自定义控件
Posted 火龙裸先生
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自定义控件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
又到月底了,这次又说道自定义View这块。主要是自己突然想起自己的开发路上,难免还是会有些对android知识的边边角角的认知不够完善,所以,这里再次写下也是为了扫除学习的盲点,写博客的目的也很简单,就是记笔记吧,怕自己忘,以后又能拿出来翻翻、、、仅此而已。
1:自定义View
我们为什么要去自定义View,Android系统已经给我们提供了大量的原生控件,可在我们的实际开发需求上,有的时候仍然是显得不够用。所以我们需要针对我们的业务需求定制我们想要的View。自定义View我们大部分时候只需重写两个函数:onMeasure()、onDraw()。onMeasure负责对当前View的尺寸进行测量,onDraw负责把当前这个View绘制出来。当然了,你还得写至少写2个构造函数:
1 public MyView(Context context) { 2 super(context); 3 } 4 5 public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 6 super(context, attrs); 7 }
第一个构造函数: 当不需要使用xml声明或者不需要使用inflate动态加载时候,实现此构造函数即可
第二个构造函数: 当需要在xml中声明此控件,则需要实现此构造函数。并且在构造函数中把自定义的属性与控件的数据成员连接起来。
1.1:onMeasure方法
我们自定义的View,首先得要测量宽高尺寸。为什么要测量宽高尺寸?我在刚学自定义View的时候非常无法理解!因为我当时觉得,我在xml文件中已经指定好了宽高尺寸了,我自定义View中有必要再次获取宽高并设置宽高吗?既然我自定义的View是继承自View类,google团队直接在View类中直接把xml设置的宽高获取,并且设置进去不就好了吗?那google为啥让我们做这样的“重复工作”呢?客官别急,马上给您上茶~
在学习Android的时候,我们就知道,在xml布局文件中,我们的layout_width和layout_height参数可以不用写具体的尺寸,而是wrap_content或者是match_parent。其意思我们都知道,就是将尺寸设置为“包住内容”和“填充父布局给我们的所有空间”。这两个设置并没有指定真正的大小,可是我们绘制到屏幕上的View必须是要有具体的宽高的,正是因为这个原因,我们必须自己去处理和设置尺寸。当然了,View类给了默认的处理,但是如果View类的默认处理不满足我们的要求,我们就得重写onMeasure函数啦~。这里举个例子,比如我们希望我们的View是个正方形,如果在xml中指定宽高为wrap_content,如果使用View类提供的measure处理方式,显然无法满足我们的需求~。
先看看onMeasure函数原型:
1 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
参数中的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec是个什么鬼?看起来很像width和height,没错,这两个参数就是包含宽和高的信息。什么?包含?难道还要其他信息?是的!它还包含测量模式,也就是说,一个int整数,里面放了测量模式和尺寸大小。那么一个数怎么放两个信息呢?我们知道,我们在设置宽高时有3个选择:wrap_content、match_parent以及指定固定尺寸,而测量模式也有3种:UNSPECIFIED,EXACTLY,AT_MOST,当然,他们并不是一一对应关系哈,这三种模式后面我会详细介绍,但测量模式无非就是这3种情况,而如果使用二进制,我们只需要使用2个bit就可以做到,因为2个bit取值范围是[0,3]里面可以存放4个数足够我们用了。那么Google是怎么把一个int同时放测量模式和尺寸信息呢?我们知道int型数据占用32个bit,而google实现的是,将int数据的前面2个bit用于区分不同的布局模式,后面30个bit存放的是尺寸的数据。
那我们怎么从int数据中提取测量模式和尺寸呢?放心,不用你每次都要写一次移位<<和取且&操作,Android内置类MeasureSpec帮我们写好啦~,我们只需按照下面方法就可以拿到啦:
1 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); 2 int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
爱思考的你肯定会问,既然我们能通过widthMeasureSpec拿到宽度尺寸大小,那我们还要测量模式干嘛?测量模式会不会是多余的?请注意:这里的的尺寸大小并不是最终我们的View的尺寸大小,而是父View提供的参考大小。我们看看测量模式,测量模式是干啥用的呢?
