predictions - Y) .^ 2; J = 1 / (2 * m) * sum(sqrErrors);
Linear regression using gradient descent
function [final_theta, Js] = gradientDescent(X, Y, init_theta, learning_rate=0.01, max_times=1000) convergence = 0; m = size(X, 1); tmp_theta = init_theta;
Js = zeros(m, 1); for i=1:max_times, tmp = learning_rate / m * ((X * tmp_theta - Y)\' * X)\'; tmp_theta -= tmp;
Js(i) = costFunction(X, Y, tmp_theta); end;
final_theta = tmp_theta;
python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def cost_function(input_X, _y, theta): """ cost function :param input_X: np.matrix input X :param _y: np.array y :param theta: np.matrix theta :return: float """ rows, cols = input_X.shape predictions = input_X * theta sqrErrors = np.array(predictions - _y) ** 2 J = 1.0 / (2 * rows) * sqrErrors.sum() return J def gradient_descent(input_X, _y, theta, learning_rate=0.1, iterate_times=3000): """ gradient descent :param input_X: np.matrix input X :param _y: np.array y :param theta: np.matrix theta :param learning_rate: float learning rate :param iterate_times: int max iteration times :return: tuple """ convergence = 0 rows, cols = input_X.shape Js = [] for i in range(iterate_times): errors = input_X * theta - _y delta = 1.0 / rows * (errors.transpose() * input_X).transpose() theta -= learning_rate * delta Js.append(cost_function(input_X, _y, theta)) return theta, Js def generate_data(): """ generate training data y = 2*x^2 + 4*x + 2 """ x = np.linspace(0, 2, 50) X = np.matrix([np.ones(50), x, x**2]).T y = 2 * X[:, 0] - 4 * X[:, 1] + 2 * X[:, 2] + np.mat(np.random.randn(50)).T / 25 np.savetxt(\'linear_regression_using_gradient_descent.csv\', np.column_stack((X, y)), delimiter=\',\') def test(): """ main :return: None """ m = np.loadtxt(\'linear_regression_using_gradient_descent.csv\', delimiter=\',\') input_X, y = np.asmatrix(m[:, :-1]), np.asmatrix(m[:, -1]).T # theta 的初始值必须是 float theta = np.matrix([[0.0], [0.0], [0.0]]) final_theta, Js = gradient_descent(input_X, y, theta) t1, t2, t3 = np.array(final_theta).reshape(-1,).tolist() print(\'对测试数据 y = 2 - 4x + 2x^2 求得的参数为: %.3f, %.3f, %.3f\\n\' % (t1, t2, t3)) plt.figure(\'theta\') predictions = np.array(input_X * final_theta).reshape(-1,).tolist() x1 = np.array(input_X[:, 1]).reshape(-1,).tolist() y1 = np.array(y).reshape(-1,).tolist() plt.plot(x1, y1, \'*\') plt.plot(x1, predictions) plt.xlabel(\'x\') plt.ylabel(\'y\') plt.title(\'y = 2 - 4x + 2x^2\') plt.figure(\'cost\') x2 = range(1, len(Js) + 1) y2 = Js plt.plot(x2, y2) plt.xlabel(\'iterate times\') plt.ylabel(\'value\') plt.title(\'cost function\') plt.show() if __name__ == \'__main__\': test()
Python 中需要注意的是, numpy.array, numpy.matrix 和 list 等进行计算时, 有时会进行默认类型转换, 默认类型转换的结果, 往往不是期望的情况.
theta 的初始值必须是 float, 因为如果是 int, 则在更新 theta 时会报错.
测试数据:

Cost function:
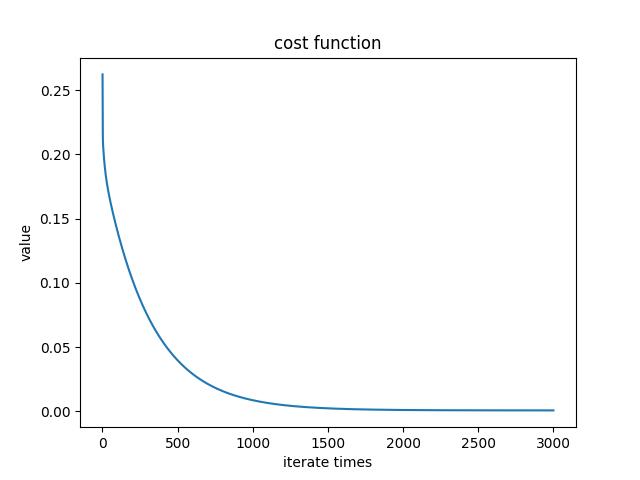
c++
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <Eigen/Dense> using namespace Eigen; using namespace std; double cost_function(MatrixXd &input_X, MatrixXd &_y, MatrixXd &theta) { double rows = input_X.rows(); MatrixXd predictions = input_X * theta; ArrayXd sqrErrors = (predictions - _y).array().square(); double J = 1.0 / (2 * rows) * sqrErrors.sum(); return J; } class Gradient_descent { public: Gradient_descent(MatrixXd &x, MatrixXd &y, MatrixXd &t, double r=0.1, int m=3000): input_X(x), _y(y), theta(t), learning_rate(r), iterate_times(m){} MatrixXd theta; vector<double> Js; void run(); private: MatrixXd input_X; MatrixXd _y; double rows; double learning_rate; int iterate_times; }; void Gradient_descent::run() { double rows = input_X.rows(); for(int i=0; i < iterate_times; ++i) { MatrixXd errors = input_X * theta - _y; MatrixXd delta = 1.0 / rows * (errors.transpose() * input_X).transpose(); theta -= learning_rate * delta; double J = cost_function(input_X, _y, theta); Js.push_back(J); } } void generate_data(MatrixXd &input_X, MatrixXd &y) { ArrayXd v = ArrayXd::LinSpaced(50, 0, 2); input_X.col(0) = VectorXd::Constant(50, 1, 1); input_X.col(1) = v.matrix(); input_X.col(2) = v.square().matrix(); y.col(0) = 2 * input_X.col(0) - 4 * input_X.col(1) + 2 * input_X.col(2); y.col(0) += VectorXd::Random(50) / 25; } int main() { MatrixXd input_X(50, 3), y(50, 1); MatrixXd theta = MatrixXd::Zero(3, 1); generate_data(input_X, y); Gradient_descent gd(input_X, y, theta); gd.run(); cout << gd.theta << endl; }
3. 生产环境
Python (Scikit-learn)
todo
Python (TensorFlow)
todo
C++ (dlib)
todo
以上是关于Linear Regression Using Gradient Descent 代码实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章