学习笔记 | 回归模型 | 01 介绍
Posted W先森
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了学习笔记 | 回归模型 | 01 介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
01 Introduction
Regression toward the mean 趋均数回归
弗朗西斯·高尔顿
他在论及遗传对个体差异的影响时,首次提到了相关系数的概念。比如他研究了“居间亲”和其成年子女的身高关系,发现居间亲和其子女的身高有正相关,即父母的身材较高,其子女的身材也有较高的趋势。反之,父母的身材较低,其子女也有较矮的趋势。同时发现子女的身高常与其父母略有差别,而呈现“回中”趋势,即回到一般人身高的平均数。
R函数 ‘Jitter’ (Add Noise) to Numbers
Description 描述
Add a small amount of noise to a numeric vector.
对一个数字向量加上一些噪音(小数点后几位的数字)
Usage
jitter(x, factor = 1, amount = NULL)
Arguments
x numeric vector to which jitter should be added.
factor numeric.
amount numeric; if positive, used as amount (see below), otherwise, if = 0 the default is factor * z/50.
Default (NULL): factor * d/5 where d is about the smallest difference between x values.
Examples
round(jitter(c(rep(1, 3), rep(1.2, 4), rep(3, 3))), 3)
## These two \'fail\' with S-plus 3.x:
jitter(rep(0, 7))
jitter(rep(10000, 5))
应用:在画图时,通过制造微小的误差,可以把原本同一值上的点显示出来,才能在图上直接看出数据点的“密度”
> summary(regrline)
Call:
lm(formula = child ~ parent, data = galton)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-7.8050 -1.3661 0.0487 1.6339 5.9264
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 23.94153 2.81088 8.517 <2e-16 ***
parent 0.64629 0.04114 15.711 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 2.239 on 926 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2105, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2096
F-statistic: 246.8 on 1 and 926 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
直线的斜率 = 这条回归线summary中的 parent ~ Estimate 的值 = 0.64629
斜率的标准差 = summary 中的 parent ~ Std.Error 的值 = 0.04114
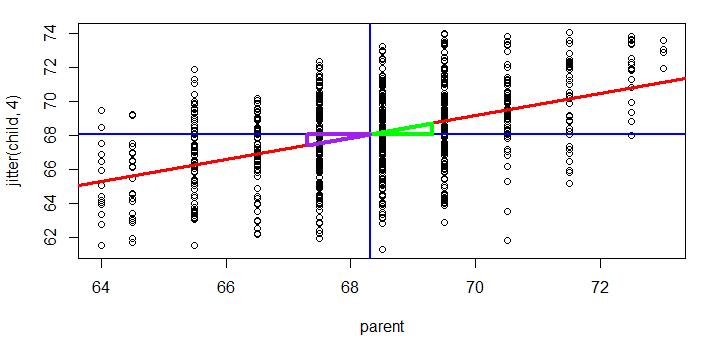
如图,纵轴蓝色线为 child 的均值,横轴蓝色线为 parent 的均值。
两条蓝色线的相交点刚好在回归线上。
向右父母身高 + 1,则子孙身高 + 0.65
同理,向左父母身高 - 1, 则子孙身高 - 0.65
plot(jitter(child,4) ~ parent, galton) regrline <- lm(child ~ parent, galton) abline(regrline,lwd=3, col=\'red\') summary(regrline)
以上是关于学习笔记 | 回归模型 | 01 介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章