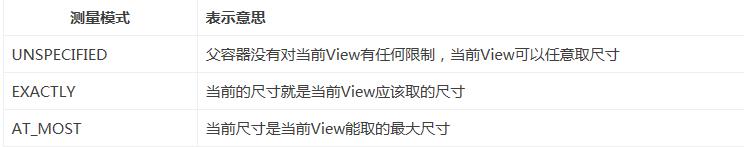
而上面的测量模式跟我们的布局时的wrap_content、match_parent以及写成固定的尺寸有什么对应关系呢?
match_parent—>EXACTLY:match_parent就是要利用父View给我们提供的所有剩余空间,而父View剩余空间是确定的,也就是这个测量模式的整数里面存放的尺寸。
wrap_content—>AT_MOST:就是我们想要将大小设置为包裹我们的view内容,那么尺寸大小就是父View给我们作为参考的尺寸,只要不超过这个尺寸就可以啦,具体尺寸就根据我们的需求去设定。
固定尺寸(如100dp)—>EXACTLY:用户自己指定了尺寸大小,我们就不用再去干涉了,当然是以指定的大小为主啦。
1.2:动手重写onMeasure方法
上面讲了太多理论,我们实际操作一下吧,感受一下onMeasure的使用,假设我们要实现这样一个效果:将当前的View以正方形的形式显示,即要宽高相等,并且默认的宽高值为100像素。就可以这些编写:
1 private int getMySize(int defaultSize, int measureSpec) { 2 int mySize = defaultSize; 3 4 int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); 5 int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); 6 7 switch (mode) { 8 case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: {//如果没有指定大小,就设置为默认大小 9 mySize = defaultSize; 10 break; 11 } 12 case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: {//如果测量模式是最大取值为size 13 //我们将大小取最大值,你也可以取其他值 14 mySize = size; 15 break; 16 } 17 case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: {//如果是固定的大小,那就不要去改变它 18 mySize = size; 19 break; 20 } 21 } 22 return mySize; 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 27 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 28 int width = getMySize(100, widthMeasureSpec); 29 int height = getMySize(100, heightMeasureSpec); 30 31 if (width < height) { 32 height = width; 33 } else { 34 width = height; 35 } 36 37 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); 38 }
我们设置一下布局:
<com.hc.studyview.MyView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#ff0000" />
看看使用了我们自己定义的onMeasure函数后的效果:

而如果我们不重写onMeasure,效果则是如下:

1.3:重写onDraw方法
上面我们学会了自定义尺寸大小,那么尺寸我们会设定了,接下来就是把我们想要的效果画出来吧~绘制我们想要的效果很简单,直接在画板Canvas对象上绘制就好啦,过于简单,我们以一个简单的例子去学习:假设我们需要实现的是,我们的View显示一个圆形,我们在上面已经实现了宽高尺寸相等的基础上,继续往下做:
1 @Override 2 protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { 3 //调用父View的onDraw函数,因为View这个类帮我们实现了一些 4 // 基本的而绘制功能,比如绘制背景颜色、背景图片等 5 super.onDraw(canvas); 6 int r = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;//也可以是getMeasuredHeight()/2,本例中我们已经将宽高设置相等了 7 //圆心的横坐标为当前的View的左边起始位置+半径 8 int centerX = getLeft() + r; 9 //圆心的纵坐标为当前的View的顶部起始位置+半径 10 int centerY = getTop() + r; 11 12 Paint paint = new Paint(); 13 paint.setColor(Color.GREEN); 14 //开始绘制 15 canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY, r, paint); 16 17 18 }

1.4:自定义布局属性
如果有些属性我们希望由用户指定,只有当用户不指定的时候才用我们硬编码的值,比如上面的默认尺寸,我们想要由用户自己在布局文件里面指定该怎么做呢?那当然是通我们自定属性,让用户用我们定义的属性啦~
首先我们需要在res/values文件下,新建一个attrs的xml文件。
<resources>
<!--name为声明的"属性集合"名,可以随便取,但是最好是设置为跟我们的View一样的名称-->
<declare-styleable name="MyView">
<!--声明我们的属性,名称为default_size,取值类型为尺寸类型(dp,px等)-->
<attr name="default_size" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
接下来就是在布局文件用上我们的自定义的属性啦~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:hc="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.hc.studyview.MyView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="100dp" hc:default_size="100dp" /> </LinearLayout>
注意:需要在根标签(LinearLayout)里面设定命名空间,命名空间名称可以随便取,比如hc,命名空间后面取得值是固定的:"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
最后就是在我们的自定义的View里面把我们自定义的属性的值取出来,在构造函数中,还记得有个AttributeSet属性吗?就是靠它帮我们把布局里面的属性取出来:
1 private int defalutSize; 2 public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 3 super(context, attrs); 4 //第二个参数就是我们在styles.xml文件中的<declare-styleable>标签 5 //即属性集合的标签,在R文件中名称为R.styleable+name 6 TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView); 7 8 //第一个参数为属性集合里面的属性,R文件名称:R.styleable+属性集合名称+下划线+属性名称 9 //第二个参数为,如果没有设置这个属性,则设置的默认的值 10 defalutSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.MyView_default_size, 100); 11 12 //最后记得将TypedArray对象回收 13 a.recycle(); 14 }
最后,把MyView的完整代码附上:
