opencv学习之路(36)运动物体检测
Posted 进击的小猴子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了opencv学习之路(36)运动物体检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、简介

二、背景减法

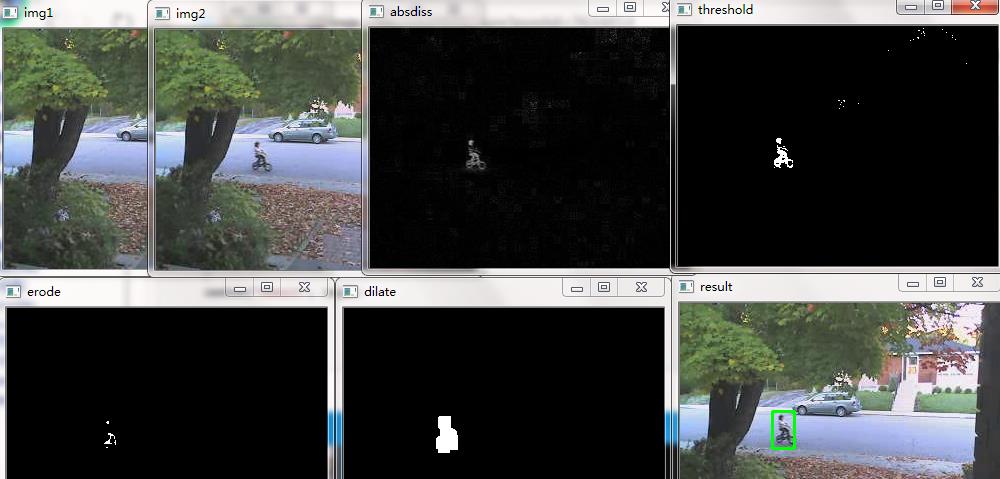
图片说明
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"using namespace cv; void main() { Mat img1 = imread("E:\\\\pic\\\\1.bmp"); Mat img2 = imread("E:\\\\pic\\\\55.bmp"); imshow("img1", img1); imshow("img2", img2); Mat gray1, gray2; cvtColor(img1, gray1, CV_BGR2GRAY); cvtColor(img2, gray2, CV_BGR2GRAY); Mat diff; absdiff(gray1, gray2, diff); imshow("absdiss", diff); threshold(diff, diff, 45, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); imshow("threshold", diff); Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3)); Mat element2 = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(11, 11)); erode(diff, diff, element); imshow("erode", diff); dilate(diff, diff, element2); imshow("dilate", diff); vector<vector<Point>> contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarcy; findContours(diff, contours, hierarcy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); //查找轮廓 vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size()); //定义外接矩形集合 //drawContours(img2, contours, -1, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8); //绘制轮廓 int x0=0, y0=0, w0=0, h0=0; for(int i=0; i<contours.size(); i++) { boundRect[i] = boundingRect((Mat)contours[i]); //查找每个轮廓的外接矩形 x0 = boundRect[i].x; //获得第i个外接矩形的左上角的x坐标 y0 = boundRect[i].y; //获得第i个外接矩形的左上角的y坐标 w0 = boundRect[i].width; //获得第i个外接矩形的宽度 h0 = boundRect[i].height; //获得第i个外接矩形的高度 rectangle(img2, Point(x0, y0), Point(x0+w0, y0+h0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); //绘制第i个外接矩形 } imshow("result", img2); waitKey(0); }
视频处理
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; using namespace cv; Mat MoveDetect(Mat background, Mat img) { Mat result = img.clone(); Mat gray1, gray2; cvtColor(background, gray1, CV_BGR2GRAY); cvtColor(img, gray2, CV_BGR2GRAY); Mat diff; absdiff(gray1, gray2, diff); //imshow("absdiss", diff); threshold(diff, diff, 45, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); //imshow("threshold", diff); Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3)); Mat element2 = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(15, 15)); erode(diff, diff, element); //imshow("erode", diff); dilate(diff, diff, element2); //imshow("dilate", diff); vector<vector<Point>> contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarcy; findContours(diff, contours, hierarcy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); //查找轮廓 vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size()); //定义外接矩形集合 //drawContours(img2, contours, -1, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8); //绘制轮廓 int x0=0, y0=0, w0=0, h0=0; for(int i=0; i<contours.size(); i++) { boundRect[i] = boundingRect((Mat)contours[i]); //查找每个轮廓的外接矩形 x0 = boundRect[i].x; //获得第i个外接矩形的左上角的x坐标 y0 = boundRect[i].y; //获得第i个外接矩形的左上角的y坐标 w0 = boundRect[i].width; //获得第i个外接矩形的宽度 h0 = boundRect[i].height; //获得第i个外接矩形的高度 rectangle(result, Point(x0, y0), Point(x0+w0, y0+h0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); //绘制第i个外接矩形 } return result; } void main() { VideoCapture cap("E://bike.avi"); if(!cap.isOpened()) //检查打开是否成功 return; Mat frame; Mat background; Mat result; int count=0; while(1) { cap>>frame; if(!frame.empty()) { count++; if(count==1) background = frame.clone(); //提取第一帧为背景帧 imshow("video", frame); result = MoveDetect(background, frame); imshow("result", result); if(waitKey(50)==27) break; } else break; } cap.release(); }
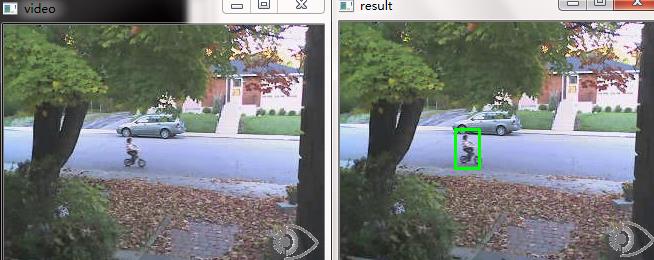

注意:针对不同场景不同目标,腐蚀膨胀等参数会有变化
三、帧差法

void main() { VideoCapture cap("bike.avi"); if(!cap.isOpened()) //检查打开是否成功 return; Mat frame; Mat result; Mat temp; int count=0; while(1) { cap>>frame; if(!frame.empty()) { count++; if(count==1) result = MoveDetect(frame, frame); else result = MoveDetect(temp, frame); imshow("video", frame); imshow("result", result); temp = frame.clone(); if(waitKey(50)==27) break; } else break; } cap.release(); }
其余代码相同
以上是关于opencv学习之路(36)运动物体检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章