package com.huolongluo.studyview; import android.content.Context; import android.content.res.TypedArray; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Color; import android.graphics.Paint; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.view.View; /** * Package com.huolongluo.studyview * Created by 火龙裸 on 2017/9/28. */ public class MyView extends View { private int defalutSize; public MyView(Context context) { super(context); } public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); //第二个参数就是我们在styles.xml文件中的<declare-styleable>标签 //即属性集合的标签,在R文件中名称为R.styleable+name TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView); //第一个参数为属性集合里面的属性,R文件名称:R.styleable+属性集合名称+下划线+属性名称 //第二个参数为,如果没有设置这个属性,则设置的默认的值 defalutSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.MyView_default_size, 100); //最后记得将TypedArray对象回收 a.recycle(); } private int getMySize(int defaultSize, int measureSpec) { int mySize = defaultSize; int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); switch (mode) { case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: {//如果没有指定大小,就设置为默认大小 mySize = defaultSize; break; } case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: {//如果测量模式是最大取值为size //我们将大小取最大值,你也可以取其他值 mySize = size; break; } case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: {//如果是固定的大小,那就不要去改变它 mySize = size; break; } } return mySize; } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int width = getMySize(defalutSize, widthMeasureSpec); int height = getMySize(defalutSize, heightMeasureSpec); if (width < height) { height = width; } else { width = height; } setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { //调用父View的onDraw函数,因为View这个类帮我们实现了一些 // 基本的而绘制功能,比如绘制背景颜色、背景图片等 super.onDraw(canvas); int r = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;//也可以是getMeasuredHeight()/2,本例中我们已经将宽高设置相等了 //圆心的横坐标为当前的View的左边起始位置+半径 int centerX = getLeft() + r; //圆心的纵坐标为当前的View的顶部起始位置+半径 int centerY = getTop() + r; Paint paint = new Paint(); paint.setColor(Color.GREEN); //开始绘制 canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY, r, paint); } }
2:自定义ViewGroup
自定义View的过程很简单,就那几步,可自定义ViewGroup可就没那么简单啦~,因为它不仅要管好自己的,还要兼顾它的子View。我们都知道ViewGroup是个View容器,它装纳child View并且负责把child View放入指定的位置。我们假象一下,如果是让你负责设计ViewGroup,你会怎么去设计呢?
1.首先,我们得知道各个子View的大小吧,只有先知道子View的大小,我们才知道当前的ViewGroup该设置为多大去容纳它们。
2.根据子View的大小,以及我们的ViewGroup要实现的功能,决定出ViewGroup的大小
3.ViewGroup和子View的大小算出来了之后,接下来就是去摆放了吧,具体怎么去摆放呢?这得根据你定制的需求去摆放了,比如,你想让子View按照垂直顺序一个挨着一个放,或者是按照先后顺序一个叠一个去放,这是你自己决定的。
4.已经知道怎么去摆放还不行啊,决定了怎么摆放就是相当于把已有的空间”分割”成大大小小的空间,每个空间对应一个子View,我们接下来就是把子View对号入座了,把它们放进它们该放的地方去。
现在就完成了ViewGroup的设计了,我们来个具体的案例:将子View按从上到下垂直顺序一个挨着一个摆放,即模仿实现LinearLayout的垂直布局。
首先重写onMeasure,实现测量子View大小以及设定ViewGroup的大小:
1 @Override 2 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 3 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 4 //将所有的子View进行测量,这会触发每个子View的onMeasure函数 5 //注意要与measureChild区分,measureChild是对单个view进行测量 6 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 7 8 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); 9 int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); 10 int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); 11 int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); 12 13 int childCount = getChildCount(); 14 15 if (childCount == 0) {//如果没有子View,当前ViewGroup没有存在的意义,不用占用空间 16 setMeasuredDimension(0, 0); 17 } else { 18 //如果宽高都是包裹内容 19 if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { 20 //我们将高度设置为所有子View的高度相加,宽度设为子View中最大的宽度 21 int height = getTotleHeight(); 22 int width = getMaxChildWidth(); 23 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); 24 25 } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有高度是包裹内容 26 //宽度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量宽度,高度设置为所有子View的高度总和 27 setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, getTotleHeight()); 28 } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有宽度是包裹内容 29 //宽度设置为子View中宽度最大的值,高度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量值 30 setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightSize); 31 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 /*** 36 * 获取子View中宽度最大的值 37 */ 38 private int getMaxChildWidth() { 39 int childCount = getChildCount(); 40 int maxWidth = 0; 41 for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { 42 View childView = getChildAt(i); 43 if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > maxWidth) 44 maxWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 45 46 } 47 48 return maxWidth; 49 } 50 51 /*** 52 * 将所有子View的高度相加 53 **/ 54 private int getTotleHeight() { 55 int childCount = getChildCount(); 56 int height = 0; 57 for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { 58 View childView = getChildAt(i); 59 height += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 60 61 } 62 63 return height; 64 }
代码中的注释我已经写得很详细,不再对每一行代码进行讲解。上面的onMeasure将子View测量好了,以及把自己的尺寸也设置好了,接下来我们去摆放子View吧~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.hc.studyview.MyViewGroup android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ff9900"> <Button android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="btn" /> <Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="btn" /> <Button android:layout_width="50dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="btn" /> </com.hc.studyview.MyViewGroup> </LinearLayout>
看看最后的效果吧~

是不是很激动~我们自己也可以实现LinearLayout的效果啦~~~~
最后附上MyViewGroup的完整源码:
1 package com.huolongluo.studyview; 2 3 import android.content.Context; 4 import android.util.AttributeSet; 5 import android.view.MotionEvent; 6 import android.view.View; 7 import android.view.ViewGroup; 8 9 /** 10 * Package com.huolongluo.studyview 11 * Created by 火龙裸on 2017/9/28. 12 */ 13 public class MyViewGroup extends ViewGroup { 14 public MyViewGroup(Context context) { 15 super(context); 16 } 17 18 public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 19 20 super(context, attrs); 21 } 22 23 /*** 24 * 获取子View中宽度最大的值 25 */ 26 private int getMaxChildWidth() { 27 int childCount = getChildCount(); 28 int maxWidth = 0; 29 for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { 30 View childView = getChildAt(i); 31 if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > maxWidth) 32 maxWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 33 34 } 35 36 return maxWidth; 37 } 38 39 /*** 40 * 将所有子View的高度相加 41 **/ 42 private int getTotleHeight() { 43 int childCount = getChildCount(); 44 int height = 0; 45 for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { 46 View childView = getChildAt(i); 47 height += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 48 49 } 50 51 return height; 52 } 53 54 @Override 55 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 56 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 57 //将所有的子View进行测量,这会触发每个子View的onMeasure函数 58 //注意要与measureChild区分,measureChild是对单个view进行测量 59 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 60 61 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); 62 int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); 63 int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); 64 int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); 65 66 int childCount = getChildCount(); 67 68 if (childCount == 0) {//如果没有子View,当前ViewGroup没有存在的意义,不用占用空间 69 setMeasuredDimension(0, 0); 70 } else { 71 //如果宽高都是包裹内容 72 if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { 73 //我们将高度设置为所有子View的高度相加,宽度设为子View中最大的宽度 74 int height = getTotleHeight(); 75 int width = getMaxChildWidth(); 76 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); 77 78 } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有高度是包裹内容 79 //宽度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量宽度,高度设置为所有子View的高度总和 80 setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, getTotleHeight()); 81 } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有宽度是包裹内容 82 //宽度设置为子View中宽度最大的值,高度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量值 83 setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightSize); 84 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 89 @Override 90 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 91 int count = getChildCount(); 92 //记录当前的高度位置 93 int curHeight = t; 94 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 95 View child = getChildAt(i); 96 int height = child.getMeasuredHeight(); 97 int width = child.getMeasuredWidth(); 98 child.layout(l, curHeight, l + width, curHeight + height); 99 curHeight += height; 100 } 101 } 102 103 }
自定义View的学习暂且到这儿吧。后续跟进。
以上是关于自定义控件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章